Less Frequent Vital Signs Monitoring In Low Risk Hematology Oncology

Less Frequent Vital Signs Monitoring In Low Risk Hematology Oncology Tham sm, kasinathan s, lui pk, et al. nurse led vital signs monitoring can safely identify low risk hematology oncology patients for de escalation [published online june 23, 2020]. jco oncol pract. Purpose: it is routine practice for patients to be on vital signs monitoring (vsm) once every 4 hours, which is laborious and disruptive. vsm de escalation has been demonstrated to be safe in low risk (lr) patients, but it has not been well studied in the hematology oncology setting. methods: a quality improvement project was conducted in 3 hematology oncology inpatient wards within a.
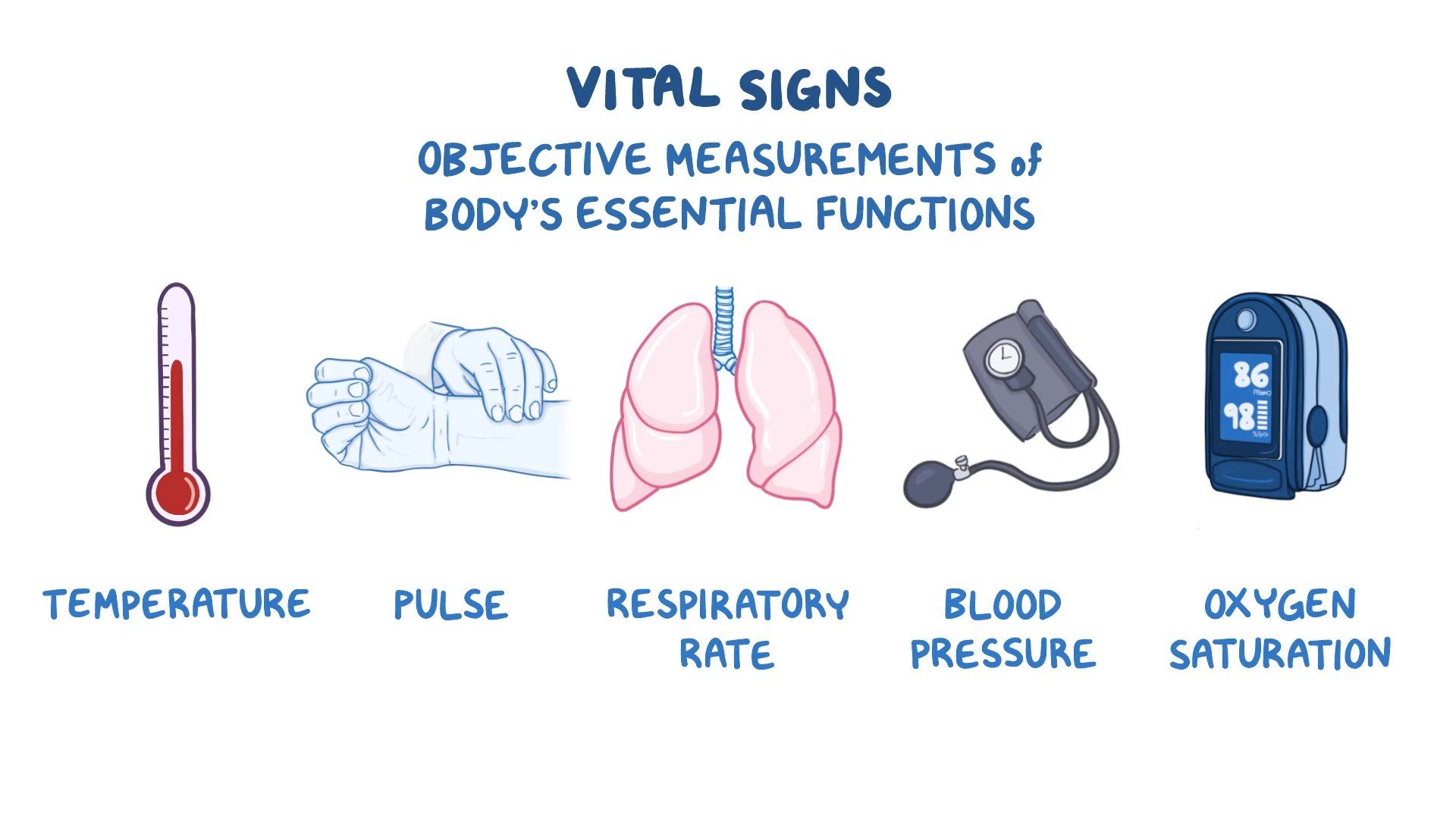
Assessment Of Vital Signs Osmosis Video Library Vsm de escalation has been demonstrated to be safe in low risk (lr) patients, but it has not been well studied in the hematology oncology setting. methods: a quality improvement project was conducted in 3 hematology oncology inpatient wards within a comprehensive cancer center, from march 2017 to july 2017 (pilot phase) and from october 2017 to. In the last few decades, vital signs have become an area of active research and numerous studies have reported that changes in vital signs occur several hours prior to a serious adverse event [3–7]. today, vital signs play an important role in emergency departments (ed) and on the wards, to determine patients at risk of deterioration [6–11]. Practice recommendation #3: nurses closely monitor vital signs of febrile patients and those at increased risk of developing severe crs . nurses are well positioned to mitigate the risk of crs related morbidity and mortality through early recognition of crs signs such as fever, hypotension, tachycardia, and hypoxia. Patients with cancer are often dependent on blood transfusions during treatment. frequent vital sign monitoring during transfusions may inter rupt sleep and the pa tient s ability to ambulate or participate in unit activities. relying heavily on vital sign ndings may also overshadow unmeasurable symptoms of transfusion reaction. the.

Comments are closed.