Multi Colour Biological Electron Microscopy Using Eds

Multi Colour Biological Electron Microscopy Using Eds Youtube Presented by: louise hughesspeaker biography: louise is the product manager for life sciences at oxford instruments nanoanalysis. louise specialises in 3d el. Multi colour electron microscopy (mcem) combines ultrastructural electron data with elemental information, transforming traditionally grey scale electron micrographs into colourful images that combine structure and composition.

Multi Colour Biological Electron Microscopy Using Eds Wu, j. et al. imaging and elemental mapping of biological specimens with a dual eds dedicated scanning transmission electron microscope. ultramicroscopy 128 , 24–31 (2013). article cas google. Literature seminar – contrast allows us to distinguish an object from its background. in biological electron microscopy it is challenging to see the details inside of cells due to the relatively similar atomic makeup of all biomolecular building blocks. to remedy this, molecular species of interest are often “tagged” in order to provide contrast, typically […]. Energy dispersive x ray spectrometry (eds) provides elemental contrast and analytical capabilities within an electron microscope, supplying an opportunity for researchers to analyse ultrastructure and composition within the same session. we used eds on two research topics investigating tissue interactions with implants and biomaterials. 1. Energy dispersive x ray spectroscopy (eds) carried out alongside scanning electron microscopy (sem) is a common technique for elemental analysis. to investigate “wet” biological specimens.
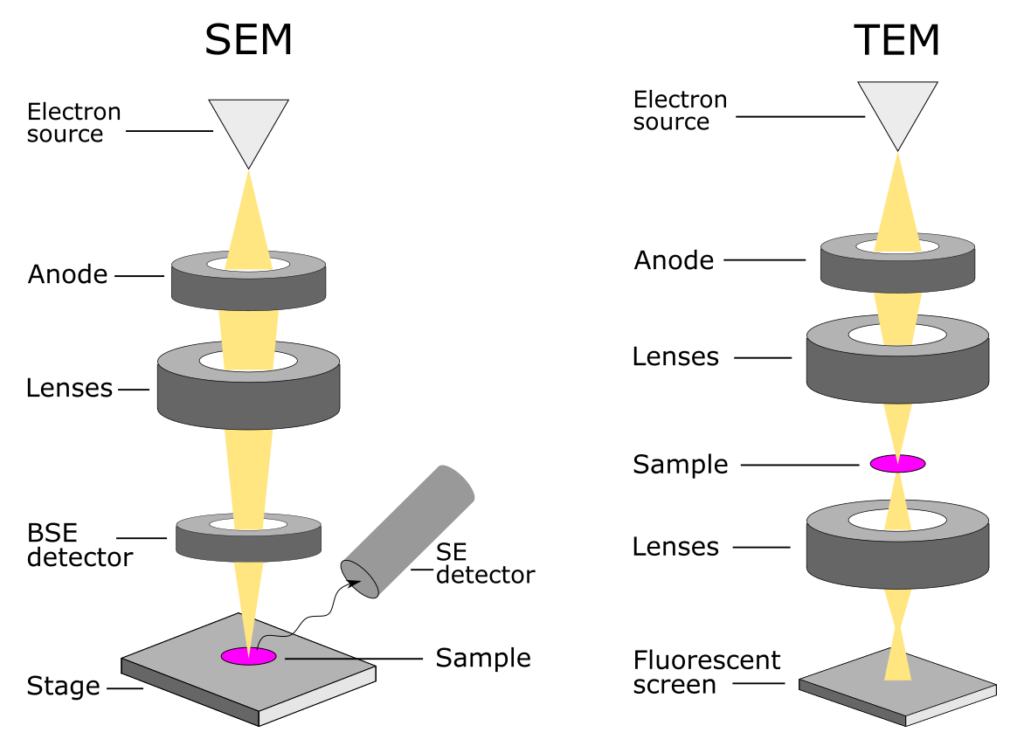
Electron Microscopy Anapath Energy dispersive x ray spectrometry (eds) provides elemental contrast and analytical capabilities within an electron microscope, supplying an opportunity for researchers to analyse ultrastructure and composition within the same session. we used eds on two research topics investigating tissue interactions with implants and biomaterials. 1. Energy dispersive x ray spectroscopy (eds) carried out alongside scanning electron microscopy (sem) is a common technique for elemental analysis. to investigate “wet” biological specimens. This protocol, combined with focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy, makes it possible to study 3d ultrastructure of complex biological samples, e.g., whole insect heads, over their entire. To prepare your biological samples for eds. biological eds complements electron microscopy as an imaging technique. eds enables you to navigate your sample easily and efficiently with azteclive. to monitor chemical variables with ultrastructural context and distinguishing features with and without labelling. watch on demand.

Comments are closed.