Muscle Contraction And Relaxation

A By Product Of Involuntary Muscle Contraction And Relaxation Is Learn how muscle fibers contract and relax in response to signals from motor neurons, calcium ions, and atp. see the sliding filament model of contraction and the cross bridge cycle in action. Figure 10.9 relaxation of a muscle fiber ca ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. a muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of atp and becomes fatigued. interactive link. the release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions.

Muscle Contraction And Relaxation At The Sarcomere Level Exercise Learn how motor neurons signal skeletal muscle fibers to contract and relax through the neuromuscular junction, excitation contraction coupling, and calcium handling. explore the structure and function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum, t tubules, and cross bridge cycling. Figure 2. relaxation of a muscle fiber. ca ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. a muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of atp and becomes fatigued. the release of calcium ions initiates muscle contractions. Figure 9.4.1 9.4. 1: contraction of a muscle fiber. a cross bridge forms between actin and the myosin heads initiating contraction. as long as ca ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten. Learn how muscles contract and relax due to the sliding of actin and myosin filaments within sarcomeres. understand the role of calcium, atp, and troponin in the process of muscle contraction.
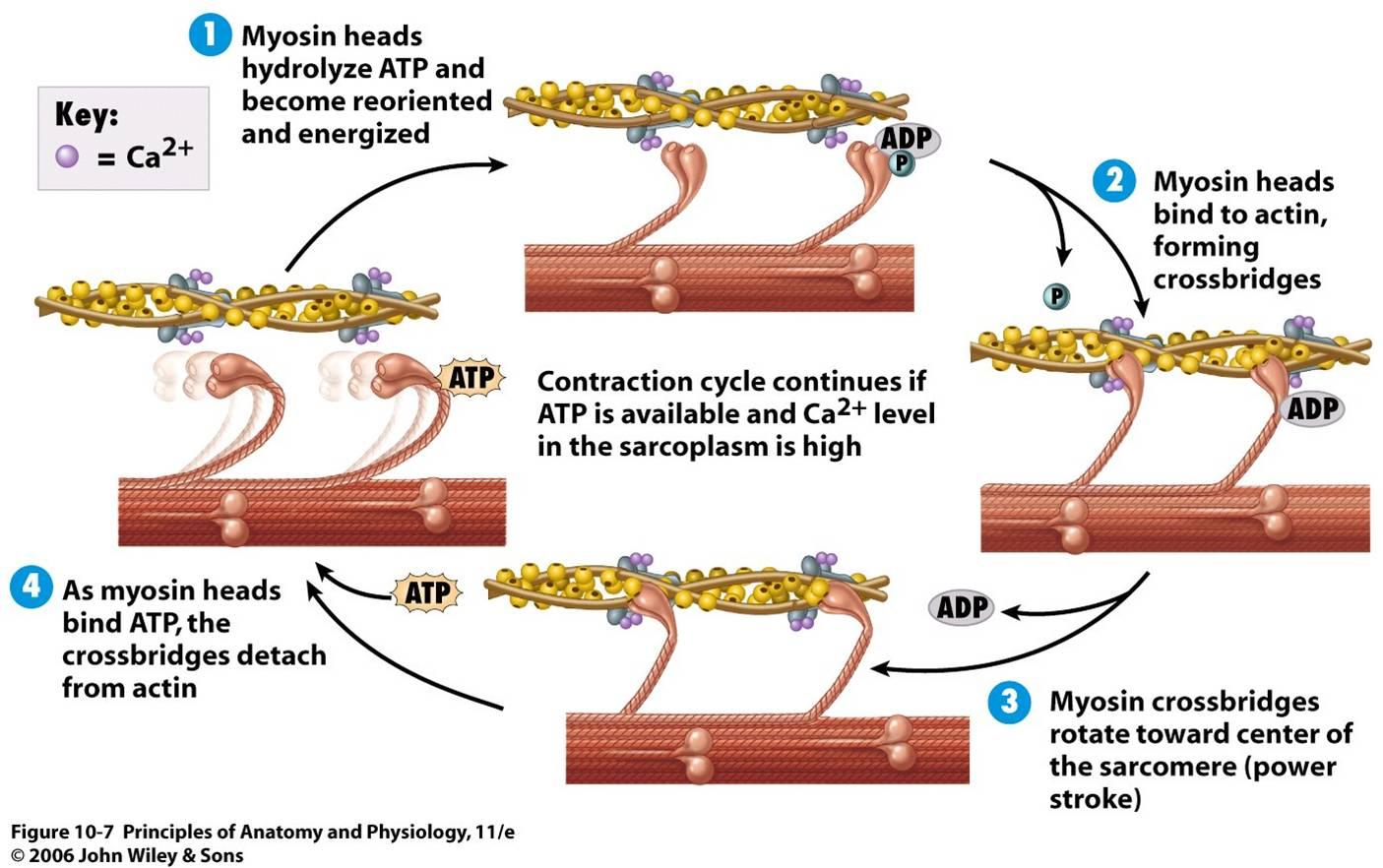
Mungposst Figure 9.4.1 9.4. 1: contraction of a muscle fiber. a cross bridge forms between actin and the myosin heads initiating contraction. as long as ca ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten. Learn how muscles contract and relax due to the sliding of actin and myosin filaments within sarcomeres. understand the role of calcium, atp, and troponin in the process of muscle contraction. Figure 2. relaxation of a muscle fiber. ca ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. a muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of atp and becomes fatigued. watch this video to learn more about the role of calcium. Upon termination of muscle contraction, muscle relaxation occurs, which is the return of muscle fibers to a low tension state. mammals have three types of muscles: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. skeletal muscles are attached to bones and give the body structure and strength.

Muscle Contraction Anatomy Diagram Quizlet Vrogue Co Figure 2. relaxation of a muscle fiber. ca ions are pumped back into the sr, which causes the tropomyosin to reshield the binding sites on the actin strands. a muscle may also stop contracting when it runs out of atp and becomes fatigued. watch this video to learn more about the role of calcium. Upon termination of muscle contraction, muscle relaxation occurs, which is the return of muscle fibers to a low tension state. mammals have three types of muscles: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. skeletal muscles are attached to bones and give the body structure and strength.

Muscle Contraction Cycle Muscle Contraction Muscular System Anatomy

Comments are closed.