Muscle And Nerve Anatomy
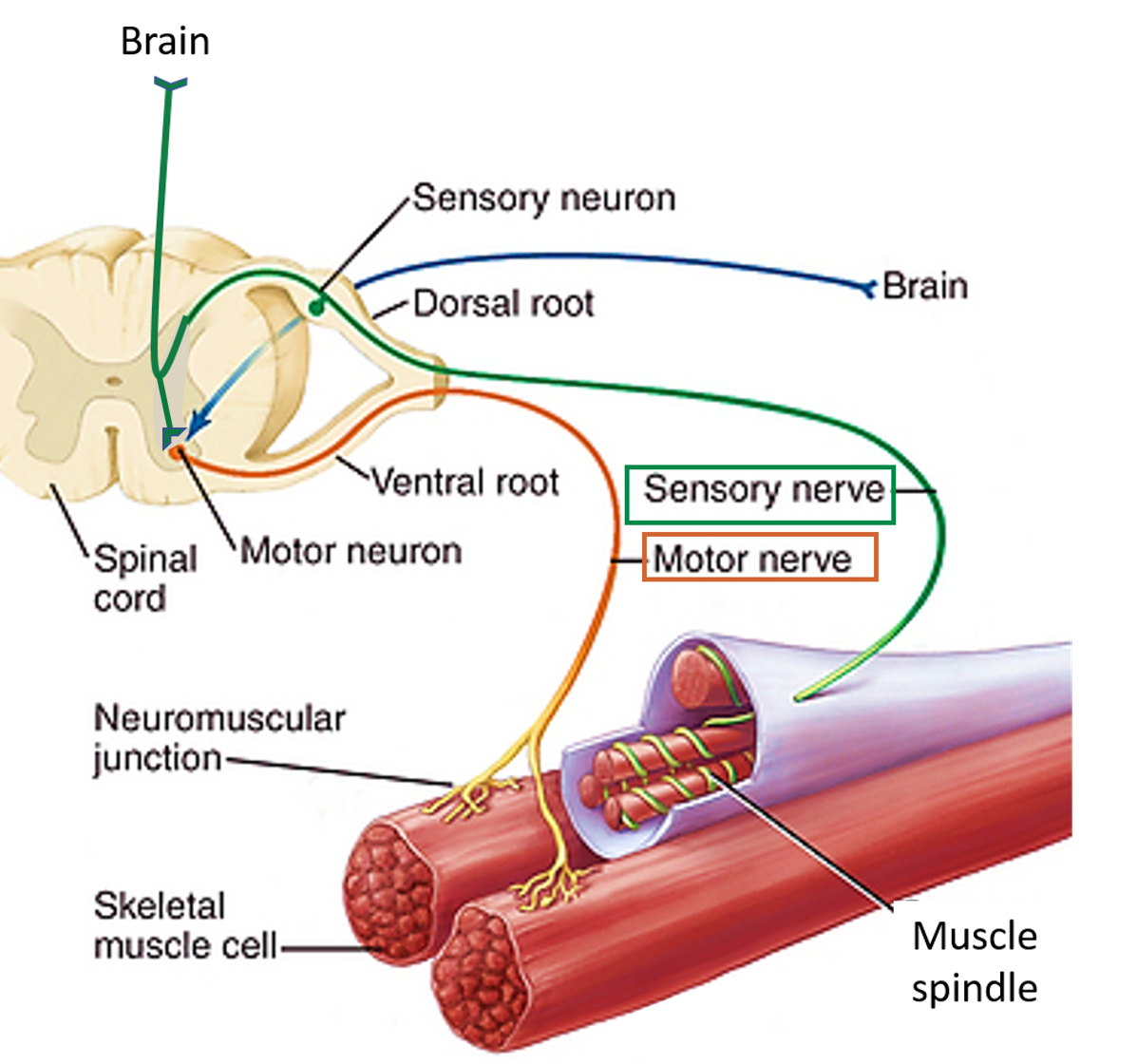
Skeletal Muscle Nerve Supply вђ Anatomy Qa Muscle & nerve is devoted to publishing new clinical and research studies on the most important findings on neuromuscular disorders and treatment options from a range of medical fields, including: electrophysiology and electrodiagnosis • anatomy • biochemistry • cell biology • epidemiology • genetics • immunology • pathology • pharmacology • physiology • toxicology • virology. Associating muscles to a common nerve group is an excellent way to memorize muscle innervations. for example, when you realize that the radial nerve innervates the majority of the hand and wrist extensor muscles, you can form better associations and quickly reference this knowledge when you’re tested on it during anatomy lab or an exam.
