Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspressmagazine
96 Best Ideas For Coloring Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspress lets you save time and helps students learn for students k 12. sign up now. sign in if you’re already a member. access to 6,000 resources. unlimited downloads. homework ready. essential school bundles. math, science, reading, cognitive games. coloring pages, projects, experiments. Inside, it begins to grow and change. during this stage, it is called a chrysalis. the chrysalis starts to grow all of the parts that we recognize on butterflies, like wings, legs, and a long mouth. again, this stage may last a few weeks or months. adult butterfly (imago) – finally, the adult butterfly emerges from its hard casing and starts.
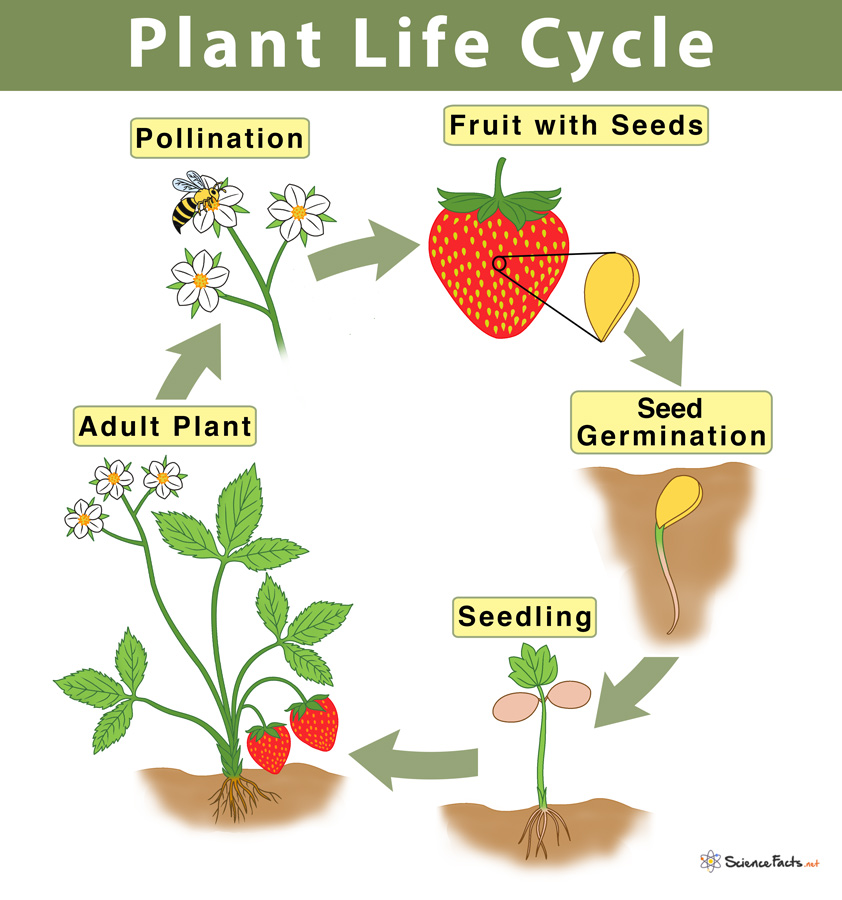
Plant Life Cycle Study Guide Inspirit Learning Inc Join ms tree as she walks down memory lane through the stages of the plant cycle, to see how she transformed from a seed to a beautiful plant that bears frui. The plant life cycle describes the stages that the plant goes through from its birth until its death. they are found in all types of plants ; flowering or non flowering and vascular or nonvascular. in flowering plants, the process starts with seed formation, which then germinates to give rise to a new plant. Instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. throughout the plant life cycle, all plants undergo the alternation of generations. this cycle of generations include both diploid (2n) phase, the sporophyte, and the haploid (n) phase gametophyte. in this page, explore at how these generations differ with each. Filament: supports the anther. pistil: the female part of the plant, sometimes called the ‘carpel’. stigma: collects pollen grains. style: allows pollen to pass to the ovary. ovary: produces seeds inside tiny ‘ovules’. sepal: found outside the petals, the sepal protects the flower when it’s unopened.
