Microfilaments Microtubules And Intermediate Filaments

Differences Between Microfilaments Microtubules And Intermediate Intermediate filaments have an average diameter of 10 nanometers, which is between that of 7 nm actin (microfilaments), and that of 25 nm microtubules, although they were initially designated ‘intermediate’ because their average diameter is between those of narrower microfilaments (actin) and wider myosin filaments found in muscle cells. Microtubules are the largest type of filament, with a diameter of about 25 nanometers (nm), and they are composed of a protein called tubulin . actin filaments are the smallest type, with a.
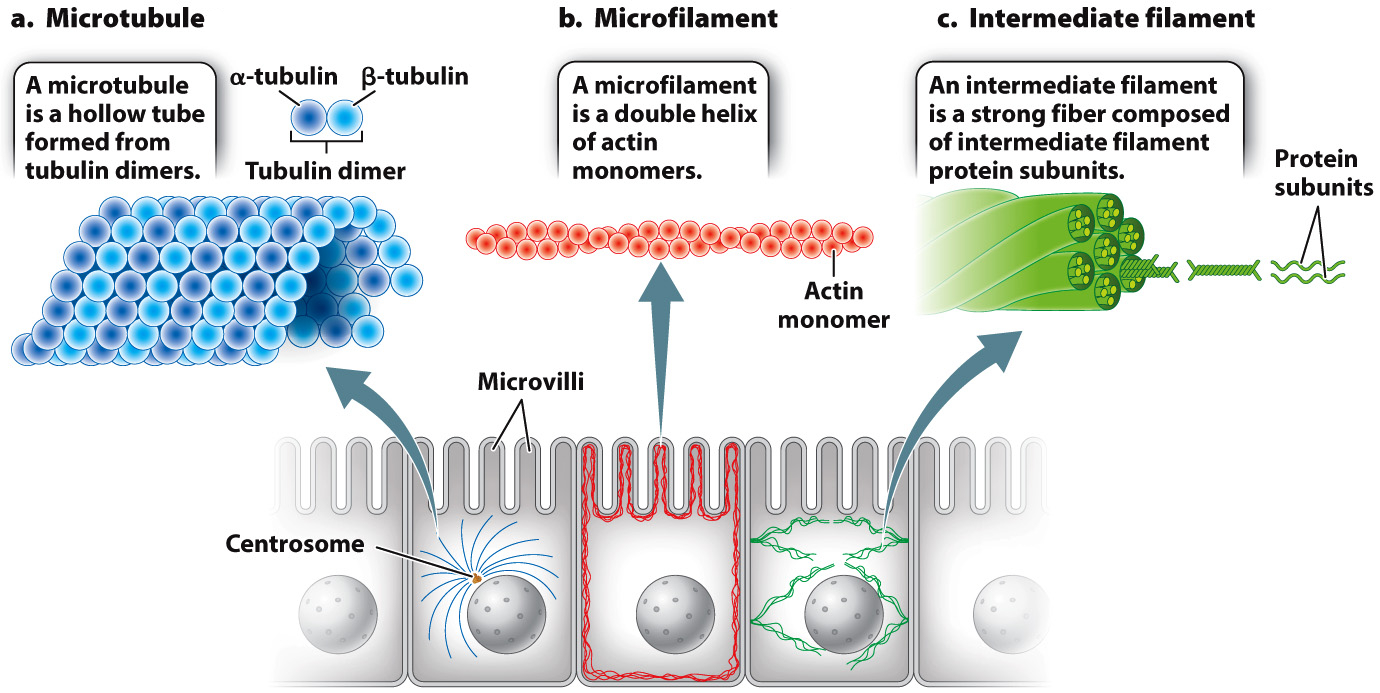
Chapter 10 Cell And Tissue Architecture Cytoskeleton Cell Junctions The intermediate filaments are the most diverse group of cytoskeletal elements. several fibrous protein types are in the intermediate filaments. you are probably most familiar with keratin, the fibrous protein that strengthens your hair, nails, and the skin's epidermis. microtubules. as their name implies, microtubules are small hollow tubes. Khanmigo is now free for all us educators! plan lessons, develop exit tickets, and so much more with our ai teaching assistant. There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules (figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1). here, we will examine each. figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1: microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell; like rubber bands, they resist tension. The cytoskeleton consists of (a) microtubules, (b) microfilaments, and (c) intermediate filaments. [1] the cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. [2] in eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is.

Comments are closed.