Monitoring During Anesthesia
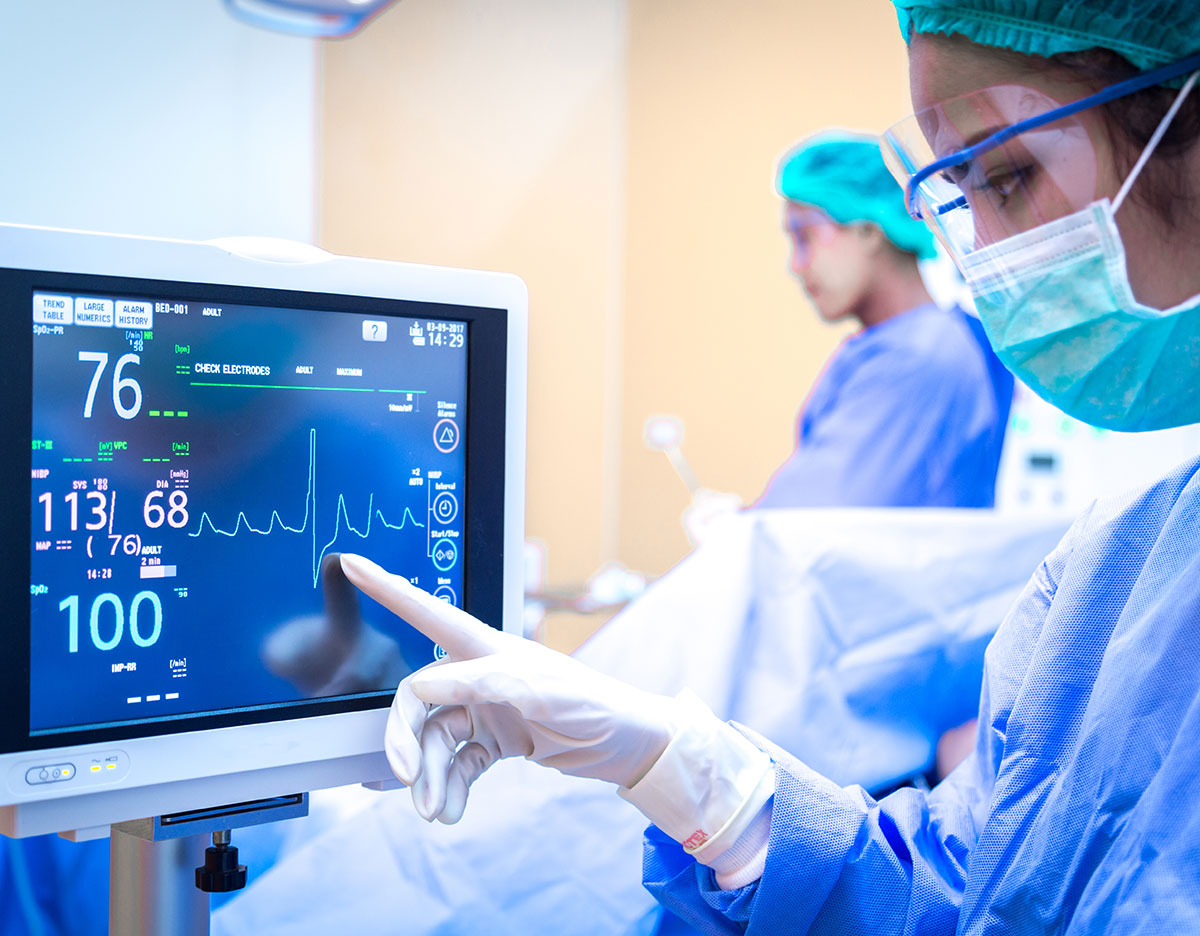
Apsf Endorsed Statement On Revising Recommendations For Patient Introduction. monitoring is an essential component of’ anesthesia care. anesthesia clinicians must monitor patient physiologic variables and anesthesia equipment during all types of anesthesia, as anesthesia and surgery can cause rapid changes in vital functions. patient and equipment monitoring is used to titrate administration of anesthetic. Learn about the standards for oxygenation, ventilation, circulation and temperature during all anesthetics, developed by the committee on standards and practice parameters. these standards apply to general, regional and monitored anesthesia care and may be exceeded or waived in certain circumstances.
