Management Of Hyperkalemia An Update For The Internist The American

Management Of Hyperkalemia An Update For The Internist The American Hyperkalemia is a clinically important electrolyte abnormality that occurs most commonly in patients with chronic kidney disease. due to its propensity to induce electrophysiological disturbances, severe hyperkalemia is considered a medical emergency. the management of acute and chronic hyperkalemia can be achieved through the implementation of various interventions, one of which is the. The management of acute and chronic hyperkalemia can be achieved through the implementation of various interventions, one of which is the elimination of medications that can raise serum potassium levels. because many such medications (especially inhibitors of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system) have shown beneficial effects in patients.
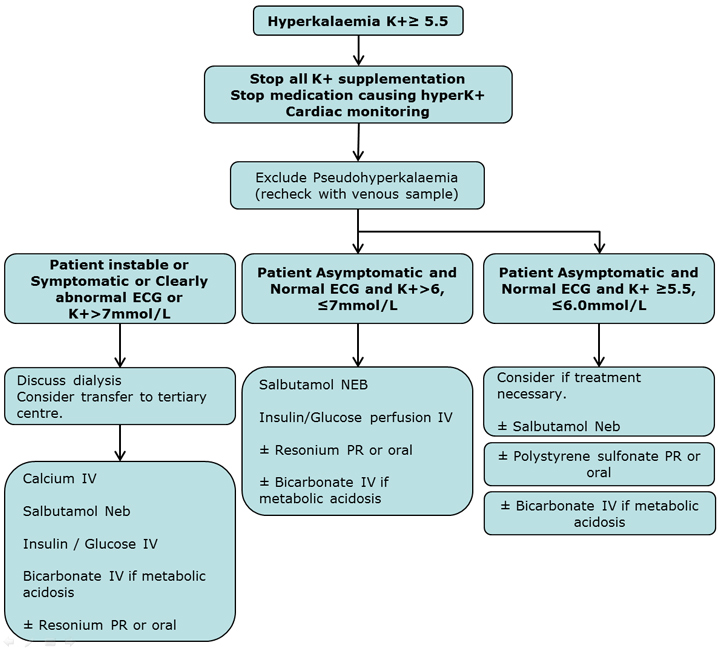
Clinical Practice Guidelines Hyperkalaemia For chronic management of hyperkalemia, the goal is to prevent the development of hyperkalemia by identifying and correcting the proximal defect(s) in potassium homeostasis. this typically starts by eliminating correctable causes, such as high potassium intake in diet or in supplements, hyperkalemia inducing medications, or metabolic acidosis. Acute hyperkalemia is a clinical emergency, which, depending on its severity, may warrant interventions such as cardiac monitoring, administration of potassium lowering medications, or emergency dialysis. the immediate goal of acute management in hyperkalemia is the stabilization of the membrane potential, with or without changing the serum. 2016. tldr. the development of novel potassium binders has ushered in a new era of hyperkalemia management, with a focus on chronic therapy while maintaining the use of beneficial, but hyperkalemia inducing medications such as renin angiotensin aldosterone system inhibitors. expand. 83. Exposures hyperkalemia defined with the presence of at least 2 serum potassium values ≥ 5.1 mmol l. outcome measures direct health care costs and resource use in patients with hyperkalemia.
Management Of Hyperkalemia An Update For The Internist Em Consulte 2016. tldr. the development of novel potassium binders has ushered in a new era of hyperkalemia management, with a focus on chronic therapy while maintaining the use of beneficial, but hyperkalemia inducing medications such as renin angiotensin aldosterone system inhibitors. expand. 83. Exposures hyperkalemia defined with the presence of at least 2 serum potassium values ≥ 5.1 mmol l. outcome measures direct health care costs and resource use in patients with hyperkalemia. Management of hyperkalemia: an update for the internist. am j med. 2015 jun 17; authors: kovesdy cp. abstract hyperkalemia is a clinically important electrolyte abnormality which occurs most commonly in patients with chronic kidney disease. Hyperkalemia is an electrolyte abnormality with potentially life threatening consequences. despite various guidelines, no universally accepted consensus exists on best practices for hyperkalemia monitoring, with variations in precise potassium (k ) concentration thresholds or for the management of acute or chronic hyperkalemia.

Comments are closed.