Muscles Of Breathing Inspiration Inhalation

Respiratory Muscle Training Physiopedia The muscles of respiration are also called the 'breathing pump muscles', they form a complex arrangement in the form of semi rigid bellows around the lungs. all muscles that are attached to the human rib cage have the inherent potential to cause a breathing action. muscles that are helpful in expanding the thoracic cavity are called the. Respiratory zone: respiratory bronchioles, alveoli. breathing cycle. inspiration diaphragm contracts and pulls down, intercostal muscles contract and expand the rib cage > air enters the lungs. expiration diaphragm relaxes and goes up, intercostal muscles relax and rib cage collapses > air exits the lungs.

Ppt Respiratory Physiology Powerpoint Presentation Free Download The muscles of respiration are the muscles that contribute to inhalation and exhalation, by aiding in the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity. the diaphragm and, to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles drive respiration during quiet breathing. the elasticity of these muscles is crucial to the health of the respiratory system. Pulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration. inspiration is the process that causes air to enter the lungs, and expiration is the process that causes air to leave the lungs ( figure 22.3.3 ). a respiratory cycle is one sequence of inspiration and expiration. The processes of inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out) are vital for providing oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide from the body. inspiration occurs via active contraction of muscles – such as the diaphragm – whereas expiration tends to be passive, unless it is forced. in this article, we shall look at the. The diaphragm is the primary muscle involved in breathing, however several other muscles play a role in certain circumstances. these muscles are referred to as accessory muscles of inhalation. external intercostal muscles: muscles located between the ribs that help the thoracic cavity and pleural cavity expand during quiet and forced inspiration.
