Mixed Mode Passive Design Strategies
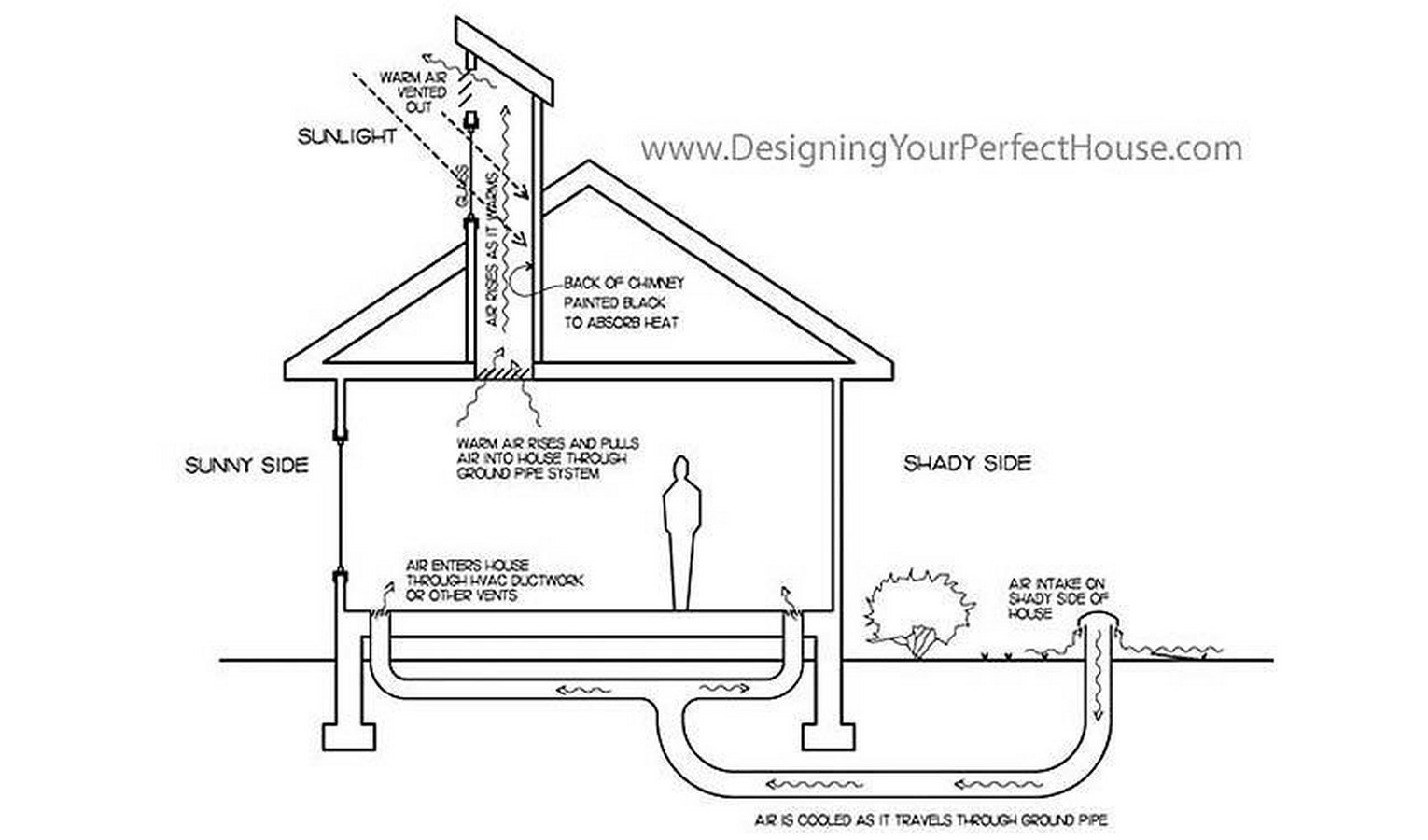
What Are Passive Design Strategies Rtf Mixed mode ventilation or hybrid ventilation is a relatively new concept that is a sustainable and cost effective way to provide thermal comfort to occupants by regulating the indoor temperature. this ventilation strategy not only offers a means of indoor climate control but also enhances indoor air quality by lowering co2 levels, creating a. Natural ventilation uses passive strategies to supply outdoor air to a building’s interior for ventilation and cooling. [1] natural ventilation systems rely on natural forces, such as wind and temperature differences between a building and its environment, to drive the flow of fresh air through a building. cross ventilation uses air pressure.
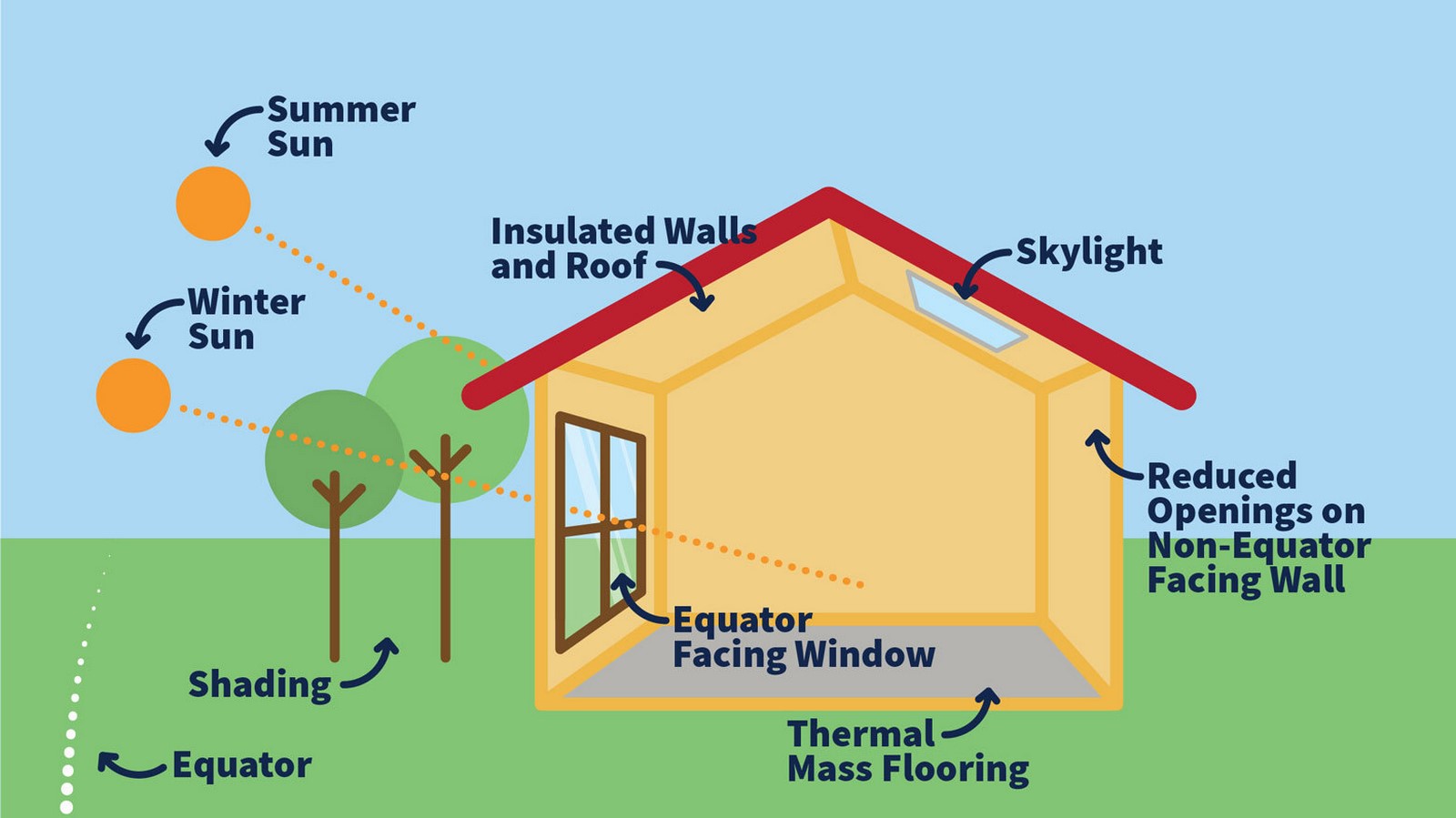
What Are Passive Design Strategies Rtf Rethinking The Future Their results revealed that the acm, when combined with other design strategies, can counteract the climate change and associated cooling energy demand. the study concluded that the acm plays a valuable role in a changing climatic environment as it provides a buffer for the potential implementation of passive design strategies. It is mostly known in three different types: mechanical, natural, and mixed mode. managing the air exchange and circulation with the outdoors is crucial for a comfortable atmosphere. Mixed mode ventilation. mixed mode ventilation is a hybrid approach to space conditioning that uses a combination of natural ventilation from operable windows (either manually or automatically controlled), and mechanical systems that include air distribution equipment and refrigeration equipment for cooling. a well designed mixed mode building. In mixed mode (mm) buildings, the active system is used only when natural ventilation alone is incapable of providing occupants with comfortable indoor conditions. there are several mixed mode operational strategies, classified as [2]: • concurrent active cooling and natural ventilation being operated simultaneously in the same space, •.