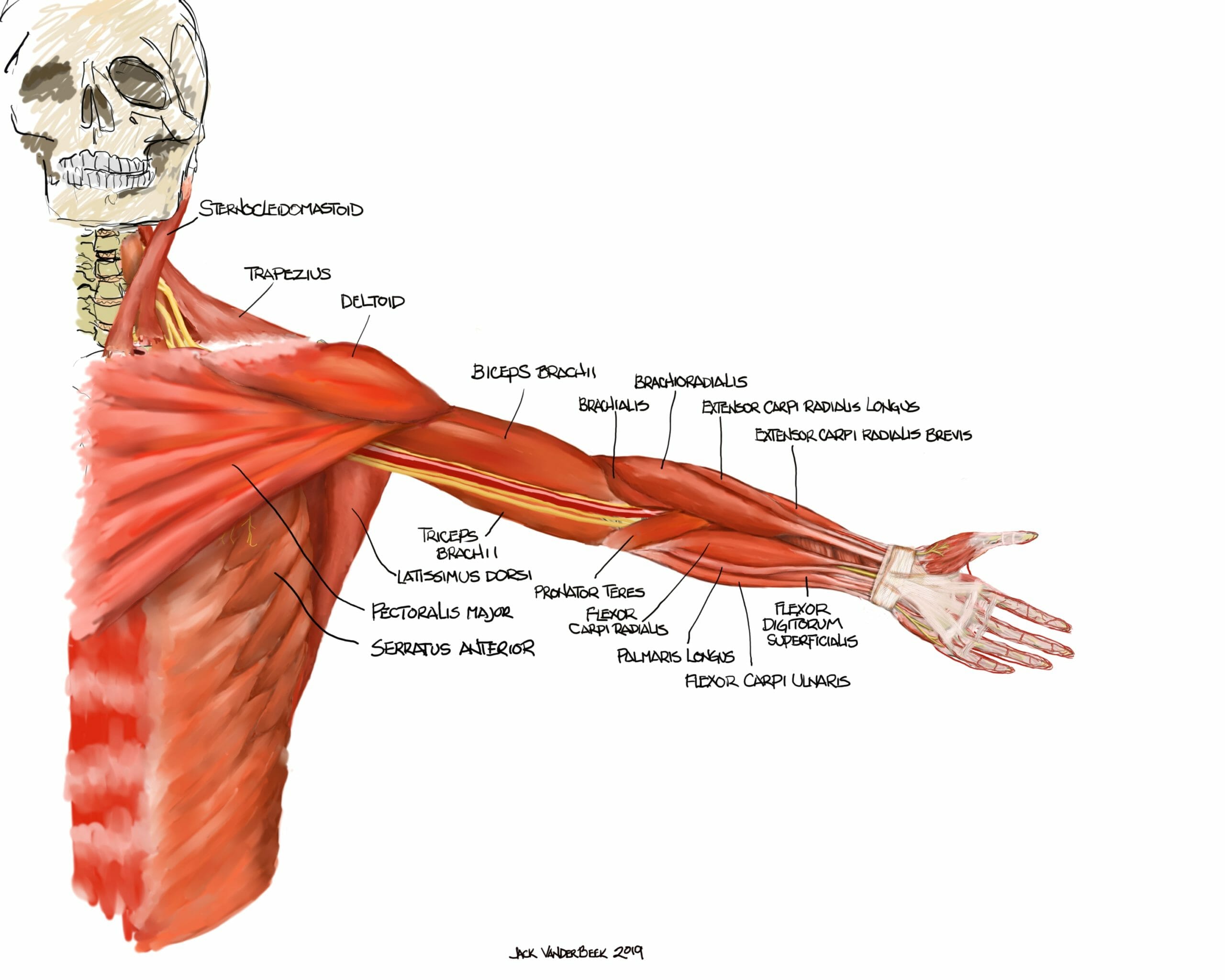
Peripheral Nerves And Muscles Neuraxiom Efferent nerves convey motor impulses away from the cns, to effector organs such as muscles and glands. they can be divided into two types: somatic motor nerves (they provide innervation to the skeletal muscles) and visceral motor nerves (they are part of the autonomic nervous system and they innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands). You have two main types of nerves: sensory nerves carry signals to your brain to help you touch, taste, smell and see. motor nerves carry signals to your muscles or glands to help you move and function. you also have two main groups of nerves branching out from your brain and spinal cord: cranial nerves: these 12 nerve pairs originate in your. Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles. blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. The sensory nerves and sense organs of the peripheral nervous system (pns) monitor conditions inside and outside of the body and send this information to the cns. efferent nerves in the pns carry signals from the control center to the muscles, glands, and organs to regulate their functions. nervous system anatomy nervous tissue.