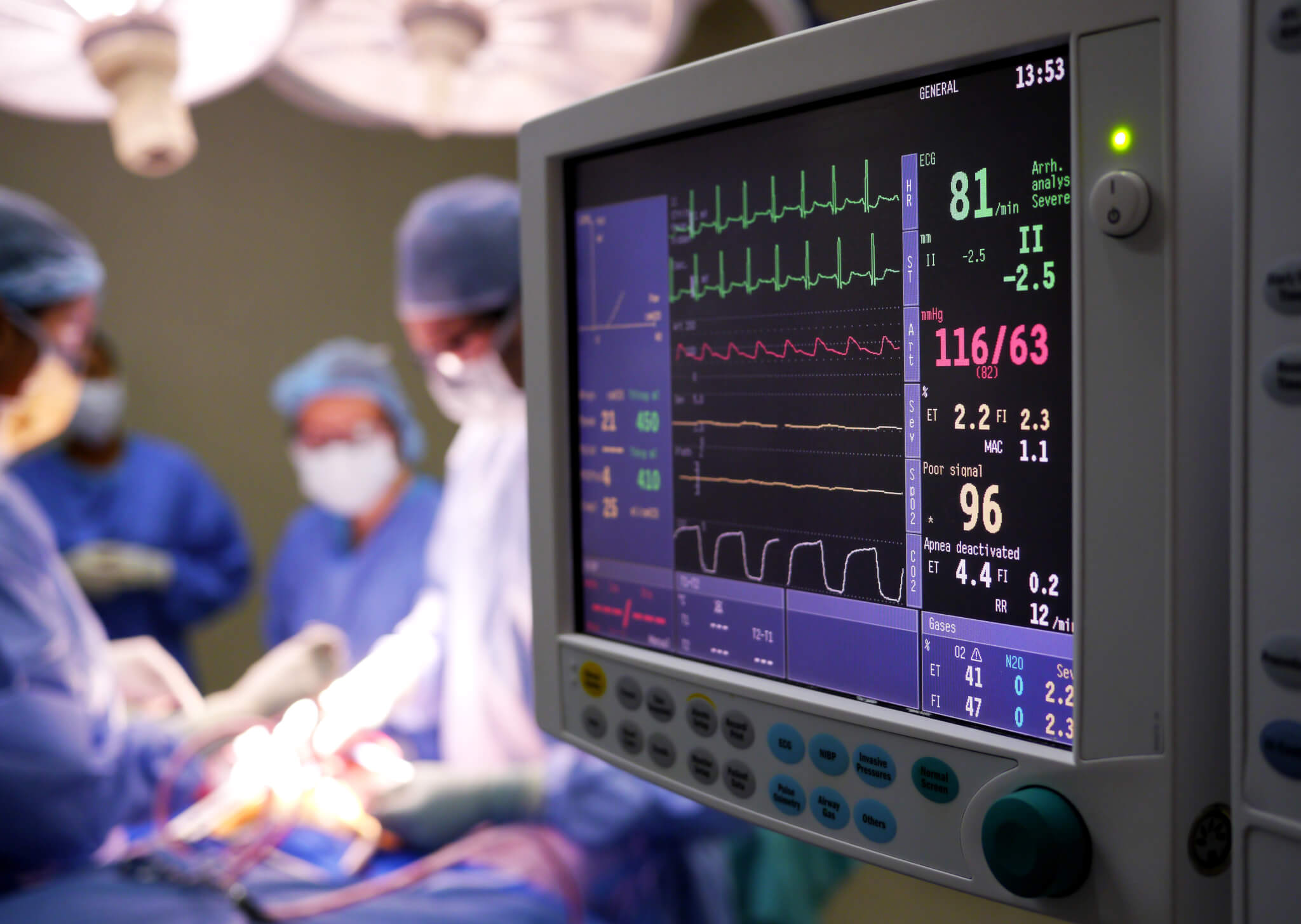
How Ambient Music Is Used To Make Hospital Patients Happier Telekom Adequate supervision requires that an anaesthetist should be present throughout the conduct of anaesthesia or the administration of procedural sedation *.; general anaesthesia requires minimum monitoring of ecg, spo 2, nibp and capnography, which should be checked for correct function and begun before induction of anaesthesia and continue throughout anaesthesia, transfer to the post. A “pop” may be felt and there should be no resistance to injection. y. considerations: (1) pelvic limb motor function is not blocked unless the volume of local anesthetic is large, causing cranial spread to the motor nerves of the pelvic limbs. stay at or below the 0.2 ml kg volume. This topic will discuss preoperative evaluation for patients who will receive mac, monitoring during mac, and the medications and sedation techniques commonly used during mac. procedural sedation by non anesthesia clinicians and the drugs and techniques used for general anesthesia are discussed separately. Continuous waveform carbon dioxide concentration monitoring will detect most of these problems, so this is an essential part of routine monitoring during anaesthesia. the 2011 aagbi position statement on capnography outside the operating theatre recommended that it should be used for all unconscious anaesthetised patients regardless of the.
