Mechanisms Involved In Inflammation Tissue Injury And Progression Of
Mechanisms Involved In Inflammation Tissue Injury And Progression Of Chronic inflammation occurs when acute inflammatory mechanisms fail to eliminate tissue injury , and may lead to a host of diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis, type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancers . understanding the common mechanisms that orchestrate dysfunction in the various organ systems will allow for. Inflammation is an essential aspect of the innate defense mechanism of the body against infectious or noninfectious etiologies. this mechanism is nonspecific and immediate.[1] the 5 fundamental signs of inflammation include heat, redness, swelling, pain, and loss of function. increased blood flow leads to redness and heat, while swelling results from fluid accumulation. pain arises from.
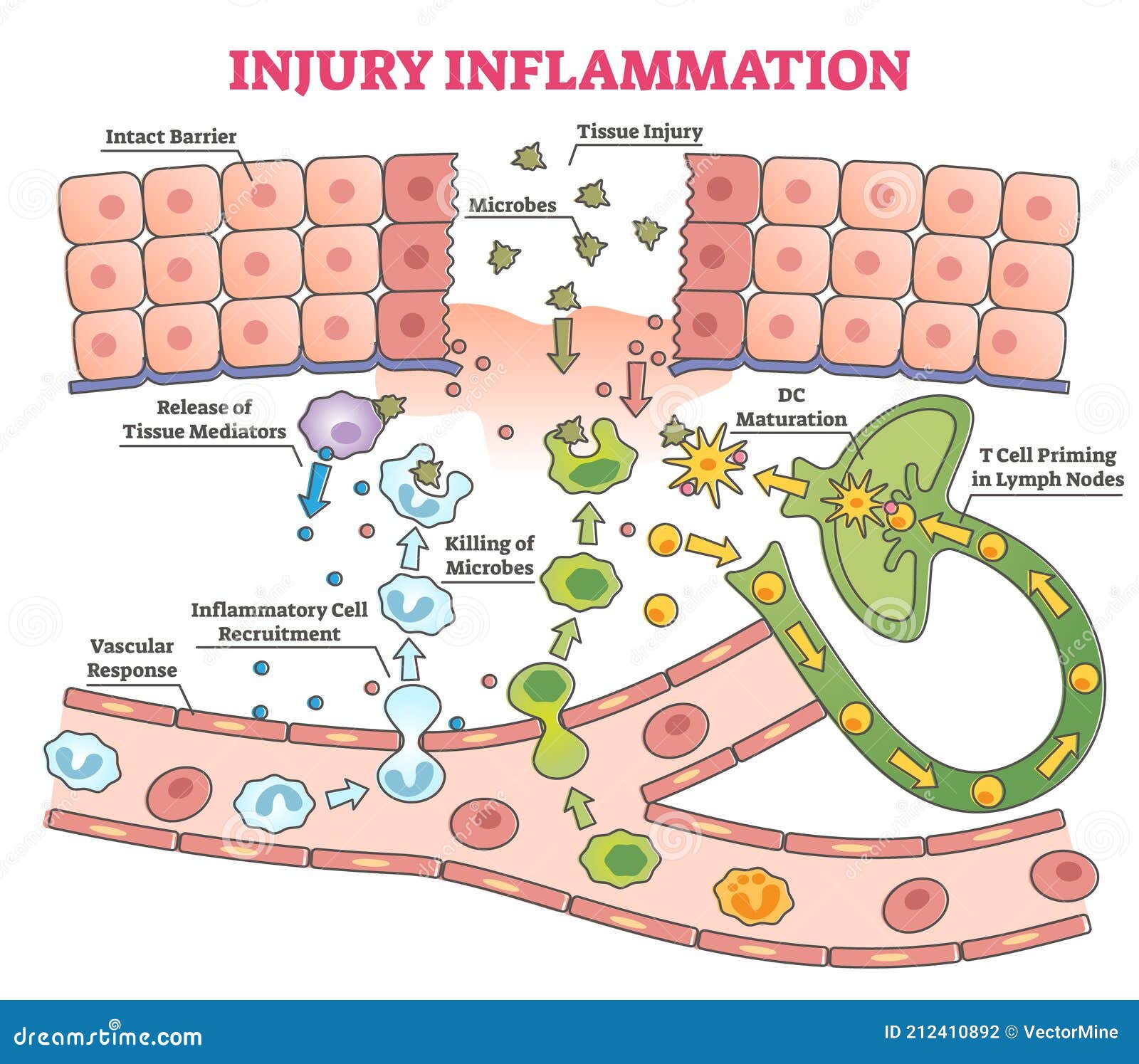
Injury Inflammation As Body Response Process In Educational Outline Download scientific diagram | mechanisms involved in inflammation, tissue injury and progression of renal damage in diabetic nephropathy (dn). from publication: pathogenic pathways and therapeutic. The inflammatory response is complex, modulated by a multitude host of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. uncontrolled and excessive inflammation promotes tissue injury and delays healing (as in diabetic mice ). however, insufficient immune cell recruitment, for example in tlr3 knockout mice, also hinders repair . thus, immune cell responses must. Interactions of cells in the innate immune system, adaptive immune system, and inflammatory mediators orchestrate aspects of the acute and chronic inflammation that underlie diseases of many organs. a coordinated series of common effector mechanisms of inflammation contribute to tissue injury, oxidative stress, remodeling of the extracellular. Review. inflammation predisposes to the development of cancer and promotes all stages of tumorigenesis. cancer cells, as well as surrounding stromal and inflammatory cells, engage in well orchestrated reciprocal interactions to form an inflammatory tumor microenvironment (tme). cells within the tme are highly plastic, continuously changing.

Comments are closed.