Motor Neuron Motoneuron Diagram Transmission Of The Nerve Signal From
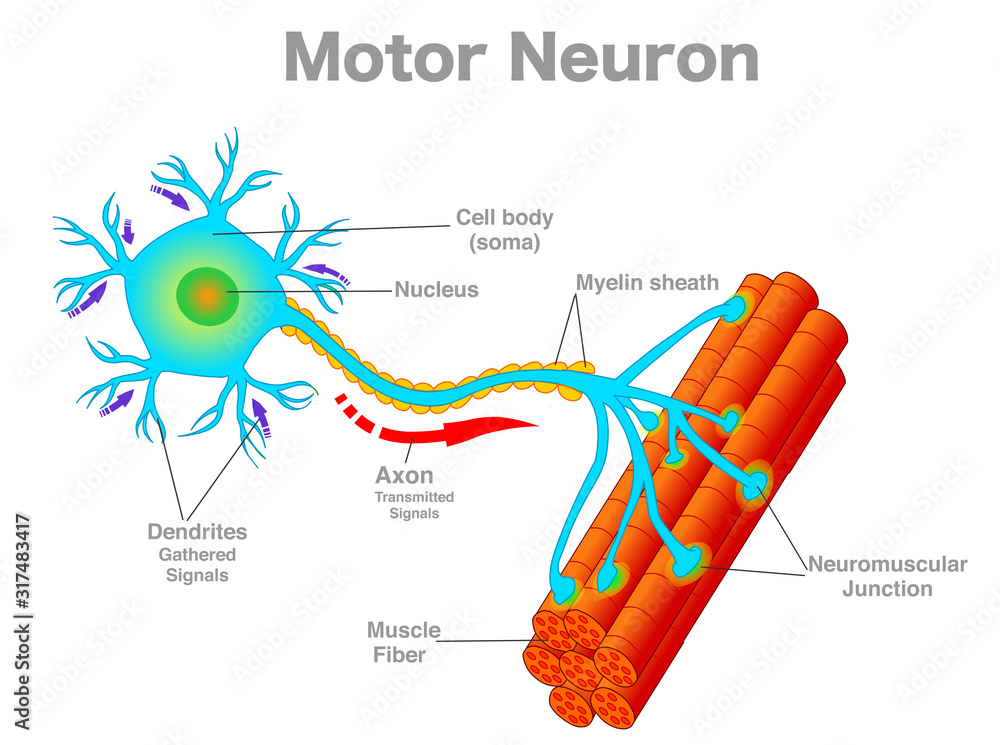
Motor Neuron Motoneuron Diagram Transmission Of The Nerve Signal From The structure of a motor neuron is characterized by three components: the soma, the axon, and the dendrites. motor neurons have a large cell body, or soma, and long projections used in transmitting information away from the soma. these projections are referred to as axons and dendrites. axons send impulses away from the soma and dendrites carry. Damage. motor neurons (also referred to as efferent neurons) are the nerve cells responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system towards muscles to cause movement. they release neurotransmitters to trigger responses leading to muscle movement. these movements can be voluntary, such as reaching out to pick up an item, or.

Labeled Diagram Of A Motor Neuron A motor neuron is a cell of the central nervous system. motor neurons transmit signals to muscle cells or glands to control their functional output. when these cells are damaged in some way, motor neuron disease can arise. this is characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy) and loss of motor function. motor neuron. Nerve impulse transmission within a neuron. for the nervous system to function, neurons must be able to send and receive signals. these signals are possible because each neuron has a charged cellular membrane (a voltage difference between the inside and the outside), and the charge of this membrane can change in response to neurotransmitter molecules released from other neurons and. The lower motor neuron is responsible for transmitting the signal from the upper motor neuron to the effector muscle to perform a movement. there are three broad types of lower motor neurons: somatic motor neurons, special visceral efferent (branchial) motor neurons, and general visceral motor neurons. [1]. Transmission of a signal within a neuron (in one direction only, from dendrite to axon terminal) is carried out by the opening and closing of voltage gated ion channels, which cause a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential to create an action potential. as an action potential travels down the axon, the polarity changes across the.

Motor Neuron Function Transmission Of The Nerve Signal From The Neuron The lower motor neuron is responsible for transmitting the signal from the upper motor neuron to the effector muscle to perform a movement. there are three broad types of lower motor neurons: somatic motor neurons, special visceral efferent (branchial) motor neurons, and general visceral motor neurons. [1]. Transmission of a signal within a neuron (in one direction only, from dendrite to axon terminal) is carried out by the opening and closing of voltage gated ion channels, which cause a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential to create an action potential. as an action potential travels down the axon, the polarity changes across the. It is the synaptic end bulb of the motor neuron that comprises the nervous system component of the neuromuscular junction. the muscular component is a region of the muscle fiber referred to as the motor end plate. between the synaptic end bulbs of the neuron and the cell membrane of the muscle fiber (the sarcolemma) lies a space known as the. A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron[1]) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. [2] there are two types of motor neuron.

Comments are closed.