Meeting The Nutritional Needs Of Preterm Infants
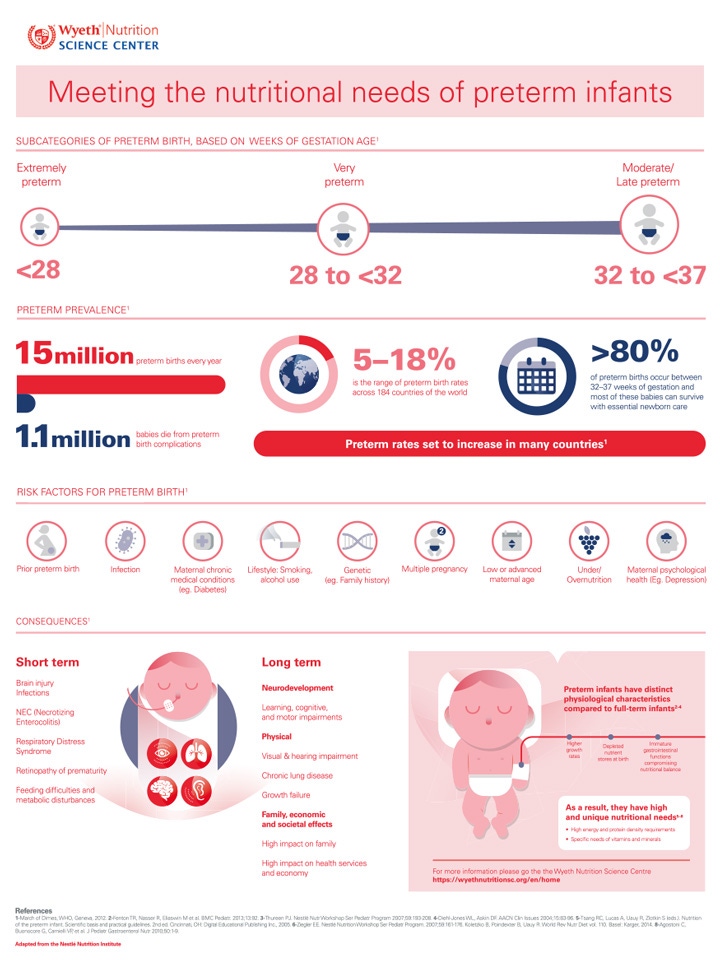
Infographic вђ Meeting The Nutritional Needs Of Preterm Infants Wyeth The goals of early nutrition in preterm infants are to provide all the necessary vital nutrients, achieve extra uterine growth rates similar to fetuses of the same gestational age, and support functional neurodevelopmental outcomes that are comparable to those of infants born at term. it is vital to provide nutrition that will maximally support. Water soluble vitamins b and c, on the other hand, require daily intake to meet their requirements. preterm infants. preterm infants are a unique population with specialized needs. the nutritional requirements of preterm infants are diverse and vary significantly with gestational age and stage of growth.

Meeting The Nutritional Needs Of Preterm Infants A research and clinical focus specifically on the moderate to late preterm infants is relatively recent, with increasing numbers of studies only in the past 10–15 years. 61, 62 although it is possible that nutrition interventions might have similar effects on outcomes of preterm infants of different gestational ages and birth weights (so. Most moderate to late–preterm infants need nutritional support after birth pending a sufficient supply and intake of mother’s breast milk; however, evidence for the best strategy for nutrition. 1. background. feeding preterm infants is challenging because their nutritional needs are higher than those of term infants. this is due to their 4 fold higher physiological growth rate during this developmental period—the last trimester of fetal development—which occurs in the neonatal intensive care unit (nicu) rather than in utero. Preterm infants have distinct physiological characteristics compared to term infants, which result in high and unique nutritional needs. human milk is the preferred nutrition for preterm infants, but milk alone does not fully cover the needs of all preterm infants, so fortification is needed to support their optimal growth and development.

