Medical School Testing Median Radial And Ulnar Nerves Physical

Medical School Testing Median Radial And Ulnar Nerves Hand Midcarpal instability. examiner stabilizes distal radius and ulna with non dominant hand and moves patients wrist from radial deviation to ulnar deviation, whilst applying an axial load. a positive test occurs when a clunk is felt when the wrist is ulnarly deviated. ulnar carpal abutement. tests for tfcc tear or ulnar carpal impingement. Radial and ulnar pulse. palpate the radial and ulnar pulse to confirm adequate blood supply to the hand. thenar and hypothenar eminence bulk. palpate the muscle bulk of the thenar and hypothenar eminences: wasting can be caused by disuse atrophy as well as lower motor neuron lesions (e.g. ulnar and median nerve). palmar thickening.

Motor Examination Of The Hand I Median Nerve Ii Ulnar Nerve Iii Check the individual digital sensory nerves to any finger by testing the radial and ulnar sides of each digit if the patient can perform each of the above functions and has intact sensation, as well as good cap refill and pulses, they have passed the basic screening exam and are “neurovascularly intact.”. When examining the hand, it is always important to document assessment of the ulnar, median, and radial nerves. the motor function of the hand can quickly and simply be assessed with the following examination techniques: ulnar motor function >> ask patient to first turn hand prone and spread fingers apart to a maximal distance. then, ask the. Radial nerve motor – confirm mcpj extension is present (tests ed) sensation – check at the dorsal surface of first digital web space; ulnar nerve motor – confirm finger abduction & adduction (tests palmar and dorsal interossei) sensation – check at the ulnar border of tip of little finger; assess the vascular status of the hand by. This includes the ulnar, median, radial, axillary and musculocutaneous nerves. the steps are inspection followed by a screen test to decide if the lesion is likely to be radial, median or ulnar. then the nerve is examined in more detail by testing sensation and movement in relation to that nerve. provocation tests are performed if necessary.
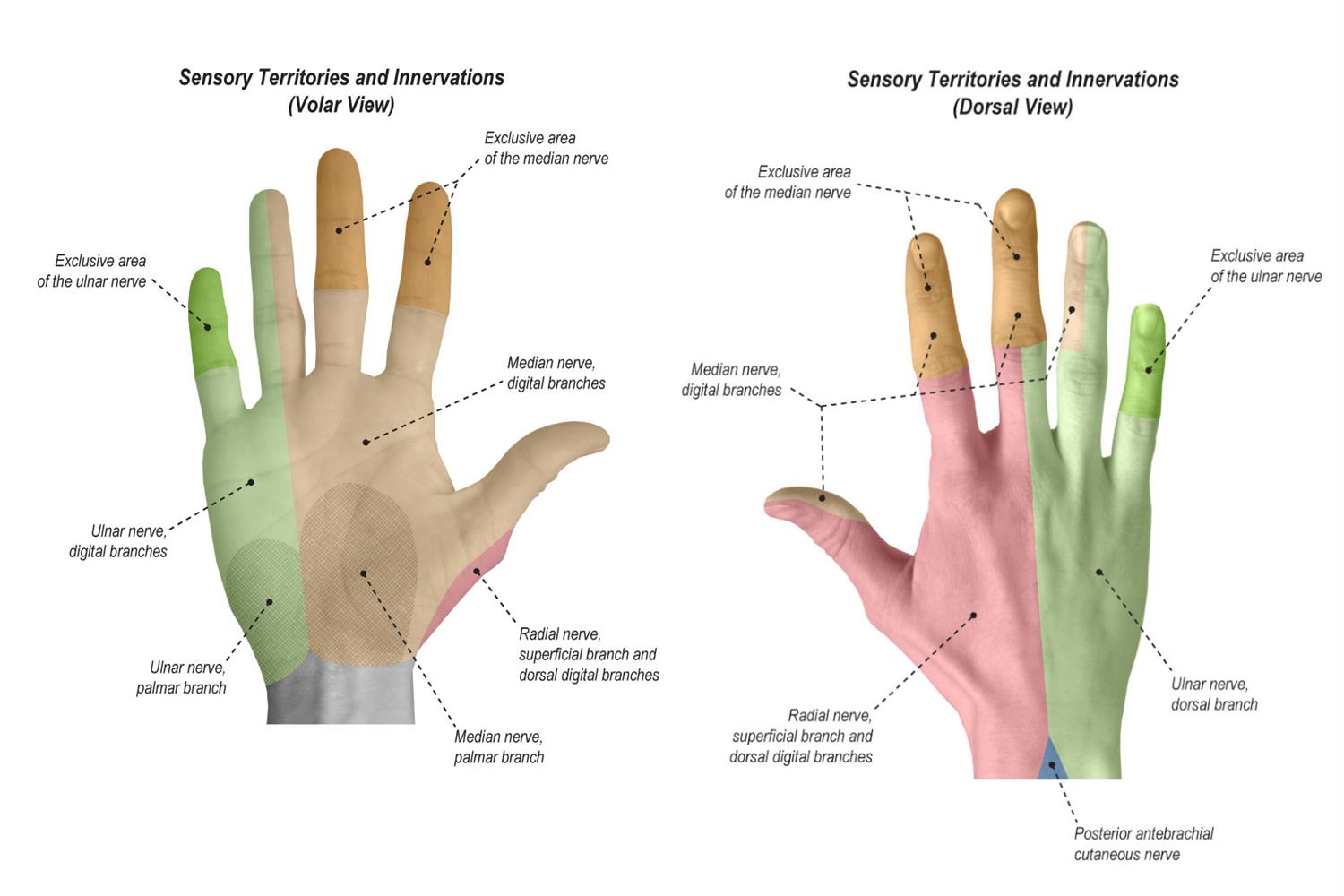
Physical Exam Of The Hand Hand Orthobullets Radial nerve motor – confirm mcpj extension is present (tests ed) sensation – check at the dorsal surface of first digital web space; ulnar nerve motor – confirm finger abduction & adduction (tests palmar and dorsal interossei) sensation – check at the ulnar border of tip of little finger; assess the vascular status of the hand by. This includes the ulnar, median, radial, axillary and musculocutaneous nerves. the steps are inspection followed by a screen test to decide if the lesion is likely to be radial, median or ulnar. then the nerve is examined in more detail by testing sensation and movement in relation to that nerve. provocation tests are performed if necessary. The ulnar nerve is a sensorimotor nerve that arises from the lower trunk of the brachial plexus and converts into the medial cord, further diving into fibers of c8 and t1. it provides motor innervation to the intrinsic hand muscles, except the flexor carpi ulnaris, the flexor digitorum profundus medially, the thenar, and the lumbrical muscles. the ulnar nerve also provides sensory innervation. The radial nerve stems from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and supplies the upper limb. it also supplies the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm (also known as the extensors), the wrist joint capsule, and aspects of the dorsal skin of the forearm and hand. the radial nerve proper innervates[1]:.

