Metabolic Map Of Carbohydrates Glycolysis Gluconeogenesis And Glycogenesis Biochemistry
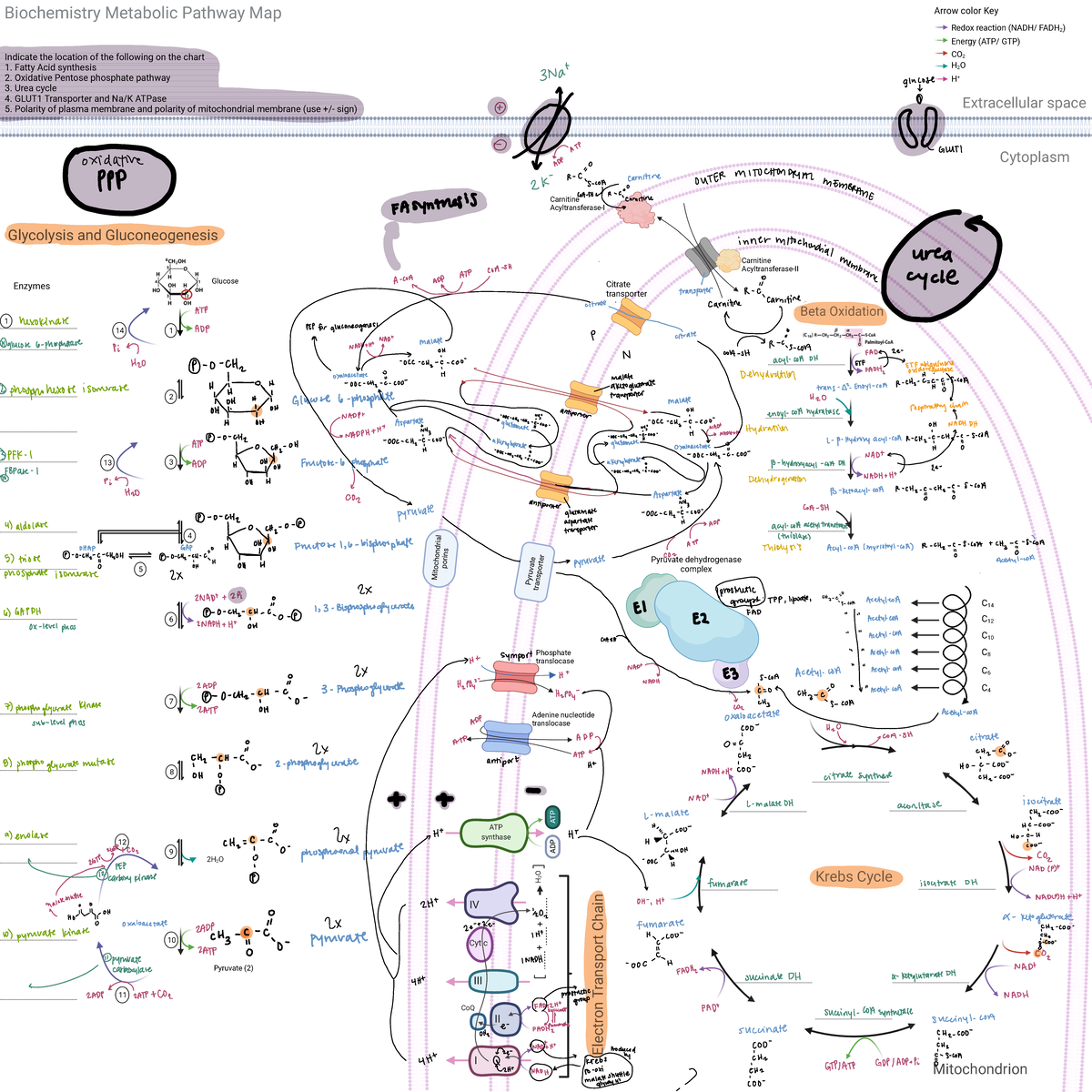
Metabolic Map Glycolysis And Gluconeogenesis Enzymes Krebs Cycle Slo1. differentiate gluconeogenesis from glycolysis, outline 3 bypass reactions that make it energetically favorable, and explain the significance of acetyl coa not being a substrate. gluconeogenesis is the process of synthesizing glucose de novo from 3 and 4 carbon precursors such as pyruvate, alanine, or glycerol. Gluconeogenesis begins with mitochondrial oxaloacetate being converted to phosphoenolpyruvate (pep) by either mitochondrial or cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (pepck) ( fig. 1 ). open in a separate window. figure 1. overview of carbohydrate metabolism. simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, or galactose, have different points of.