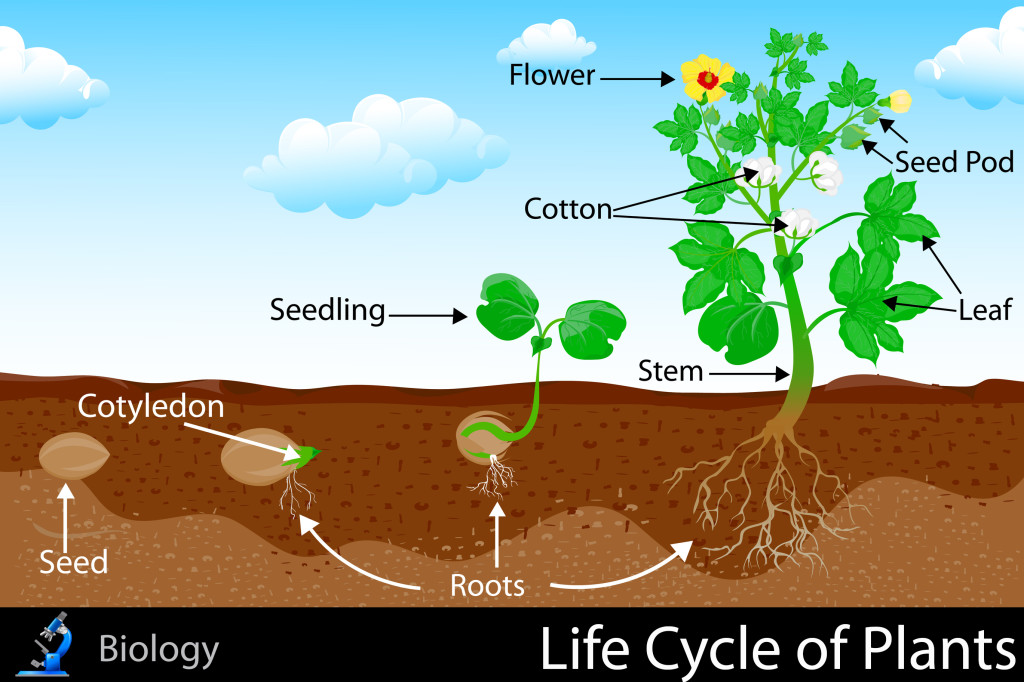
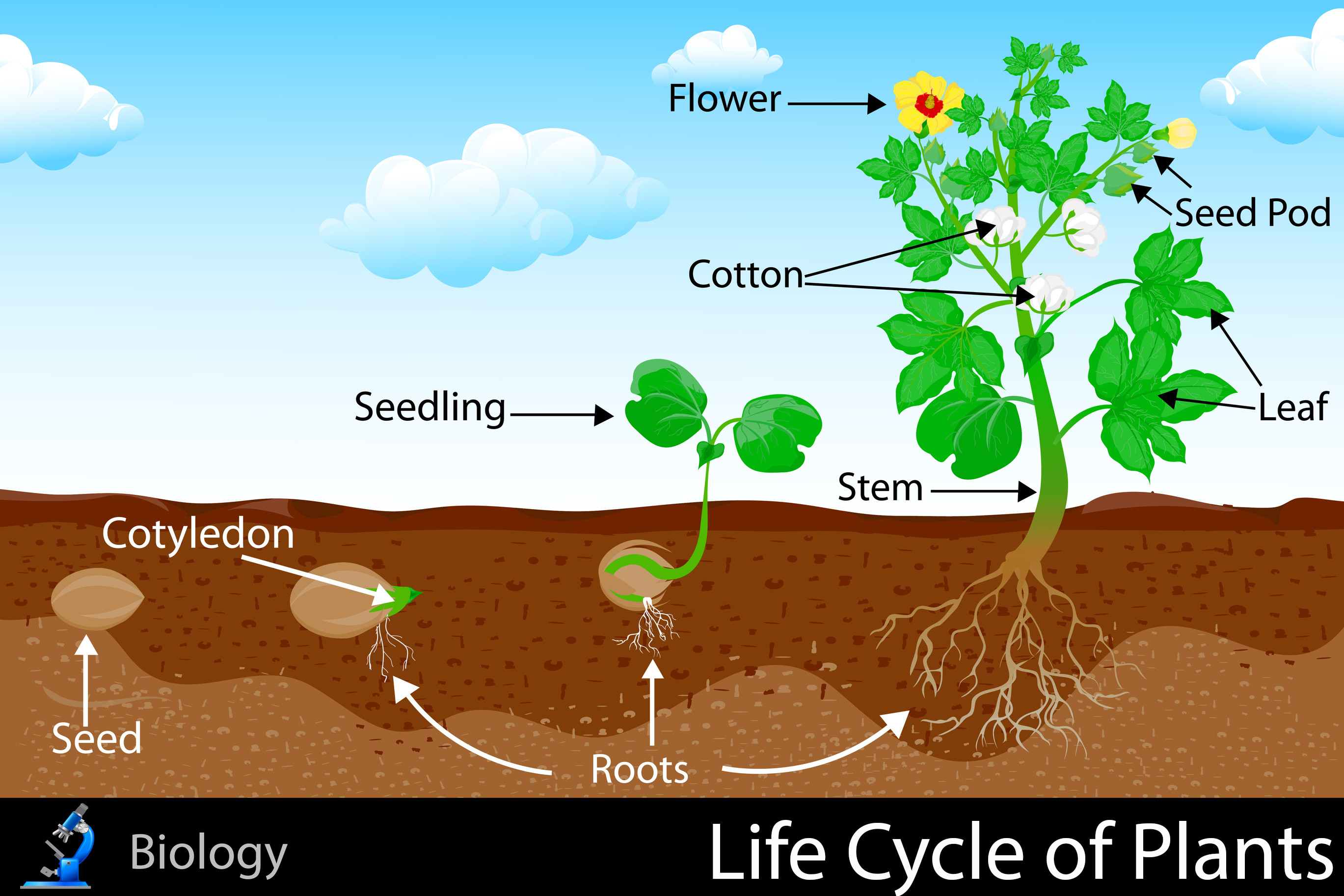
Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspressmagazine Instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. throughout the plant life cycle, all plants undergo the alternation of generations. this cycle of generations include both diploid (2n) phase, the sporophyte, and the haploid (n) phase gametophyte. in this page, explore at how these generations differ with each. Filament: supports the anther. pistil: the female part of the plant, sometimes called the ‘carpel’. stigma: collects pollen grains. style: allows pollen to pass to the ovary. ovary: produces seeds inside tiny ‘ovules’. sepal: found outside the petals, the sepal protects the flower when it’s unopened. The ovules, located in the stigma, contain the other half. when the pollen reaches the ovules of a plant, they are fertilized and become seeds. then, the plant's fertilized seeds are dispersed by wind, water, or animals, and the whole process begins again. cite this article. the plant life cycle consists of five stages, from seeds to growth to. When the seed germinates and the tiny plant emerges from the seed coat, it grows both down into the soil and up to the surface of the soil. the part of the plant that grows into the soil is called the root. the roots of a plant anchor it into the soil and give it stability. roots, also, gather water and nutrients from the soil for the rest of.

Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspressmagazine Plant Life Cycle The ovules, located in the stigma, contain the other half. when the pollen reaches the ovules of a plant, they are fertilized and become seeds. then, the plant's fertilized seeds are dispersed by wind, water, or animals, and the whole process begins again. cite this article. the plant life cycle consists of five stages, from seeds to growth to. When the seed germinates and the tiny plant emerges from the seed coat, it grows both down into the soil and up to the surface of the soil. the part of the plant that grows into the soil is called the root. the roots of a plant anchor it into the soil and give it stability. roots, also, gather water and nutrients from the soil for the rest of.

Comments are closed.