Medical School Testing Median Radial And Ulnar Nerves Vrog The ulnar nerve is a sensorimotor nerve that arises from the lower trunk of the brachial plexus and converts into the medial cord, further diving into fibers of c8 and t1. it provides motor innervation to the intrinsic hand muscles, except the flexor carpi ulnaris, the flexor digitorum profundus medially, the thenar, and the lumbrical muscles. the ulnar nerve also provides sensory innervation. The radial nerve stems from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and supplies the upper limb. it also supplies the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm (also known as the extensors), the wrist joint capsule, and aspects of the dorsal skin of the forearm and hand. the radial nerve proper innervates[1]:.
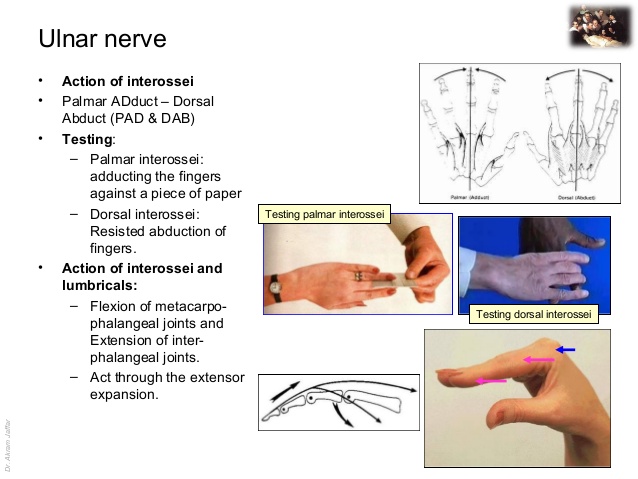
Motor Examination Of The Hand I Median Nerve Ii Ulnar Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.