Marginal Analysis Microeconomics Socratic

Marginal Analysis Definition Formula And Applications Why is it important to review marginal costs and revenues in an analysis? answer: mr and mc are used to determine a firm's equilibrium. explanation: whatever be the market form, for a firm to be in equilibrium, the two conditions are to be satisfied. 1st order condition or necessary condition. mc = mr. 2nd order condition or sufficient condition. Questions and videos on marginal analysis, within microeconomics. marginal analysis topic page marginal analysis questions. how does a review of marginal analysis assist in decisions made at a firm or economy?.
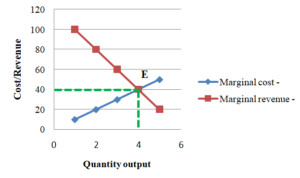
Marginal Analysis In Economics Use Of Marginal Anlsysis Income distribution. equity. sources and measures of income inequality. watch the best videos and ask and answer questions in 57 topics and 14 chapters in microeconomics. get smarter in microeconomics on socratic. The difference in cost between one week and two is $3,600 – $2,000, or $1,600. thus, while the marginal cost of the first week’s rental is $2,000, the marginal cost of the second week’s rental is $1,600. this illustrates the key rule of marginal analysis: marginal cost = the change in total cost from one option to another. To calculate, all we have to do is add up our benefits and subtract our costs. total benefit = $20 $12 = $32. total cost = $7 $7 = $14. net benefit = $32 – $14 = $18. it is important to recognize that our act of marginal analysis has maximized this benefit. consider what would happen if we purchased 3 drinks. Marginal analysis. the microeconomic analysis of decisions utilizes marginal analysis as an effective method for optimal decision making. any decision making process involves comparing the future impacts that will arise from each of the competing choices we face today. the process of marginal analysis recognizes the effects of small changes in.
