Lenses Rules To Draw Ray Diagrams Class 10 Science Part 1 Chapterођ

How To Draw Ray Diagrams Convex Lens Ray Diagrams Class ођ Rule 2 ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis. for a convex lens, we see that ray passing through focus on left becomes parallel to principal axis after refraction. for a concave lens , since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis. Rule 1 ray parallel to principal axis will pass through focus after reflection. for a concave mirror, we see that ray passes through focus after reflection. for a convex mirror , since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus after reflection.

Ray Diagram Concave And Convex Lenses By Animation Tricks To Remember Time stamp0:00 introductionfor concave mirror1:58 object at infinity (case 1)5:09 object is beyond c (case 2)7:24 object is at c (case 3)8:24 object is betwe. 📝download lecture notes from physicswallah app website.📲pw app link bit.ly ytai foundation🌐pw website pw.live🎯udaan science group. First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. so, it appears to pass through focus after reflection. we draw another ray which passes through optical center. so, the ray will go through without any deviation. where both reflected rays meet is point a'. and the image formed is a'b'. this image is formed between f 1 and optical center (o) we. Hey guys , in this video i tried to explain you ray diagrams for convex lens . #raydiagram #light #lensmake sure you like , share and subscribe !more videos.

Ray Diagramming Convex Mirror First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. so, it appears to pass through focus after reflection. we draw another ray which passes through optical center. so, the ray will go through without any deviation. where both reflected rays meet is point a'. and the image formed is a'b'. this image is formed between f 1 and optical center (o) we. Hey guys , in this video i tried to explain you ray diagrams for convex lens . #raydiagram #light #lensmake sure you like , share and subscribe !more videos. A plane mirror is a flat, smooth reflective surface with a clear, undistorted reflection. when an object is reflected in a plane mirror, it always forms a virtual image that is upright, of the same shape and size as the object. on the other hand, a spherical mirror exhibits a consistent curvature. it possesses a constant radius of curvature (in. The ray diagrams for the image formation in a convex and concave lens for a few positions of the object are shown below. rule 1: a ray of light from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a convex lens, passes through the principal focus on the other side of the lens. in the case of a concave lens, the ray appears to.
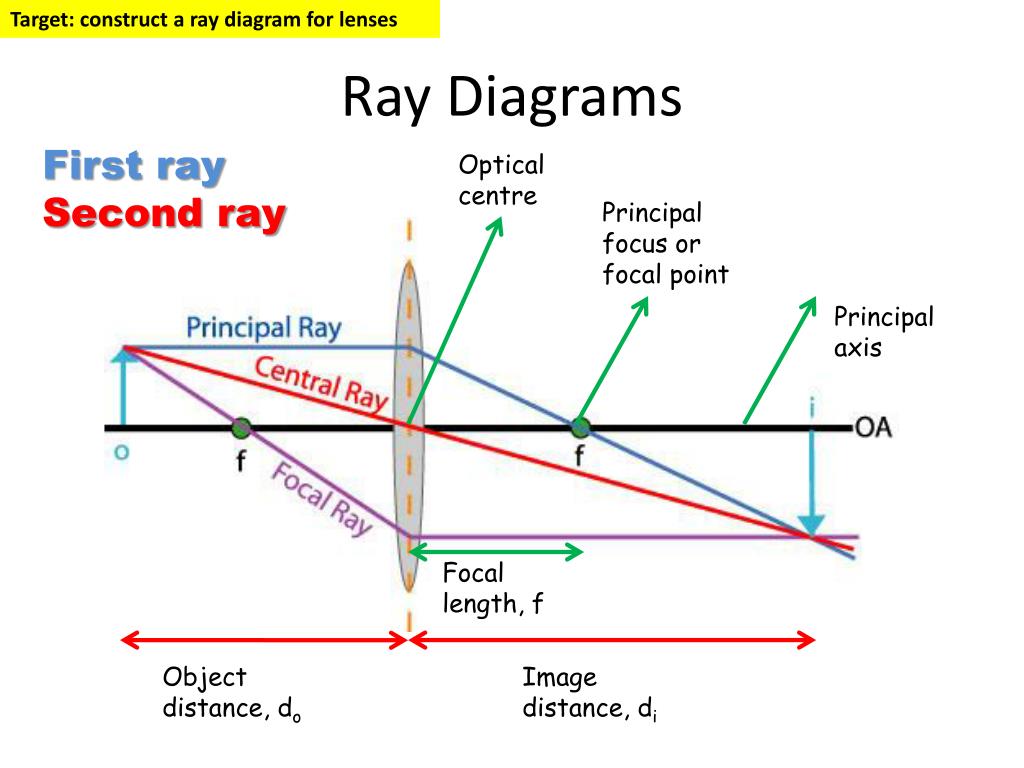
How To Draw Ray Diagrams A plane mirror is a flat, smooth reflective surface with a clear, undistorted reflection. when an object is reflected in a plane mirror, it always forms a virtual image that is upright, of the same shape and size as the object. on the other hand, a spherical mirror exhibits a consistent curvature. it possesses a constant radius of curvature (in. The ray diagrams for the image formation in a convex and concave lens for a few positions of the object are shown below. rule 1: a ray of light from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a convex lens, passes through the principal focus on the other side of the lens. in the case of a concave lens, the ray appears to.
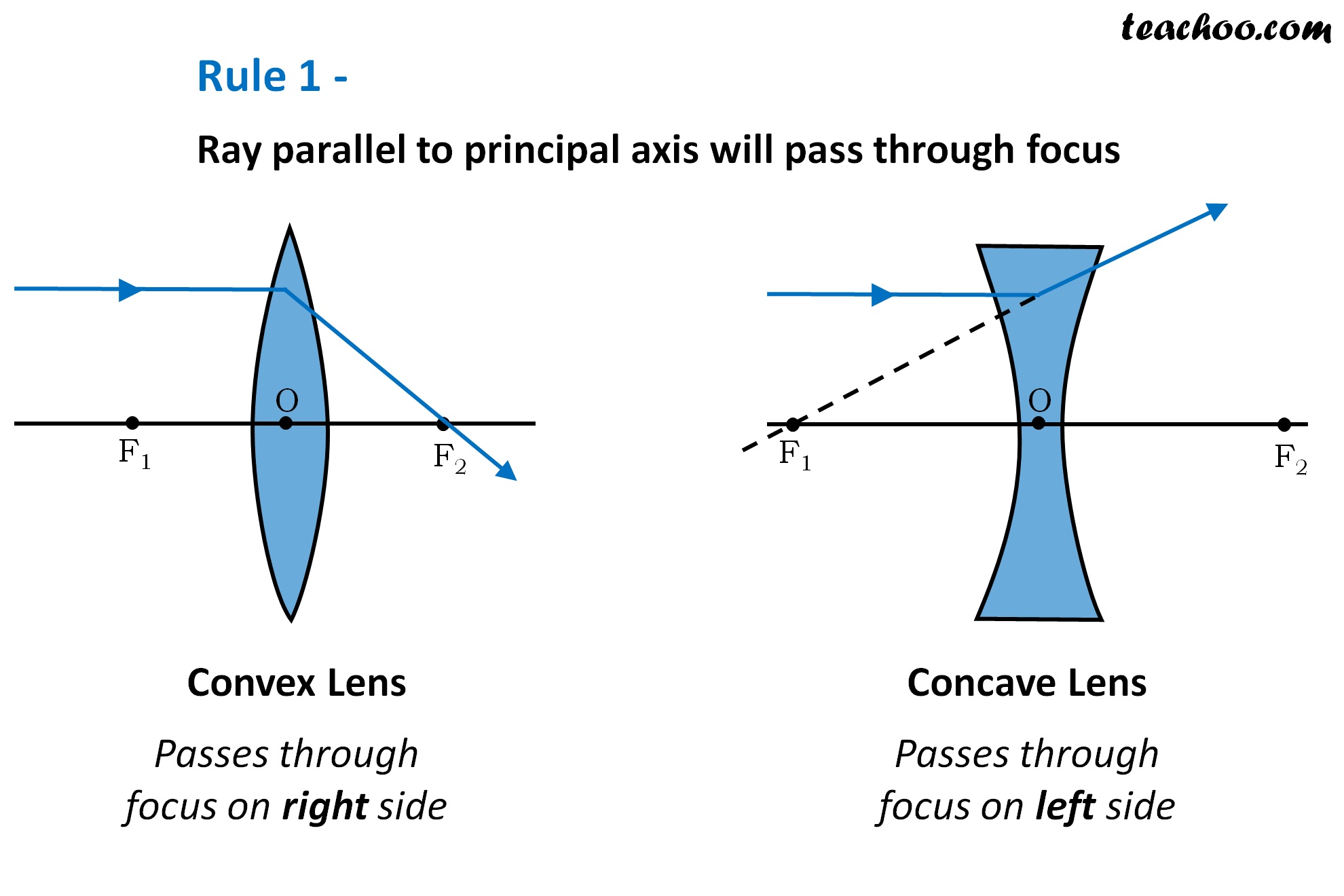
Ray Diagram For A Concave Lens

Comments are closed.