Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction And Relaxation Important Concepts For
Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction And Relaxation Important Concepts For Relaxation of a skeletal muscle. relaxing skeletal muscle fibers, and ultimately, the skeletal muscle, begins with the motor neuron, which stops releasing its chemical signal, ach, into the synapse at the nmj. the muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the sr where ca was being released. atp driven pumps will move ca out. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: length and tension. in physiology, muscle shortening and muscle contraction are not synonymous. tension within the muscle can be produced without changes in the length of the muscle, as when holding a dumbbell in the same position or holding a sleeping child in your arms. upon termination of muscle contraction, muscle.

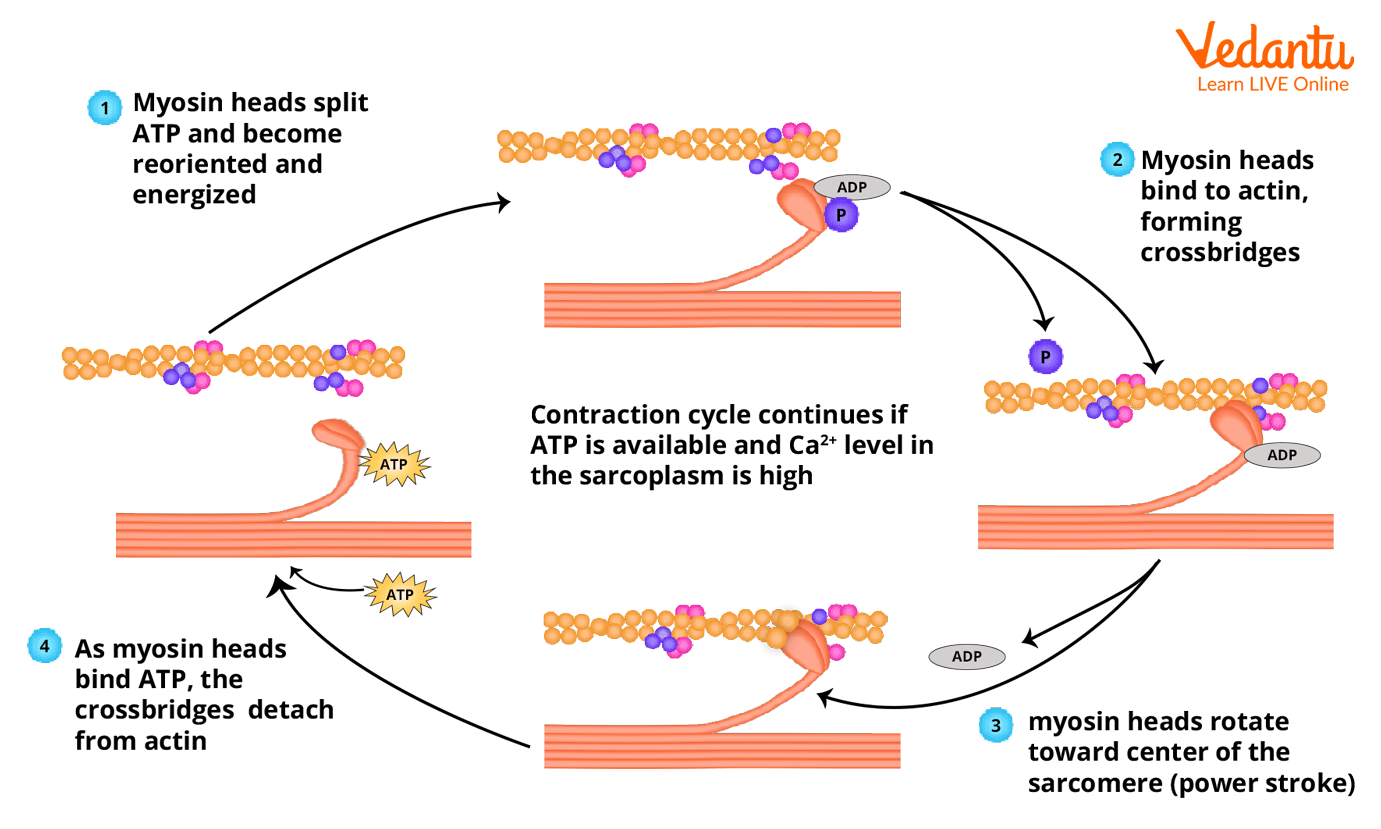
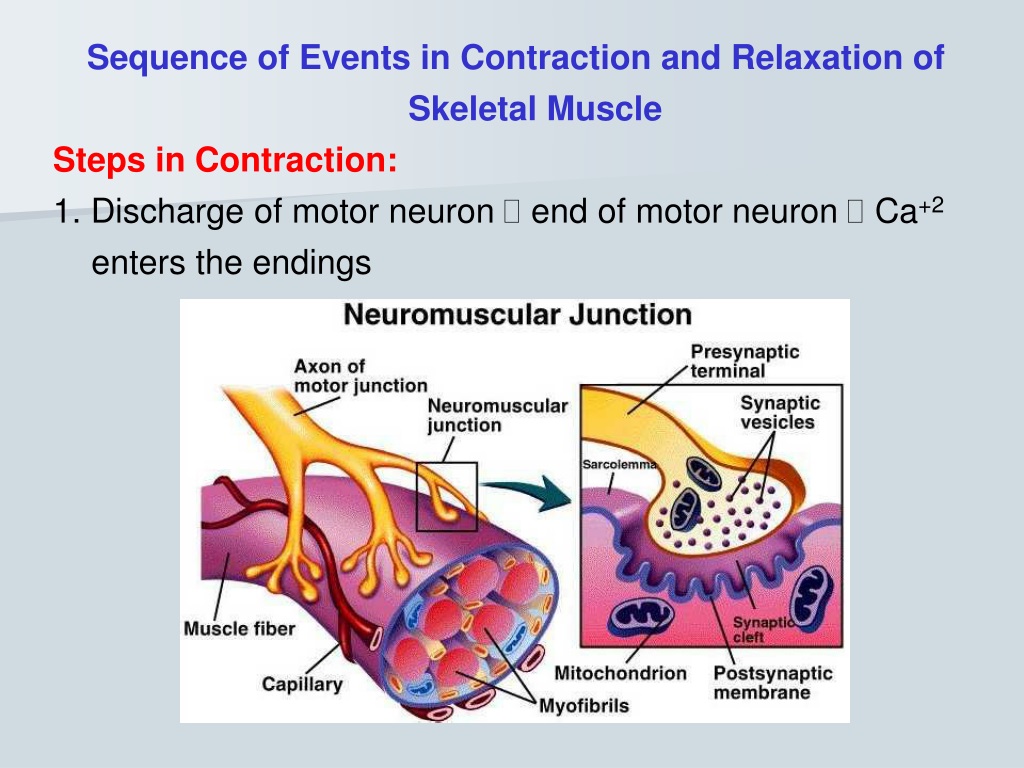
Detailed Steps Of Muscle Contraction Excitation signalling of action potentials from the motor neuron are coupled with calcium release. thus, the excitation contraction coupling process begins with signaling from the nervous system at the neuromuscular junction ( figure 10.3.1) and ends with calcium release for muscle contraction. figure 10.3.1 – motor end plate and innervation. Figure 10.9 relaxation of a muscle fiber ca ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. a muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of atp and becomes fatigued. interactive link. the release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions. Figure 9.4.1 9.4. 