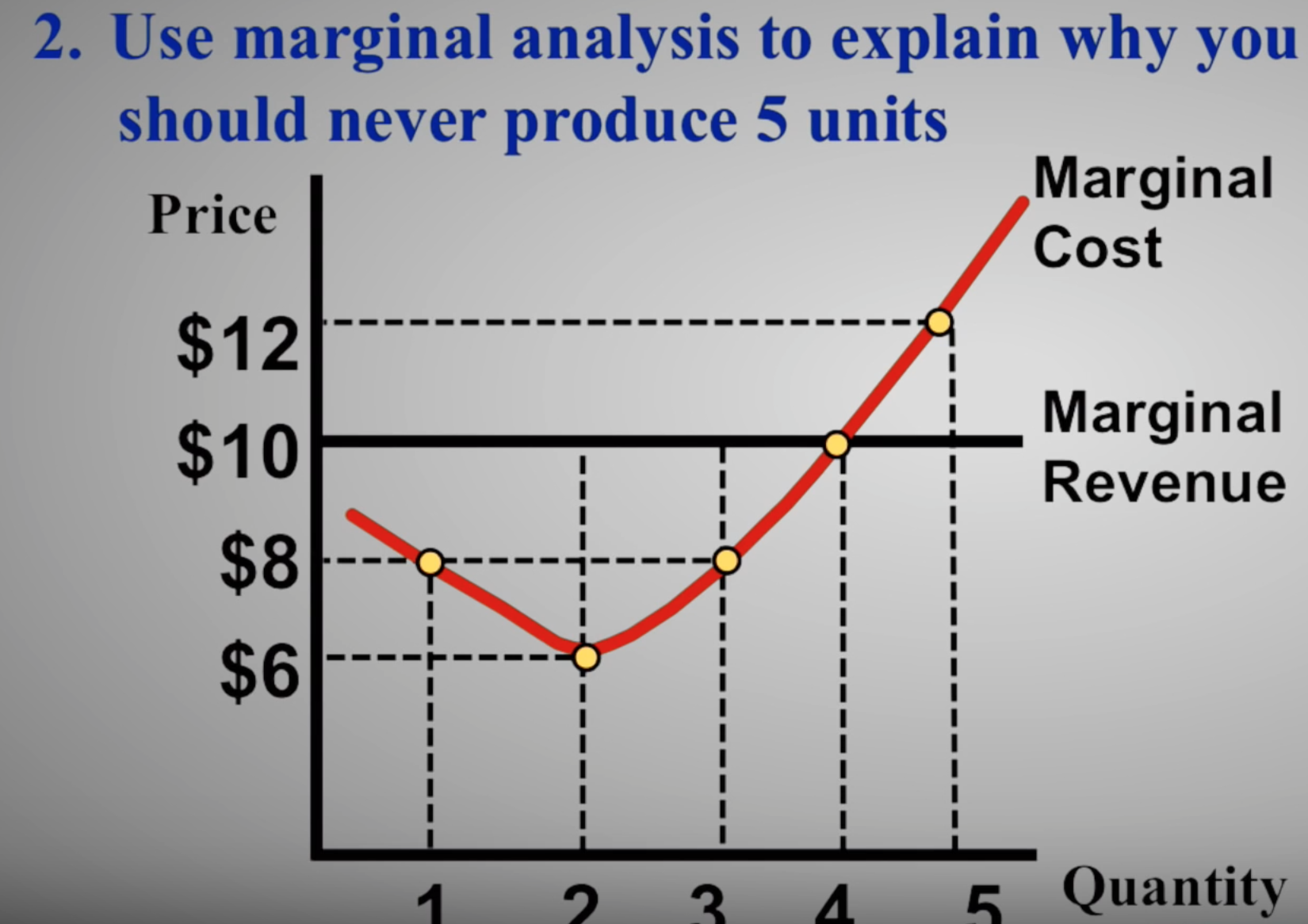
Solved Use Marginal Analysis To Explain Why You Should Never Chegg To calculate, all we have to do is add up our benefits and subtract our costs. total benefit = $20 $12 = $32. total cost = $7 $7 = $14. net benefit = $32 – $14 = $18. it is important to recognize that our act of marginal analysis has maximized this benefit. consider what would happen if we purchased 3 drinks. Marginal analysis. the microeconomic analysis of decisions utilizes marginal analysis as an effective method for optimal decision making. any decision making process involves comparing the future impacts that will arise from each of the competing choices we face today. the process of marginal analysis recognizes the effects of small changes in. Marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity compared to the additional costs incurred by that same activity. companies use marginal analysis as a decision making. The difference in cost between one week and two is $3,600 – $2,000, or $1,600. thus, while the marginal cost of the first week’s rental is $2,000, the marginal cost of the second week’s rental is $1,600. this illustrates the key rule of marginal analysis: marginal cost = the change in total cost from one option to another.
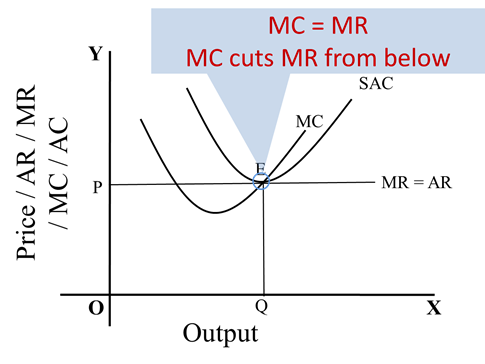
Marginal Analysis Microeconomics Socratic Marginal analysis is an examination of the additional benefits of an activity compared to the additional costs incurred by that same activity. companies use marginal analysis as a decision making. The difference in cost between one week and two is $3,600 – $2,000, or $1,600. thus, while the marginal cost of the first week’s rental is $2,000, the marginal cost of the second week’s rental is $1,600. this illustrates the key rule of marginal analysis: marginal cost = the change in total cost from one option to another.

Comments are closed.