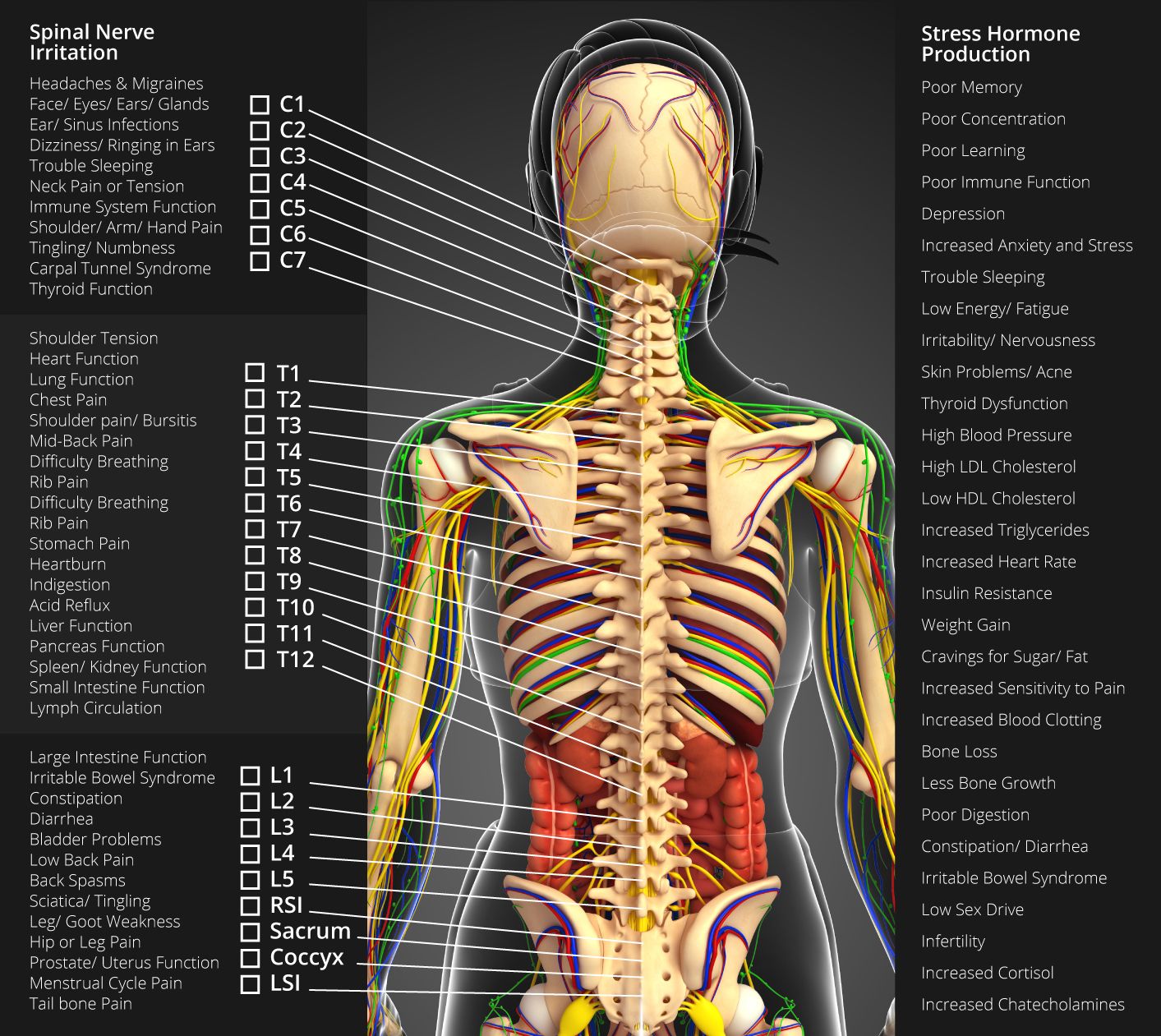
Nervous System Chart Chiropractors Ogden Utah Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles. blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. The sensory nerves and sense organs of the peripheral nervous system (pns) monitor conditions inside and outside of the body and send this information to the cns. efferent nerves in the pns carry signals from the control center to the muscles, glands, and organs to regulate their functions. nervous system anatomy nervous tissue. Muscle atrophy resulting from disease rather than disuse is generally one of two types, that resulting from damage to the nerves that supply the muscles, and disease of the muscle itself. examples of diseases affecting the nerves that control muscles would be: poliomyelitis; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (als or lou gehrig's disease);. Your l5 nerve also controls your hip, knee, foot, and