Maxillary Nerve Origin Course And Branches
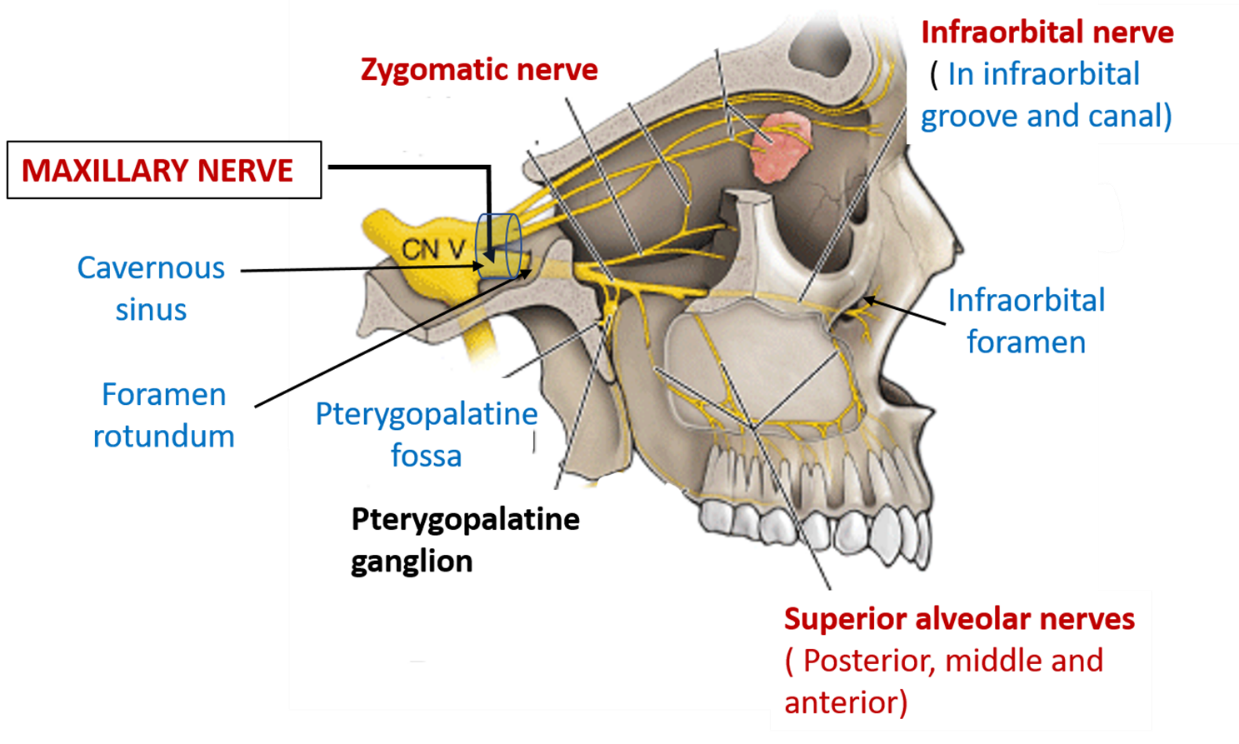
Maxillary Nerve вђ Anatomy Qa This nerve carries sensory fibers from: the dura mater of the middle cranial fossa. the mucosa of the nasopharynx, the palate, the nasal cavity and maxillary sinus. the teeth and the upper jaw. the skin that covers the side of the nose, the lower eyelid, the cheek and the upper lip. course and relations. The maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (cnv2).

Anatomy And Clinical Significance Of The Maxillary Nerve A Literature Supplied structures. the maxillary nerve conveys general sensation from portions of the skin and mucosal linings of the middle face, orbit, paranasal sinuses, nasal cavity, palate, and pharynx. some of the nerves that branch off the maxillary nerve pick up parasympathetic fibers, but the maxillary nerve itself does not have any. In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (v 2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (cn v) cranial nerve.it comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid face, [1] and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve. It is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve) which serves both a sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) function. the maxillary branch is involved mostly in the sensory function. it helps relay sensation and pain messaging from the upper teeth, jaw, the mucosa (membranes) of the nasal cavity, and part of the tongue and face. In this video, we take a comprehensive look at the maxillary nerve's journey, starting from its origin within the trigeminal ganglion. tracing its intricate.

Maxillary Nerve Origin Course And Branches Anatomy Qa It is a branch of the trigeminal nerve (the fifth cranial nerve) which serves both a sensory (afferent) and motor (efferent) function. the maxillary branch is involved mostly in the sensory function. it helps relay sensation and pain messaging from the upper teeth, jaw, the mucosa (membranes) of the nasal cavity, and part of the tongue and face. In this video, we take a comprehensive look at the maxillary nerve's journey, starting from its origin within the trigeminal ganglion. tracing its intricate. Anatomy, head and neck, maxillary nerve statpearls. The maxillary nerve, or second division of the trigeminal, is a sensory nerve that crosses the pterygopalatine fossa, traverses the orbit in the infraorbital groove and canal in the floor of the orbit, and appears upon the face at the infraorbital foramen as the infraorbital nerve. explore on sciencedirect. complete anatomy.

Comments are closed.