Marginal Analysis In Economics Study
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/marginal-cost-of-production-4193224-a510dd276d1e433ca1f2ee4f19ddfdea.jpg)
Marginal Utilities Definition Types Examples And 46 Off Marginal analysis plays a crucial role in understanding how prices are determined in a market economy. it is the backbone of the supply and demand model, which is used to explain the behavior of buyers and sellers in a competitive market. according to marginal analysis, the price of a good is determined by the intersection of the supply and. Marginal net benefit of the first drink is $13 ($20 – $7), the 2nd is $5 ($12 – $7), and the third is $1 ($6 – $7). as long as the marginal net benefit is positive, we should increase our activity! summary. marginal analysis is an essential concept for everything we learn in economics, because it lies at the core of why we make decisions.
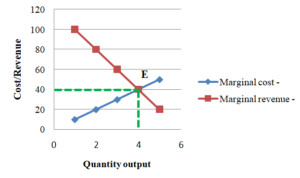
Marginal Analysis In Economics Use Of Marginal Anlsysis Marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity compared to the additional costs incurred by that same activity. companies use marginal analysis as a decision making. Marginal analysis. in the field of economics, marginal analysis entails the examination of the final or next unit of cost or of consumption. it involves a cost benefit analysis of business decisions—that is, understanding whether a particular decision provides enough benefits to be worth the cost of that decision. The difference in cost between one week and two is $3,600 – $2,000, or $1,600. thus, while the marginal cost of the first week’s rental is $2,000, the marginal cost of the second week’s rental is $1,600. this illustrates the key rule of marginal analysis: marginal cost = the change in total cost from one option to another. 2.6: marginal analysis. economists analyze relationships like revenue functions from the perspective of how the function changes in response to a small change in the quantity. these marginal measurements not only provide a numerical value to the responsiveness of the function to changes in the quantity but also can indicate whether the business.

вїquг Es El Anгўlisis Marginal Definiciгіn Sentido Contabilizar The difference in cost between one week and two is $3,600 – $2,000, or $1,600. thus, while the marginal cost of the first week’s rental is $2,000, the marginal cost of the second week’s rental is $1,600. this illustrates the key rule of marginal analysis: marginal cost = the change in total cost from one option to another. 2.6: marginal analysis. economists analyze relationships like revenue functions from the perspective of how the function changes in response to a small change in the quantity. these marginal measurements not only provide a numerical value to the responsiveness of the function to changes in the quantity but also can indicate whether the business. Marginal analysis is the analysis of economic decisions that focuses on incremental changes from a given starting point. the underlying idea is that decision makers make choices based on whether a small change from the given state of the world is better or worse than the current outcome. a decision maker assesses whether the benefits of an. Marginal analysis. marginal analysis is a decision making tool that evaluates the benefits and costs of producing or consuming one additional unit of a good or service. it involves comparing the marginal benefit with the marginal cost to determine the optimal level of production or consumption. by focusing on the incremental changes, marginal.

Comments are closed.