Preterm Baby Nutrition Scientific Research Sma Hcp 1. background. feeding preterm infants is challenging because their nutritional needs are higher than those of term infants. this is due to their 4 fold higher physiological growth rate during this developmental period—the last trimester of fetal development—which occurs in the neonatal intensive care unit (nicu) rather than in utero. Preterm infants have distinct physiological characteristics compared to term infants, which result in high and unique nutritional needs. human milk is the preferred nutrition for preterm infants, but milk alone does not fully cover the needs of all preterm infants, so fortification is needed to support their optimal growth and development. Current nutritional goals for the preterm infant are to provide nutrients to approximate the rate of growth and composition of weight gain for a normal fetus of the same postmenstrual age while maintaining normal concentrations of nutrients in blood and other tissues. 1,2 in the very low birth weight infant, considerable efforts have been made. Although feeding human milk has several proven benefits, it is essential to determine whether it can meet the higher nutritional needs of preterm infants. the recommended enteral macro and micronutrient intakes for preterm infants according to the european society of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition (espghan) have been.
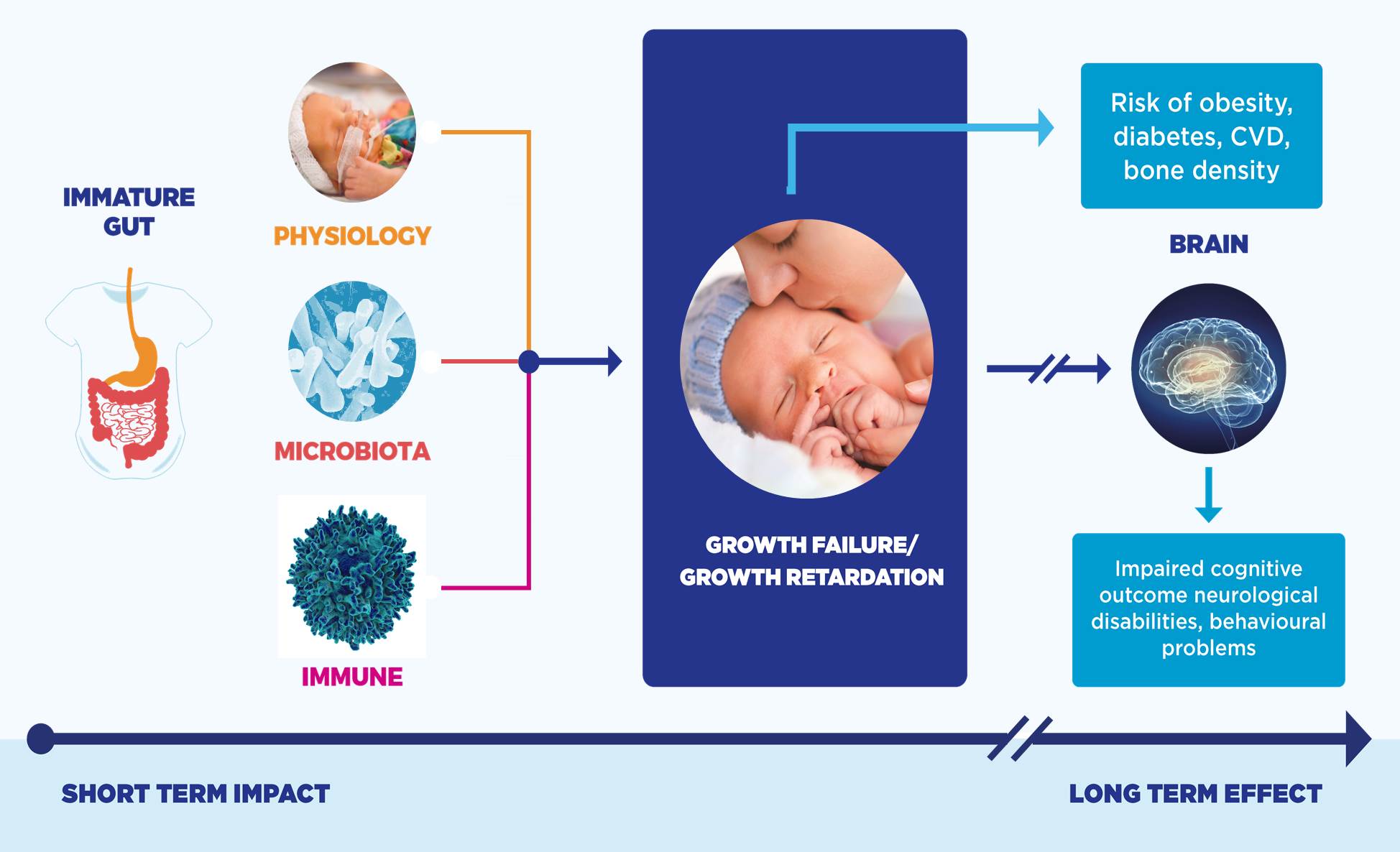
Nutritional Needs Of The Preterm Infant вђ Runners High Nutrition Current nutritional goals for the preterm infant are to provide nutrients to approximate the rate of growth and composition of weight gain for a normal fetus of the same postmenstrual age while maintaining normal concentrations of nutrients in blood and other tissues. 1,2 in the very low birth weight infant, considerable efforts have been made. Although feeding human milk has several proven benefits, it is essential to determine whether it can meet the higher nutritional needs of preterm infants. the recommended enteral macro and micronutrient intakes for preterm infants according to the european society of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition (espghan) have been.

Nutrition Needs Of Preterm Babies

Comments are closed.