1: contraction of a muscle fiber. a cross bridge forms between actin and the myosin heads initiating contraction. as long as ca ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten. The contraction of a striated muscle fiber occurs as the sarcomeres, linearly arranged within myofibrils, shorten as myosin heads pull on the actin filaments. figure 7.9: relaxation of a muscle fiber. ca 2 ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands.
Mechanism Of Contraction And Relaxation Of Muscles In Detail Figure 9.4.1 9.4. 1: contraction of a muscle fiber. a cross bridge forms between actin and the myosin heads initiating contraction. as long as ca ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten. The contraction of a striated muscle fiber occurs as the sarcomeres, linearly arranged within myofibrils, shorten as myosin heads pull on the actin filaments. figure 7.9: relaxation of a muscle fiber. ca 2 ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. Figure 2. relaxation of a muscle fiber. ca ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. a muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of atp and becomes fatigued. the release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions. By studying sarcomeres, the basic unit controlling changes in muscle length, scientists proposed the sliding filament theory to explain the molecular mechanisms behind muscle contraction. within.
Ppt Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction Powerpoint Presentation Free Figure 2. relaxation of a muscle fiber. ca ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. a muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of atp and becomes fatigued. the release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions. By studying sarcomeres, the basic unit controlling changes in muscle length, scientists proposed the sliding filament theory to explain the molecular mechanisms behind muscle contraction. within.

Comments are closed.