Muscle Fiber Diagram Labeled
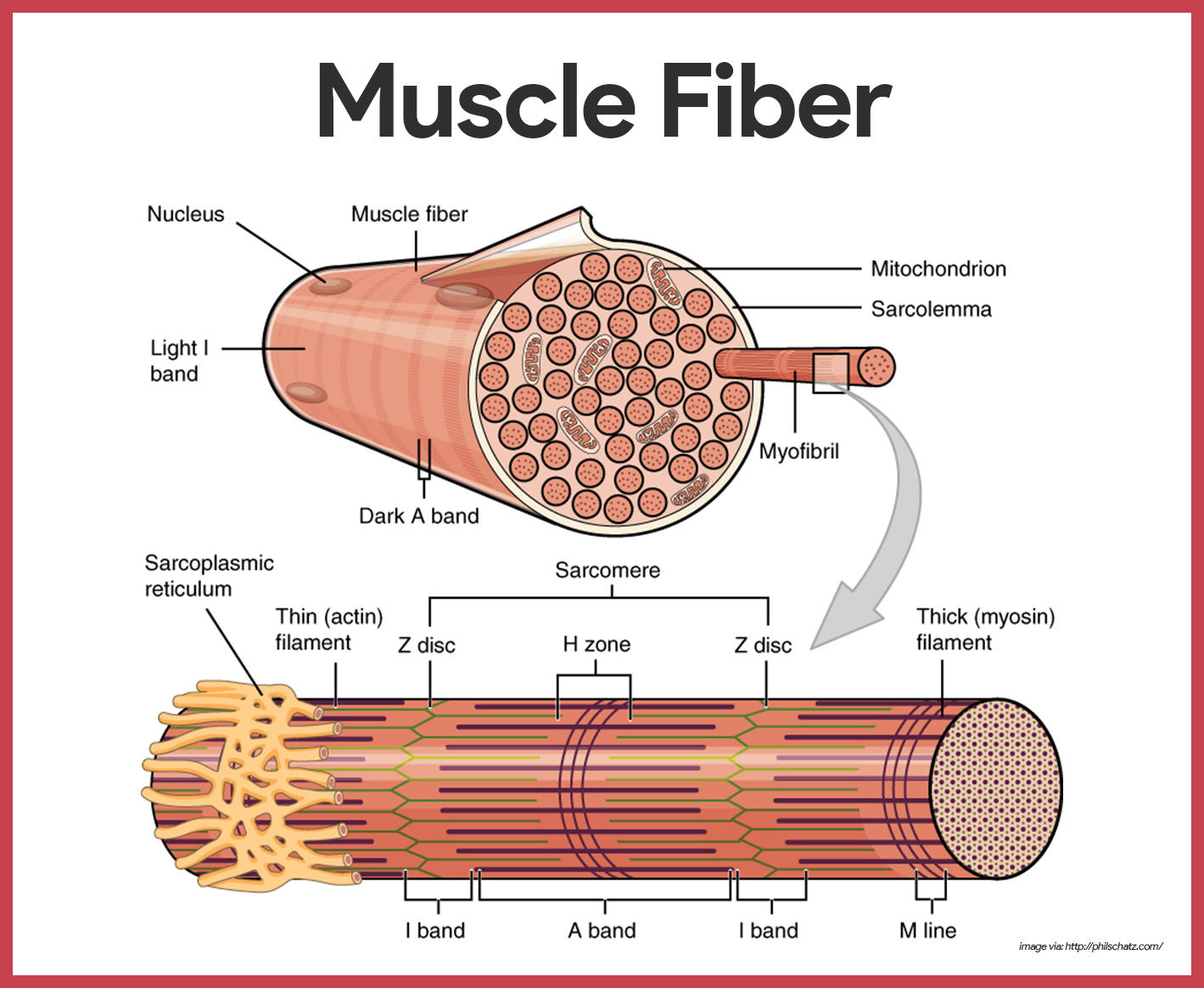
Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs Learn about the structure and function of skeletal muscle fibers, myofibrils, and sarcomeres. see diagrams of the sarcomere and its components, such as thick and thin filaments, z discs, and m line. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called “mysia”) that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (figure 10.3).

Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology I Striated just like cardiac muscle, these skeletal muscle fibers are very strong. skeletal muscle derives its name from the fact that these muscles always connect to the skeleton in at least one place. gross anatomy of a skeletal muscle. most skeletal muscles are attached to two bones through tendons. tendons are tough bands of dense regular. Learn about the structure and function of skeletal muscle, the organ that produces movement and heat in the body. see diagrams of the three connective tissue layers, the sarcomere, and the t tubule system of skeletal muscle fibers. These myoblasts asre located to the periphery of the myocyte and flattened so as not to impact myocyte contraction. myocyte: skeletal muscle cell: a skeletal muscle cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane called the sarcolemma with a cytoplasm called the sarcoplasm. a muscle fiber is composed of many myofibrils, packaged into orderly units. Fg fibers are used to produce rapid, forceful contractions to make quick, powerful movements. these fibers fatigue quickly, permitting them to only be used for short periods. most muscles possess a mixture of each fiber type. the predominant fiber type in a muscle is determined by the primary function of the muscle.

Comments are closed.