toe movements. the l4 and l5 nerves (along with other nerves) contribute to the formation of the largest nerve in your body, the sciatic nerve, which runs down from your rear pelvis, into the back of your leg, and terminates in your foot. 5 giuffre ba, jeanmonod r. anatomy, sciatic nerve.
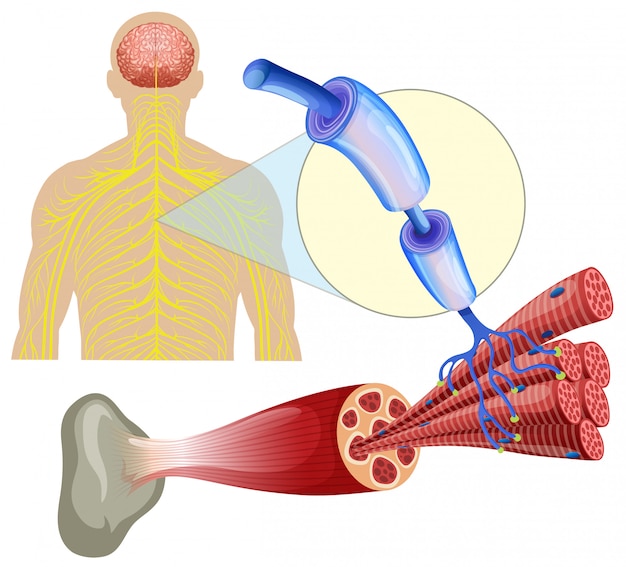
Premium Vector Human Healthy Muscle Nerves Muscle atrophy resulting from disease rather than disuse is generally one of two types, that resulting from damage to the nerves that supply the muscles, and disease of the muscle itself. examples of diseases affecting the nerves that control muscles would be: poliomyelitis; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (als or lou gehrig's disease);. Your l5 nerve also controls your hip, knee, foot, and toe movements. the l4 and l5 nerves (along with other nerves) contribute to the formation of the largest nerve in your body, the sciatic nerve, which runs down from your rear pelvis, into the back of your leg, and terminates in your foot. 5 giuffre ba, jeanmonod r. anatomy, sciatic nerve.
