Length Tension Relationship Of Skeletal Muscle Contraction
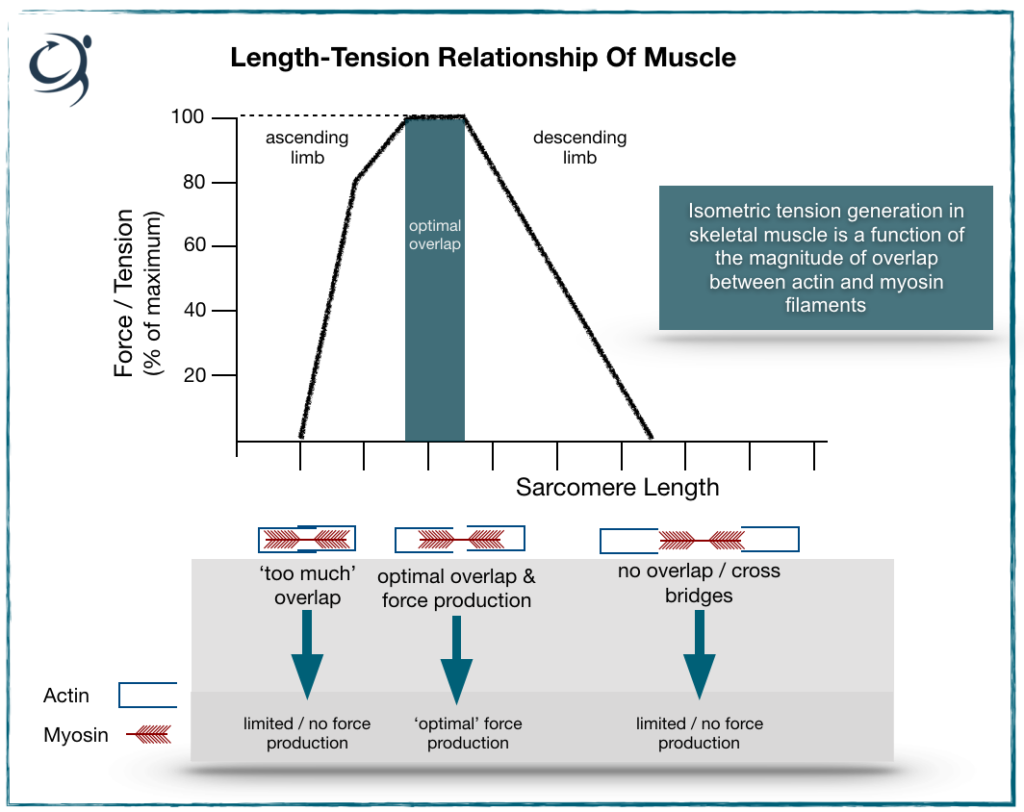
The Length Tension Relationship Using It In Rehab Get Back To Sport The length tension relationship in muscle illustrates the tensions, or forces, produced from the cross bridge cycle as a result of changes in muscle fiber length. the tension is determined by altering the resting length of a muscle that has already undergone isometric contraction. Length tension relationship: the tension generated by a sarcomere depends on the length of the sarcomere, and there is an optimal length at which tension is maximal, this is referred to as the "optimum" length. for human muscle, this corresponds to a sarcomere length of about 2.7 μm in skeletal muscle, and 2.2 μm in cardiac muscle.
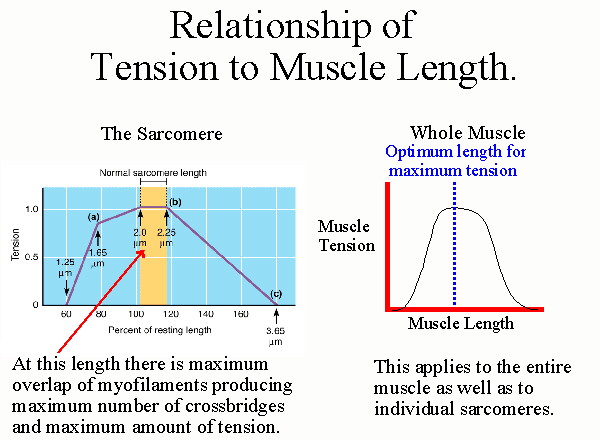
Biol 237 Class Notes Muscle Contractions And Metabolism A tetanic contraction (also called tetanized state, tetanus, or physiologic tetanus, the latter to differentiate from the disease called tetanus) is a sustai. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: length and tension. in physiology, muscle shortening and muscle contraction are not synonymous. tension within the muscle can be produced without changes in the length of the muscle, as when holding a dumbbell in the same position or holding a sleeping child in your arms. upon termination of muscle contraction, muscle. The greater the number of cross bridges attached to the actin filaments, the larger the contraction force . the length tension curve below summarizes the relationship between muscle length and tension during force production. it is important to note that two joint muscles undergo active and passive insufficiency during simultaneous movements. 1.examine basic components of skeletal muscle 2.understand the muscle length tension relationship 3. examine why the length tension relationship changes across different muscle lengths and why 4. provide practical examples to understand the applicability of the length tension relationship 5. under the other factors, in addition to ”length.
