Muscle Physiology вђ Pharma Notes вђ Medium
Muscle Physiology вђ Pharma Notes вђ Medium Composition. many levels of sub division. muscles are composed of myocytes, myocytes are seperated from each other by fascia. the entire muscle mass is encompassed in a connective tissue called. Muscle physiology classification. muscle is classified in three different ways. striation. striated — non striated; control. voluntary — involuntary.

Muscle Physiology Illustrated Notes Pdfs вђ Medicosis Perfectionalis Rx one article o.d o2 20 4 rep. 12 these notes may cause increased academic performance, statements not validated by the fda — consult your physician prior to use. Define single unit vs. multi unit smooth muscle types. muscle generates force by contracting against external load. there are three main types of muscle, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth . all three use the same fuel source, atp, which supplies chemical energy that muscles convert into mechanical work and heat. Sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. the length of the skeletal muscle shortens as thick and thin filaments of the sarcomere slide over one another, causing contraction of the skeletal muscle. the process is known as “sliding filament mechanism”. the thin filaments are made up of actin, troponin, tropomyosin. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm.

Muscular System Pharma 1 Ppt Sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. the length of the skeletal muscle shortens as thick and thin filaments of the sarcomere slide over one another, causing contraction of the skeletal muscle. the process is known as “sliding filament mechanism”. the thin filaments are made up of actin, troponin, tropomyosin. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Heart – anatomy of heart, blood circulation, blood vessels, structure and functions of artery, vein and capillaries, elements of the conduction system of heart and heartbeat, its regulation by the autonomic nervous system, cardiac output, cardiac cycle. regulation of blood pressure, pulse, electrocardiogram, and disorders of the heart. Nervous system. classification of nervous system, anatomy, and physiology of cerebrum, cerebellum, midbrain, function of the hypothalamus, medulla oblongata and basal ganglia, spinal cord structure and reflexes, names and functions of cranial nerves, anatomy and physiology of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system (ans).

Solution Muscle Physiology Notes Studypool Heart – anatomy of heart, blood circulation, blood vessels, structure and functions of artery, vein and capillaries, elements of the conduction system of heart and heartbeat, its regulation by the autonomic nervous system, cardiac output, cardiac cycle. regulation of blood pressure, pulse, electrocardiogram, and disorders of the heart. Nervous system. classification of nervous system, anatomy, and physiology of cerebrum, cerebellum, midbrain, function of the hypothalamus, medulla oblongata and basal ganglia, spinal cord structure and reflexes, names and functions of cranial nerves, anatomy and physiology of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system (ans).

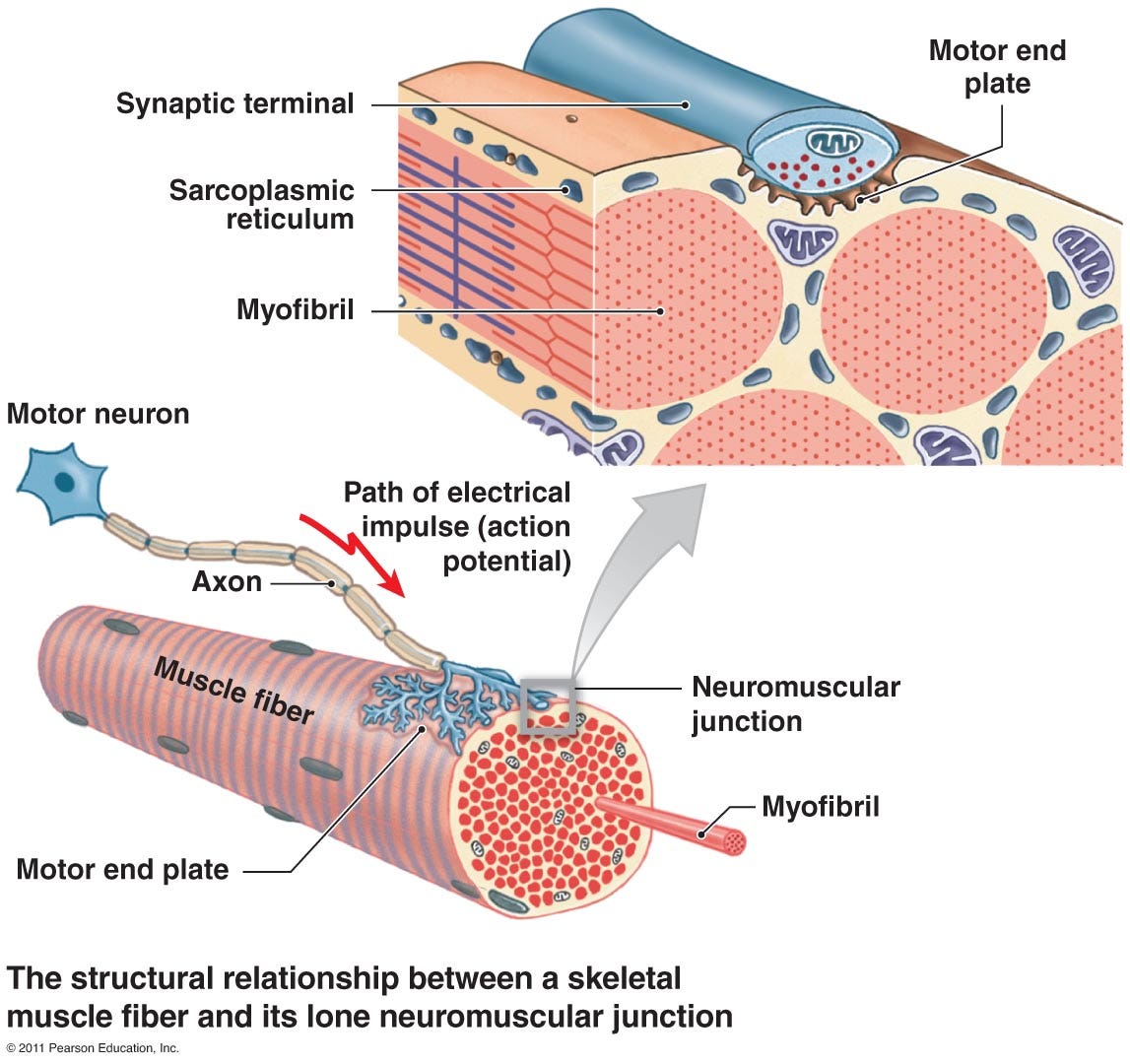
Biomedical Physiology Exam 2 Muscle Physiology Diagram Quizlet

Comments are closed.