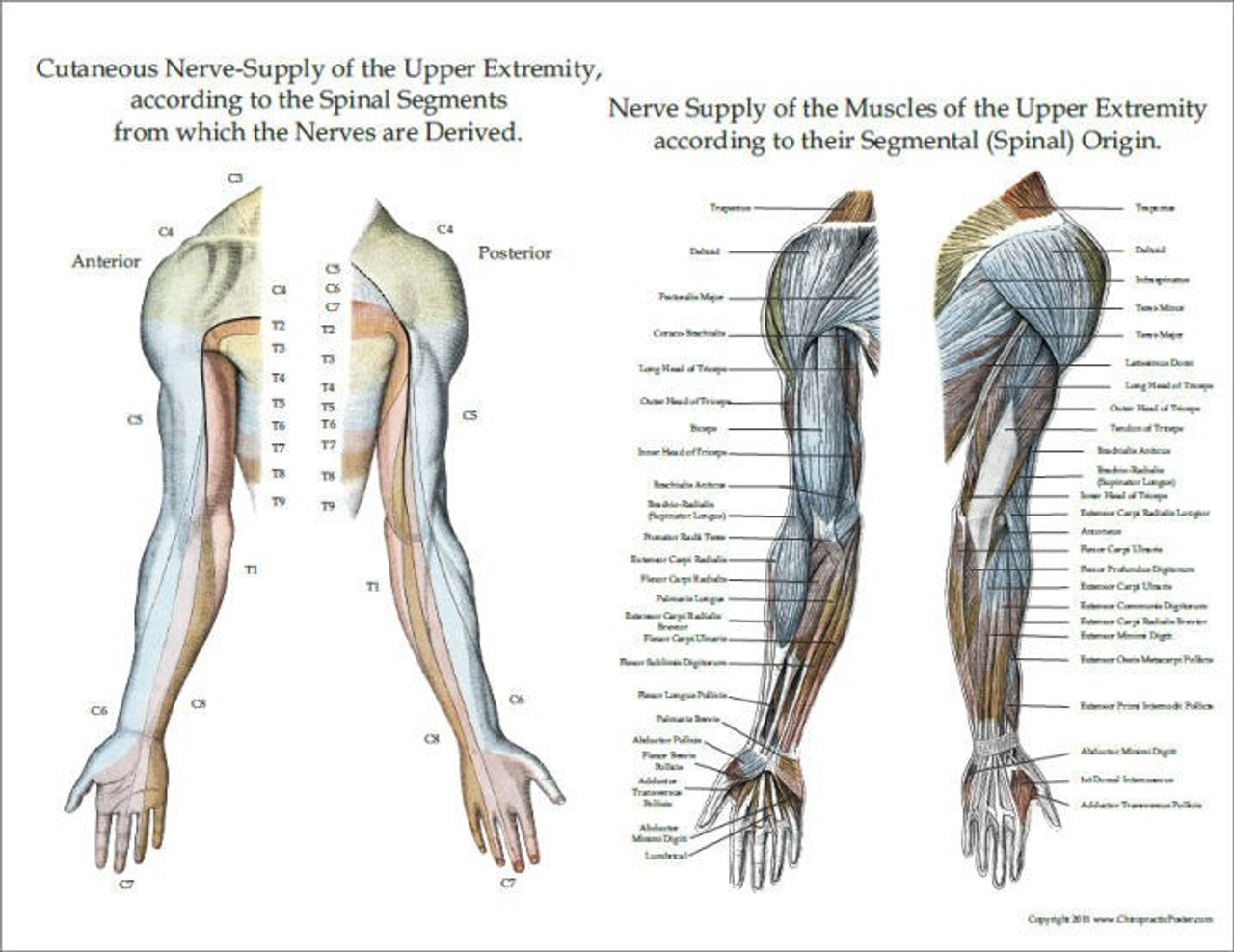
Nerve Supply Of The Upper Extremity Muscles And Skin Clinical Charts

Comments are closed.