Length Tension Relationships вђ Kinetic Flow

Length Tension Relationships вђ Kinetic Flow Healthy length tension relationships exist when our muscular recruitment patterns are optimal. this results in a coordinated synergy of levers to articulate our range of motion. in any given joint, surrounding musculature both facilitates and inhibits a given movement. joints are controlled by opposing sets of muscles, agonists and antagonists. Kinetic flow is not exclusive to athletics, it sees broader application in helping individuals to connect with and to unify their kinetic chain. it organizes the human brain, a biological supercomputer, and optimally links the software to the hardware. it is neuromuscular programming, our central nervous system’s orchestra of length tension.

Length Tension Relationships вђ Kinetic Flow At kinetic flow, we view human movement patterns as a guiding metric for structural integrity. we place an emphasis on assessing connective tissue and its relationship to: breathing. compound sagittal, frontal, and transverse movement patterns. weight displacement. prone supine movement patterns. crawling patterns. walking. Length tension relationship of a muscle is explained in this video. this topic is a part of muscle biomechanics for bachelor of physiotherapy students. 2.understand the muscle length tension relationship 3. examine why the length tension relationship changes across different muscle lengths and why 4. provide practical examples to understand the applicability of the length tension relationship 5. under the other factors, in addition to ”length tension” which. This is called the length tension relationship. the ideal length of a sarcomere to produce maximal tension occurs at 80 percent to 120 percent of its resting length, with 100 percent being the state where the medial edges of the thin filaments are just at the most medial myosin heads of the thick filaments (figure 39.4). this length maximizes.
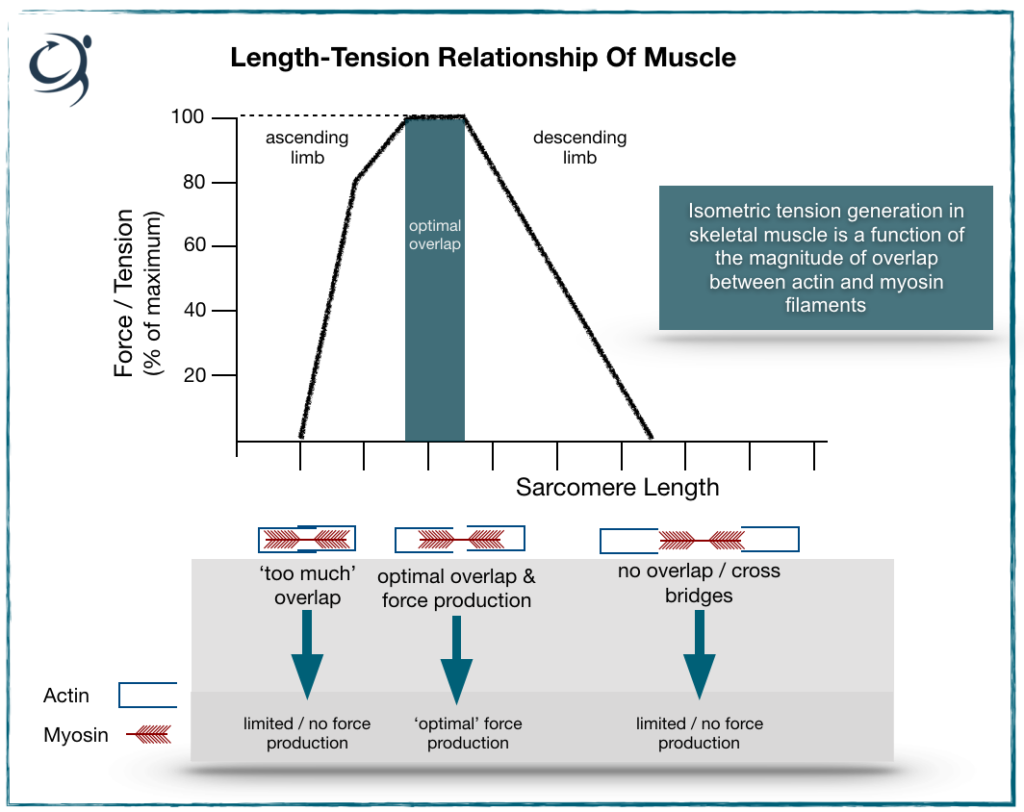