Mixed Mode Passive Design Strategies Youtube Mixed mode ventilation. mixed mode ventilation is a hybrid approach to space conditioning that uses a combination of natural ventilation from operable windows (either manually or automatically controlled), and mechanical systems that include air distribution equipment and refrigeration equipment for cooling. a well designed mixed mode building. In mixed mode (mm) buildings, the active system is used only when natural ventilation alone is incapable of providing occupants with comfortable indoor conditions. there are several mixed mode operational strategies, classified as [2]: • concurrent active cooling and natural ventilation being operated simultaneously in the same space, •. Climate design strategy in order to make suitable mixed mode ventilation and cooling operation is an passive systems strategies are only completed for. Cross ventilation. cross ventilation is achieved using windows on both sides of the room, creating a current of air across the room. if the windows on both sides of the room are open, the overpressure on the side of the building facing into the wind and or low pressure on the opposite, sheltered side will create a current of air through the room from the exposed side to the sheltered side.

Creswell 2009 Mixed Methods Climate design strategy in order to make suitable mixed mode ventilation and cooling operation is an passive systems strategies are only completed for. Cross ventilation. cross ventilation is achieved using windows on both sides of the room, creating a current of air across the room. if the windows on both sides of the room are open, the overpressure on the side of the building facing into the wind and or low pressure on the opposite, sheltered side will create a current of air through the room from the exposed side to the sheltered side.

Comments are closed.