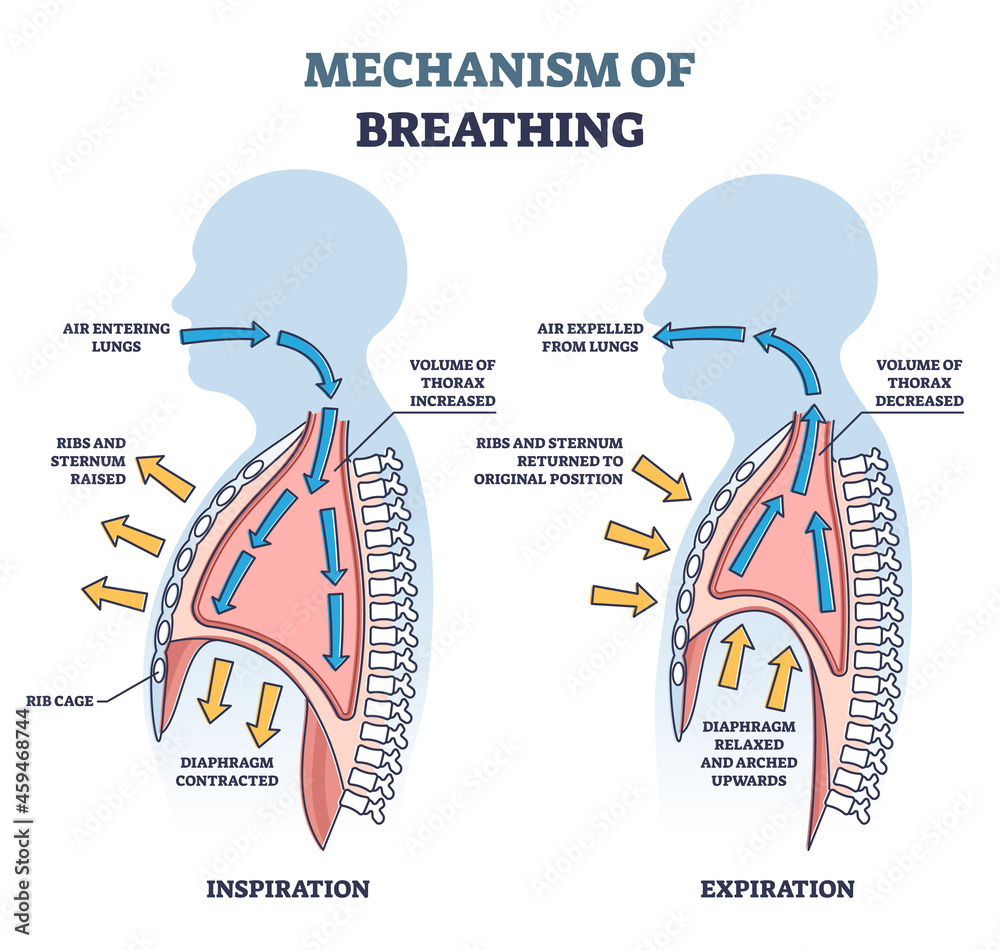
Mechanism Of Breathing As Anatomical Process Explanation Outline The processes of inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out) are vital for providing oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide from the body. inspiration occurs via active contraction of muscles – such as the diaphragm – whereas expiration tends to be passive, unless it is forced. in this article, we shall look at the. The diaphragm is the primary muscle involved in breathing, however several other muscles play a role in certain circumstances. these muscles are referred to as accessory muscles of inhalation. external intercostal muscles: muscles located between the ribs that help the thoracic cavity and pleural cavity expand during quiet and forced inspiration. The diaphragm, a dome shaped sheet of muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen, is the most important muscle used for breathing in (called inhalation or inspiration). the diaphragm is attached to the base of the sternum, the lower parts of the rib cage, and the spine. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. in addition to the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, other accessory muscles must also contract. during forced inspiration, muscles of the neck, including the scalenes, contract and lift the thoracic wall, increasing lung volume.
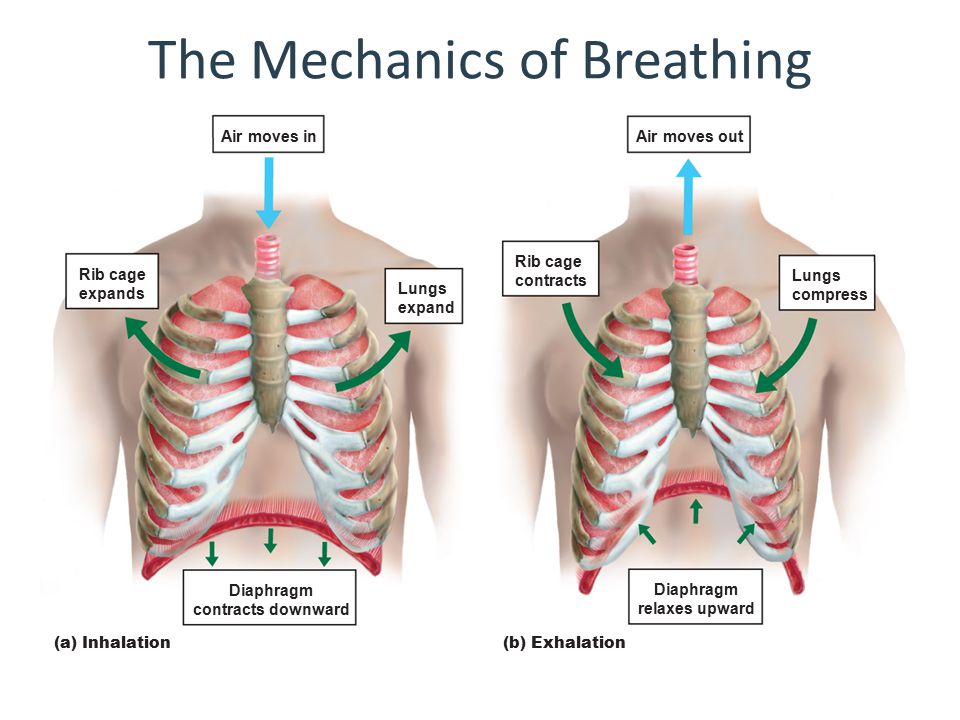
Mechanics Of Pulmonary Ventilation And Pressure Changes During The diaphragm, a dome shaped sheet of muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdomen, is the most important muscle used for breathing in (called inhalation or inspiration). the diaphragm is attached to the base of the sternum, the lower parts of the rib cage, and the spine. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. in addition to the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, other accessory muscles must also contract. during forced inspiration, muscles of the neck, including the scalenes, contract and lift the thoracic wall, increasing lung volume.

Comments are closed.