The Length Tension Relationship Using It In Rehab Get Back To Sport 2.understand the muscle length tension relationship 3. examine why the length tension relationship changes across different muscle lengths and why 4. provide practical examples to understand the applicability of the length tension relationship 5. under the other factors, in addition to ”length tension” which. This is called the length tension relationship. the ideal length of a sarcomere to produce maximal tension occurs at 80 percent to 120 percent of its resting length, with 100 percent being the state where the medial edges of the thin filaments are just at the most medial myosin heads of the thick filaments (figure 39.4). this length maximizes. Figure 10.4.1 10.4. 1: types of muscle contractions. during isotonic contractions, muscle length changes to move a load. during isometric contractions, muscle length does not change because the load exceeds the tension the muscle can generate. all of these muscle activities are under the exquisite control of the nervous system. Length tension curve measured from cat soleus. (a) data points plotted and fit with curves. (b) waveforms showing the procedures to measure the force at a single test length. the muscle is moved from slack length to the test length at time 50–100 ms. the muscle was stimulated at 100 hz from 200 to 650 ms.
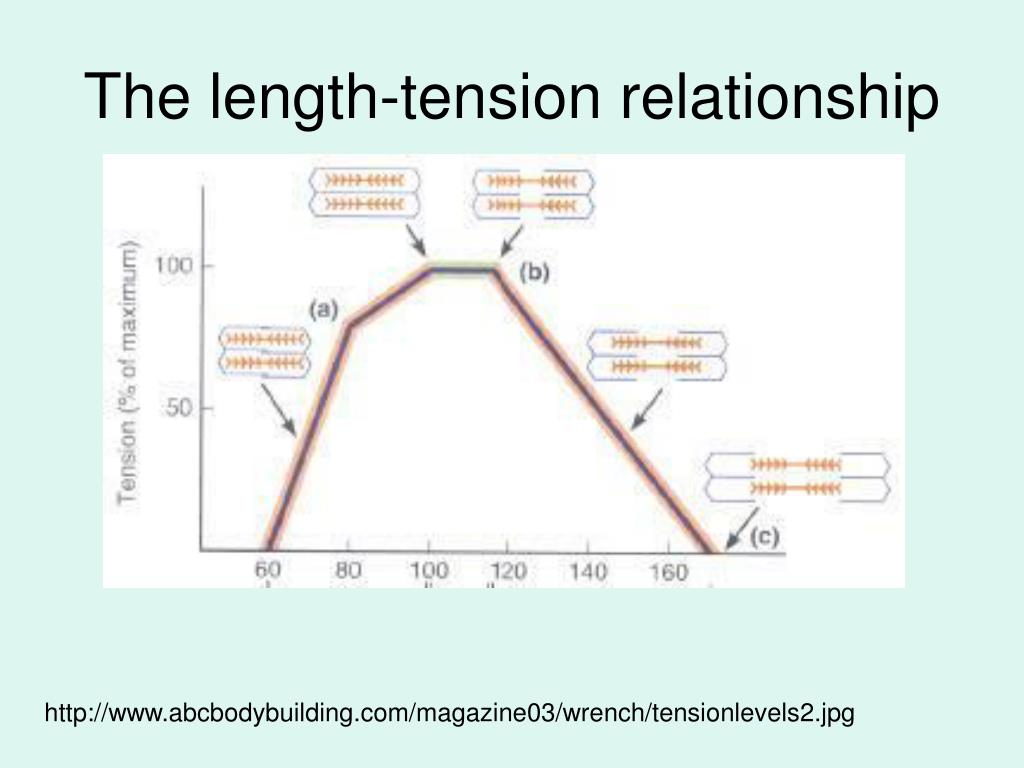
Ppt Fig 12 01 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5604131 Figure 10.4.1 10.4. 1: types of muscle contractions. during isotonic contractions, muscle length changes to move a load. during isometric contractions, muscle length does not change because the load exceeds the tension the muscle can generate. all of these muscle activities are under the exquisite control of the nervous system. Length tension curve measured from cat soleus. (a) data points plotted and fit with curves. (b) waveforms showing the procedures to measure the force at a single test length. the muscle is moved from slack length to the test length at time 50–100 ms. the muscle was stimulated at 100 hz from 200 to 650 ms.

Comments are closed.