Molecular Testing In Patients With Early Nonвђ Small Cell Lung Cancer

Mutations In Lung Cancer Driving Targeted Therapy вђ Sapien Biosciences In conclusion, the approach to molecular testing in early stage disease will continue to evolve with the inclusion of additional novel therapies in the adjuvant and neoadjuvant settings. it is indeed an exciting time to be a thoracic oncologist. in the past decade, we have seen an unprecedented improvement in the survival of patients with lung. It has been nearly 15 years since the ipass trial first demonstrated the importance of molecular testing to identify the population of patients with non–small cell lung cancer (nsclc) that benefit from molecularly targeted therapy. 1 molecular genomic testing has become more widespread since then, with an increasing number of molecular targets and molecularly targeted therapies.
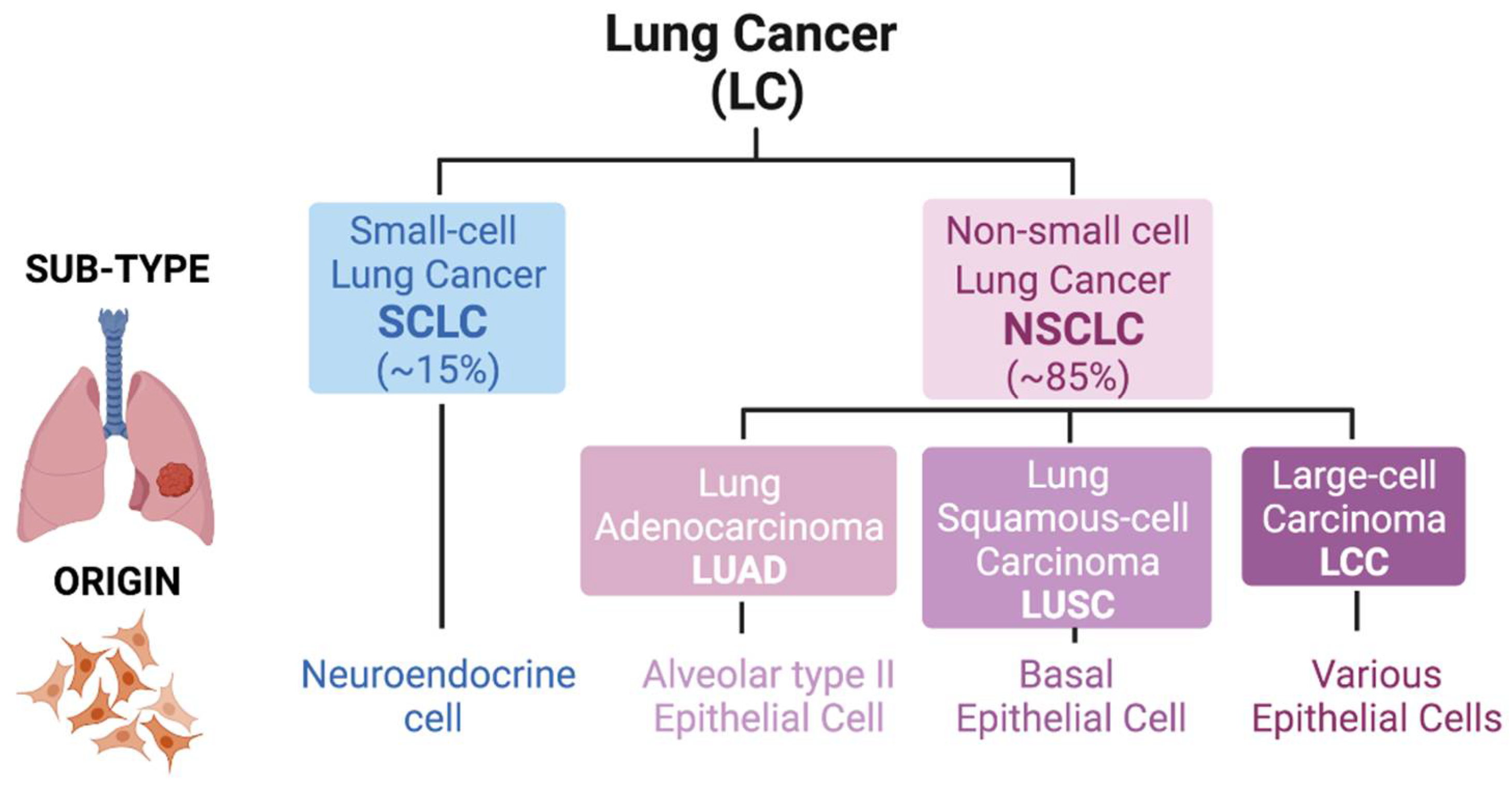
Cells Free Full Text Role Of Nrf2 In Lung Cancer Lung cancer is categorized as either small cell lung cancer in approximately 10% to 15% of cases or non small cell lung cancer (nsclc) in approximately 80% to 85% of cases . lung cancer is diagnosed at an advanced stage in 72% to 76% of patients in the uk and 57% in the us, precluding curative treatment, and is associated with poor prognosis. Only 18% of patients with single gene panels had a molecular abnormality compared with 23% of tissue based ngs and 24% of blood based ngs. approximately 40% of patients in this study had single gene testing, which is less likely to identify fusion abnormalities such as ret, met, and ntrk. Abstract. molecular testing identifies patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer (nsclc) who may benefit from targeted therapy or immunotherapy (i.e., immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment for patients with high tumor mutational burden (tmb), microsatellite instability high or mismatch repair deficient tumors). current guidelines state. Molecular biomarker testing is the standard of care for non–small cell lung cancer (nsclc) patients. in 2017, the korean cardiopulmonary pathology study group and the korean molecular pathology study group co published a molecular testing guideline which contained almost all known genetic changes that aid in treatment decisions or predict.

Pdf Pathological Diagnosis And Molecular Testing In Non Small Cell Abstract. molecular testing identifies patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer (nsclc) who may benefit from targeted therapy or immunotherapy (i.e., immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment for patients with high tumor mutational burden (tmb), microsatellite instability high or mismatch repair deficient tumors). current guidelines state. Molecular biomarker testing is the standard of care for non–small cell lung cancer (nsclc) patients. in 2017, the korean cardiopulmonary pathology study group and the korean molecular pathology study group co published a molecular testing guideline which contained almost all known genetic changes that aid in treatment decisions or predict. Abstract. precision medicine in non small cell lung cancer (nsclc) is a rapidly evolving area, with the development of targeted therapies for advanced disease and concomitant molecular testing to inform clinical decision making. in contrast, routine molecular testing in stage i iii disease has not been required, where standard of care comprises. Molecular testing has become a mandatory component of the non small cell lung cancer (nsclc) management. the detection of egfr, braf and met mutations as well as the analysis of alk, ros1, ret and ntrk translocations have already been incorporated in the nsclc diagnostic standards, and the inhibitors of these kinases are in routine clinical use.

Comments are closed.