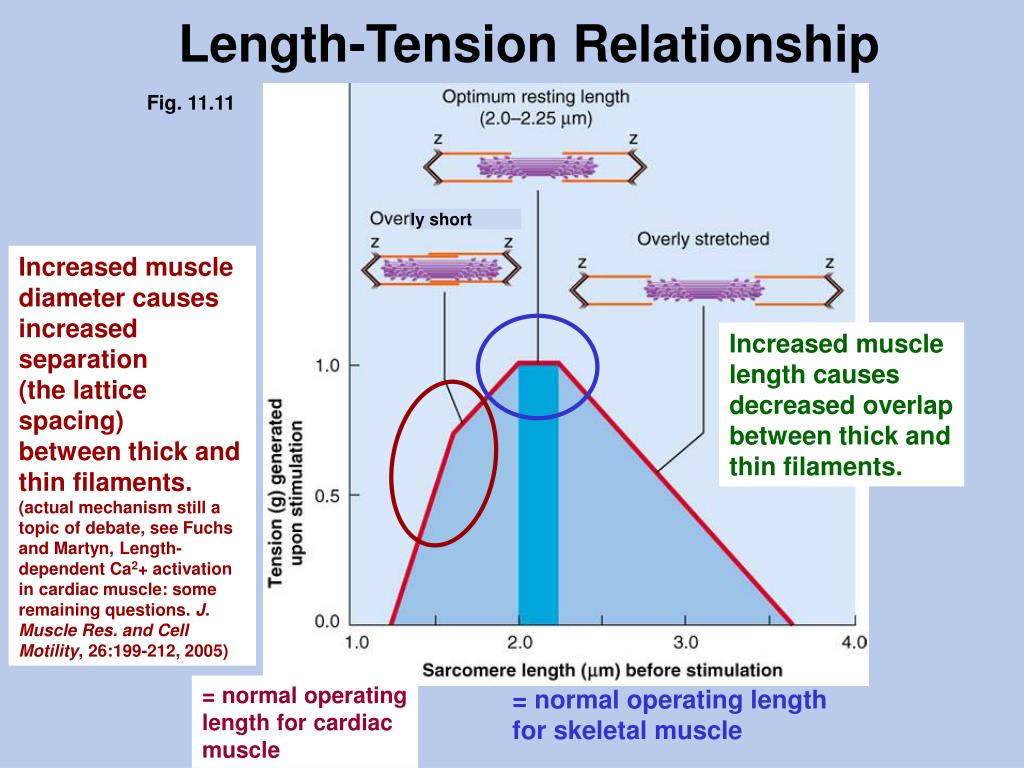
Ppt Skeletal Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Model Powerpoint The greater the number of cross bridges attached to the actin filaments, the larger the contraction force . the length tension curve below summarizes the relationship between muscle length and tension during force production. it is important to note that two joint muscles undergo active and passive insufficiency during simultaneous movements. 1.examine basic components of skeletal muscle 2.understand the muscle length tension relationship 3. examine why the length tension relationship changes across different muscle lengths and why 4. provide practical examples to understand the applicability of the length tension relationship 5. under the other factors, in addition to ”length. The only difference between the two is whether the muscle length is shortening or elongating during the contraction. figure 39.2 – skeletal muscle contractions. an isometric contraction occurs when a muscle produces tension without a change in muscle length. isometric contractions involve sarcomere shortening and increasing muscle tension. Length tension curve measured from cat soleus. (a) data points plotted and fit with curves. (b) waveforms showing the procedures to measure the force at a single test length. the muscle is moved from slack length to the test length at time 50–100 ms. the muscle was stimulated at 100 hz from 200 to 650 ms.

Ppt Introduction To Muscle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download The only difference between the two is whether the muscle length is shortening or elongating during the contraction. figure 39.2 – skeletal muscle contractions. an isometric contraction occurs when a muscle produces tension without a change in muscle length. isometric contractions involve sarcomere shortening and increasing muscle tension. Length tension curve measured from cat soleus. (a) data points plotted and fit with curves. (b) waveforms showing the procedures to measure the force at a single test length. the muscle is moved from slack length to the test length at time 50–100 ms. the muscle was stimulated at 100 hz from 200 to 650 ms.

Comments are closed.