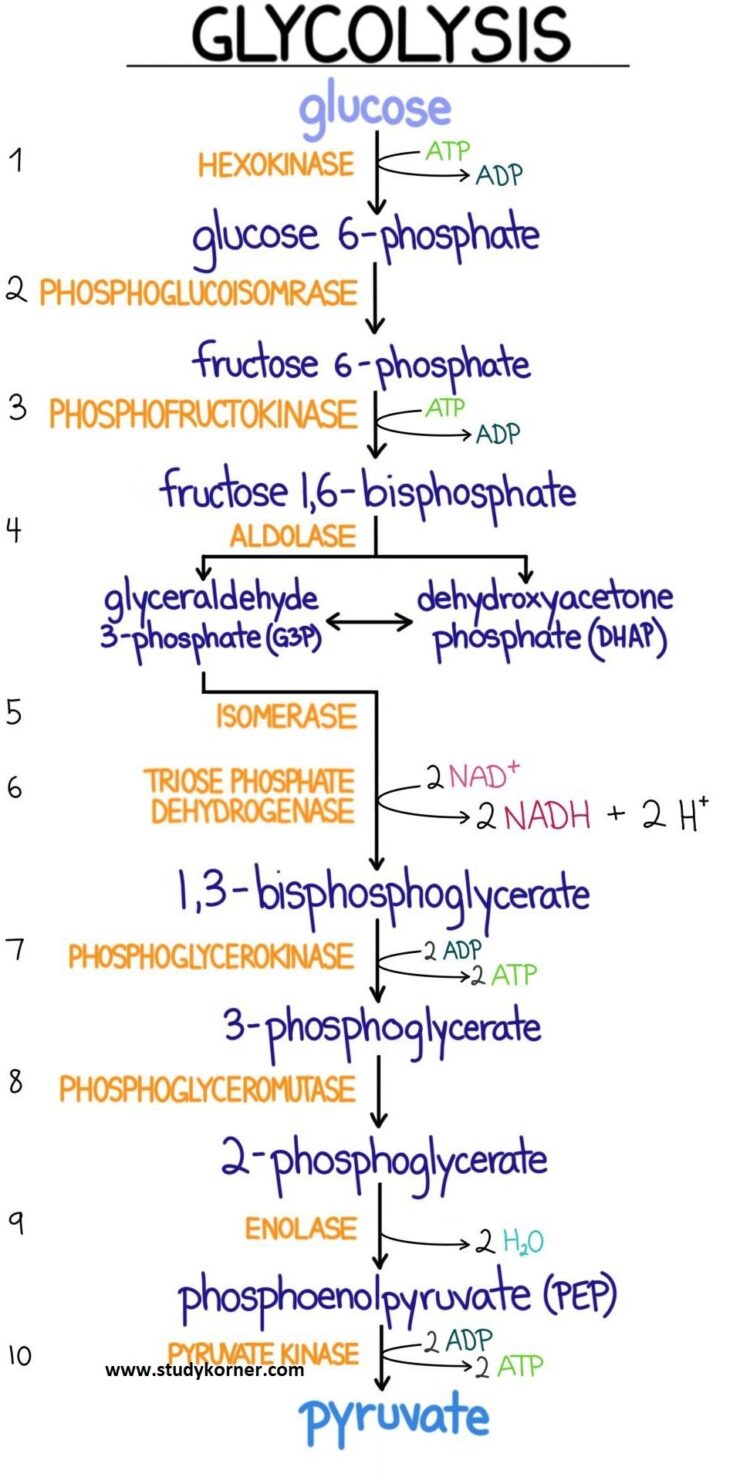
Glycolysis Flow Chart Introduction Pathway Diagram Summary Studypk Official sqadia website: 🌐 sqadia catalog🎬 5500 medical videos☛📄 descriptionmetabolism of carbs involves different cycles. the metabo. 13.3: gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids. it is one of the two main mechanisms humans and many other animals use to keep blood glucose levels from dropping too low (hypoglycemia). Finally, a series of reactions generates glucose itself. in gluconeogenesis (as compared to glycolysis), the enzyme hexokinase is replaced by glucose 6 phosphatase, and the enzyme phosphofructokinase 1 is replaced by fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase. this helps the cell to regulate glycolysis and gluconeogenesis independently of each other. Gluconeogenesis refers to a group of metabolic reactions in cytosol and mitochondria to maintain the blood glucose level constant throughout the fasting state. reactions in the gluconeogenesis pathway are regulated locally and globally (by insulin, glucagon, and cortisol), and some of them are highly exergonic and irreversible.[1] the balance between stimulatory and inhibitory hormones.

Comments are closed.