Microfilaments A Comprehensive Review In Questions And Answers

Microfilament Structure Function And Location Microfilaments. composed of actin and myosin; involved in many processes in the body, very flexible network of proteins; very involved in plasma membrane contractions movement. f actin. a unit of actin referred to as filamentous. g actin. 2 units of these monomers makes up a filamentous. myosin ii. Microfilament definition. microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are polymers of the protein actin that are part of a cell’s cytoskeleton. the cytoskeleton is the network of protein filaments that extends throughout the cell, giving the cell structure and keeping organelles in place. microfilaments are the smallest filaments of the.
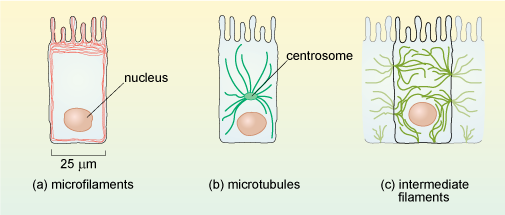
A Tour Of The Cell Microfilaments Openlearn Open University Structure and functions of microfilaments. microfilaments are the leanest filaments of the cytoskeleton present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells with a diameter of about 5 to 8 nanometers. the polymers of these filaments are flexible but very strong and resist buckling and crushing while offering support to the cell. Usmleqa ?p=7811question: what are microfilaments?answer: microfilaments are a type of filament.question: what is the predominant function of micr. Contributors and attributions. figure 1. microfilaments are made of two intertwined strands of actin. of the three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton, microfilaments are the narrowest. they function in cellular movement, have a diameter of about 7 nm, and are made of two intertwined strands of a globular protein called actin (figure 1). Microfilaments are long, thin, and stringy proteins. when first produced by the cell, the actin monomers join together to form two parallel polymers of globular (g) actin . once they are joined, the elongated strands twist around each other into a helical orientation having a diameter of about 6 7 nm and are called filamentous (f) actin .

Microfilaments Structure And Function Youtube Contributors and attributions. figure 1. microfilaments are made of two intertwined strands of actin. of the three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton, microfilaments are the narrowest. they function in cellular movement, have a diameter of about 7 nm, and are made of two intertwined strands of a globular protein called actin (figure 1). Microfilaments are long, thin, and stringy proteins. when first produced by the cell, the actin monomers join together to form two parallel polymers of globular (g) actin . once they are joined, the elongated strands twist around each other into a helical orientation having a diameter of about 6 7 nm and are called filamentous (f) actin . There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules (figure 4.6.1 4.6. 1 ). here, we will examine each. figure 4.6.1 4.6. 1: microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell; like rubber bands, they resist tension. microtubules are found in the interior of the cell. For this reason, microfilaments are also known as actin filaments. figure 4.16.1 4.16. 1: microfilaments are the thinnest component of the cytoskeleton.: microfilaments are made of two intertwined strands of actin. actin is powered by atp to assemble its filamentous form, which serves as a track for the movement of a motor protein called myosin.
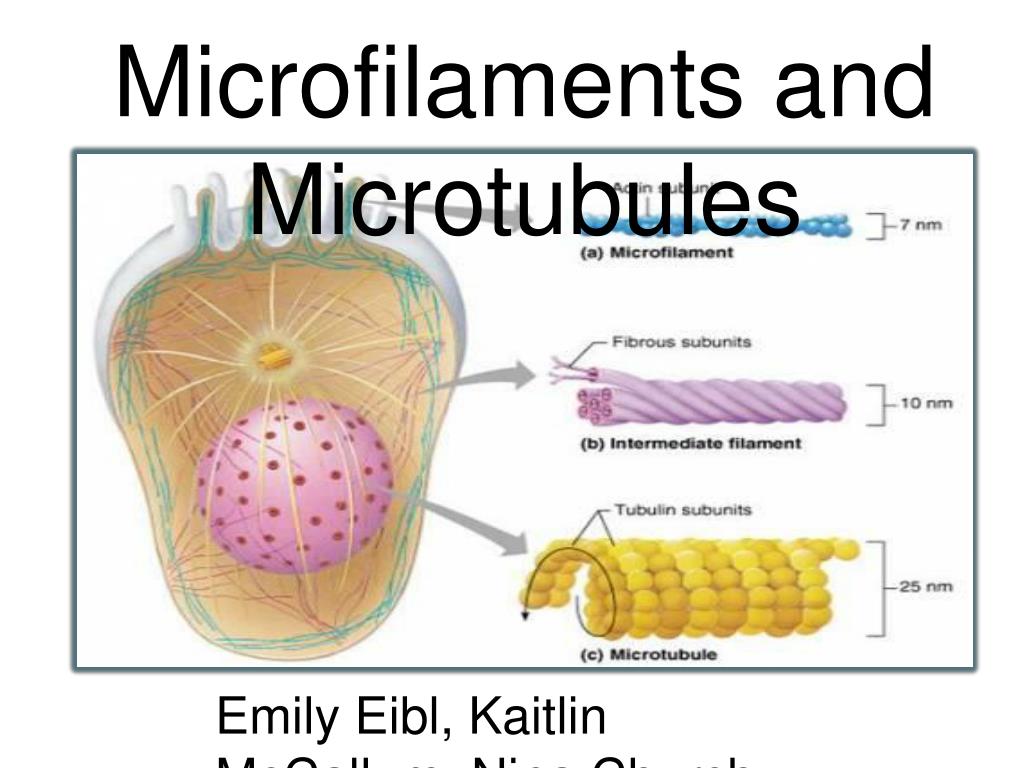
Microfilaments And Microtubules There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules (figure 4.6.1 4.6. 1 ). here, we will examine each. figure 4.6.1 4.6. 1: microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell; like rubber bands, they resist tension. microtubules are found in the interior of the cell. For this reason, microfilaments are also known as actin filaments. figure 4.16.1 4.16. 1: microfilaments are the thinnest component of the cytoskeleton.: microfilaments are made of two intertwined strands of actin. actin is powered by atp to assemble its filamentous form, which serves as a track for the movement of a motor protein called myosin.

Comments are closed.