Memorize Structure Of Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine And Uracil Mcat

Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine Molecules Sticker Zazzle Tl;dr: it is important to memorize the structures of the nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil so that you are able to recognize. For this, you have to be able to distinguish the nucleotides as either a purine or pyramidine, and know that purine has two rings. for purines: guanine is a guy because the carbonyl resembles a penis. adenine is simply the two ring nucleotide w o the carbonyl. for pyrimidines: thymine has two tits (aka two carbonyls).
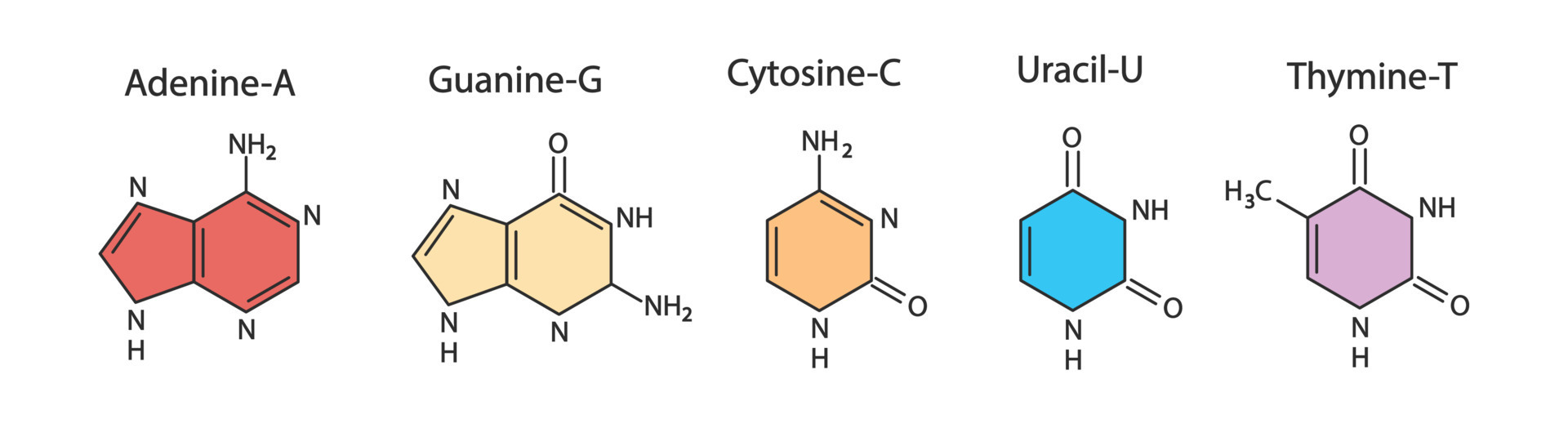
Adenine And Guanine Structure Mcat molecules to memorize. 4.8 (12 reviews) thymine. uracil. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like adenine, guanine, cytosine and. Adenine (“a”) and thymine (“t”) each have one donor and one acceptor, whereas cytosine (“c”) has one donor and two acceptors, and guanine (“g”) has one acceptor and two donors. the a nucleotides are always hydrogen bonded to t nucleotides, and c nucleotides are always hydrogen bonded to g nucleotides. Molecular structure of dna. dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. the bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. The double helix, made up of a pair of dna strands, has at its core, bases joined by hydrogen bonds to form base pairs adenine always paired with thymine, and guanine invariably paired with cytosine. two hydrogen bonds are formed between adenine and thymine, but three hydrogen bonds hold together guanine and cytosine (figure 2.127).

Adenine Definition Molecular structure of dna. dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. the bases, adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, pair up through hydrogen bonds, creating the rungs of the dna ladder. The double helix, made up of a pair of dna strands, has at its core, bases joined by hydrogen bonds to form base pairs adenine always paired with thymine, and guanine invariably paired with cytosine. two hydrogen bonds are formed between adenine and thymine, but three hydrogen bonds hold together guanine and cytosine (figure 2.127). Molecular structure of rna. dna and rna have different sugar backbones: deoxyribose for dna and ribose for rna. notably, rna has uracil instead of thymine as a nitrogenous base. rna plays various roles in cells, including messenger rna (mrna), transfer rna (trna), ribosomal rna (rrna), and microrna, and it is a vital part of processes such as. Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the thymine, another pyrimidine that is found in dna. like.

Comments are closed.