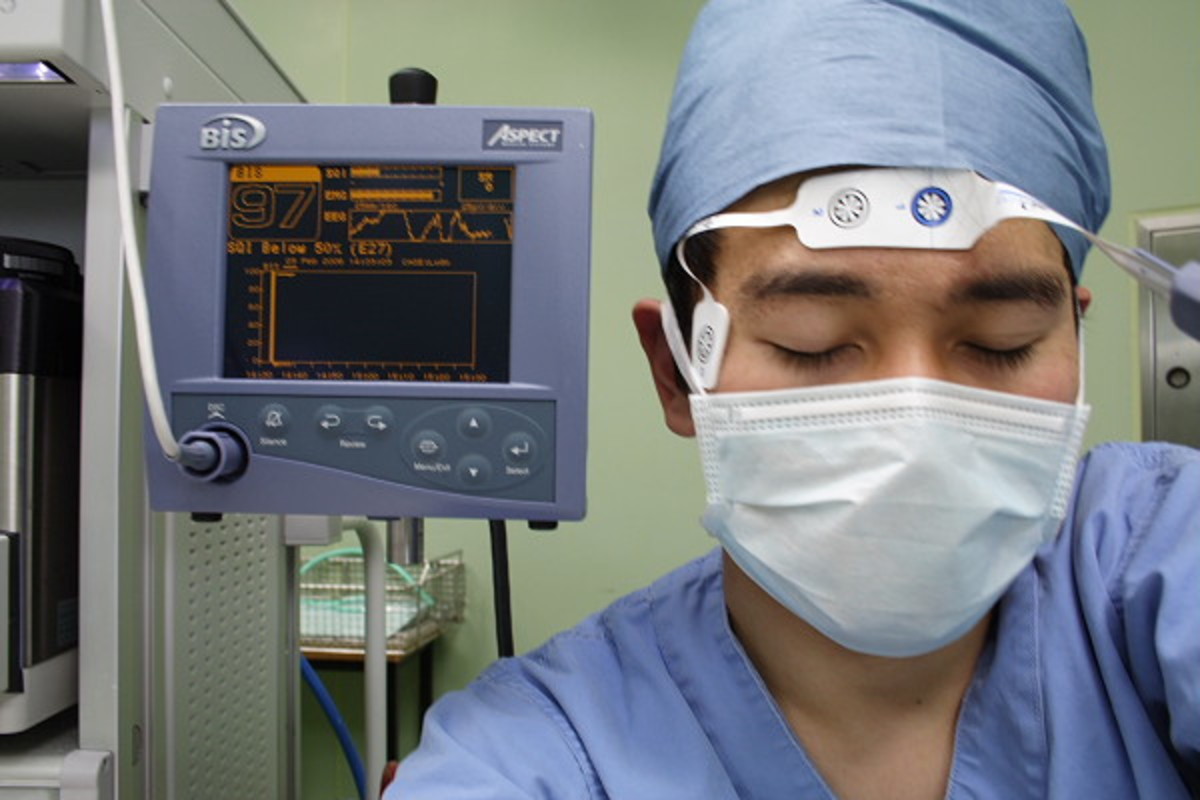
Patient Monitoring During Anesthesia Owlcation This topic will discuss preoperative evaluation for patients who will receive mac, monitoring during mac, and the medications and sedation techniques commonly used during mac. procedural sedation by non anesthesia clinicians and the drugs and techniques used for general anesthesia are discussed separately. Continuous waveform carbon dioxide concentration monitoring will detect most of these problems, so this is an essential part of routine monitoring during anaesthesia. the 2011 aagbi position statement on capnography outside the operating theatre recommended that it should be used for all unconscious anaesthetised patients regardless of the. Under anesthesia •after induction is performed, a patient should be placed on monitoring equipment. •as the anesthetist, you should be monitoring the monitor as well as the patient themselves. •if the monitor seems to good to be true or if it is showing you something unusual, check your patient. •key vitals to check first hr, rr and effort,. This guideline updates and replaces the 5th edition of the standards of monitoring published in 2015. the aim of this document is to provide guidance on the minimum standards for monitoring of any patient undergoing anaesthesia or sedation under the care of an anaesthetist.

General Anesthesia Definition Side Effects When Seconds Count Under anesthesia •after induction is performed, a patient should be placed on monitoring equipment. •as the anesthetist, you should be monitoring the monitor as well as the patient themselves. •if the monitor seems to good to be true or if it is showing you something unusual, check your patient. •key vitals to check first hr, rr and effort,. This guideline updates and replaces the 5th edition of the standards of monitoring published in 2015. the aim of this document is to provide guidance on the minimum standards for monitoring of any patient undergoing anaesthesia or sedation under the care of an anaesthetist.

Anesthetic Monitoring Interpreting The Readings

Comments are closed.