Muscles Of The Face Anatomy

Muscles In The Face How Can Facial Expressions Be Collected And The facial muscles, also called craniofacial muscles, are a group of about 20 flat skeletal muscles lying underneath the skin of the face and scalp. most of them originate from the bones or fibrous structures of the skull and radiate to insert on the skin. contrary to the other skeletal muscles they are not surrounded by a fascia, with the. The human face is the most anterior portion of the human head. it refers to the area that extends from the superior margin of the forehead to the chin, and from one ear to another. the basic shape of the human face is determined by the underlying facial skeleton (i.e. viscerocranium ), the facial muscles and the amount of subcutaneous tissue.
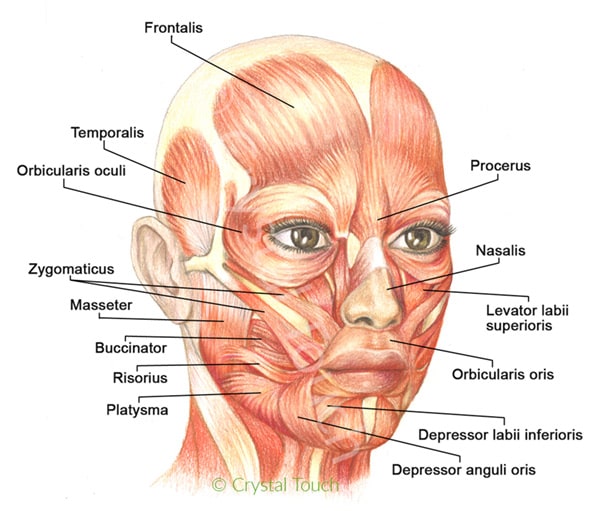
Our Facial Muscles And Their Functions вђў Crystal Touch Bell S Palsy Clinic The facial muscles involved in chewing are: buccinator, a thin muscle in your cheek that holds each cheek toward your teeth. lateral pterygoid, a fan shaped muscle that helps your jaw open. masseter, a muscle that runs from each cheek to each side of your jaw and helps your jaw close. medial pterygoid, a thick muscle that helps your jaw close. The orbital group of facial muscles contains two muscles associated with the eye socket. these muscles control the movements of the eyelids, important in protecting the cornea from damage. they are both innervated by the facial nerve. orbicularis oculi. the orbicularis oculi muscle surrounds the eye socket and extends into the eyelid. it has. The human face possesses around 30 muscles on each side, depending on how they are counted. the facial muscles are striated muscles that link the facial skin to the skull bone to perform important daily life functions, such as mastication and emotion expression. the facial muscles produce various movements but are often categorized into facial expression (mimetic) and mastication muscles. the. The first three layers skin, connective tissue, and the aponeurosis are connected tightly together, forming a single unit called the scalp proper. muscles of facial expression, simply known as the facial muscles are found deep to the skin of the scalp, face, and neck. most facial muscles are attached to bones or fascia on one end, and skin.

Facial Muscles Joi Jacksonville Orthopaedic Institute The human face possesses around 30 muscles on each side, depending on how they are counted. the facial muscles are striated muscles that link the facial skin to the skull bone to perform important daily life functions, such as mastication and emotion expression. the facial muscles produce various movements but are often categorized into facial expression (mimetic) and mastication muscles. the. The first three layers skin, connective tissue, and the aponeurosis are connected tightly together, forming a single unit called the scalp proper. muscles of facial expression, simply known as the facial muscles are found deep to the skin of the scalp, face, and neck. most facial muscles are attached to bones or fascia on one end, and skin. The facial muscles are just under the skin (subcutaneous) muscles that control facial expression. they generally originate from the surface of the skull bone (rarely the fascia), and insert on the skin of the face. when they contract, the skin moves. these muscles also cause wrinkles at right angles to the muscles’ action line. Face muscle anatomy. found situated around openings like the mouth, eyes and nose or stretched across the skull and neck, the facial muscles are a group of around 20 skeletal muscles which lie underneath the facial skin. the majority originate from the skull or fibrous structures, and connect to the skin through an elastic tendon.
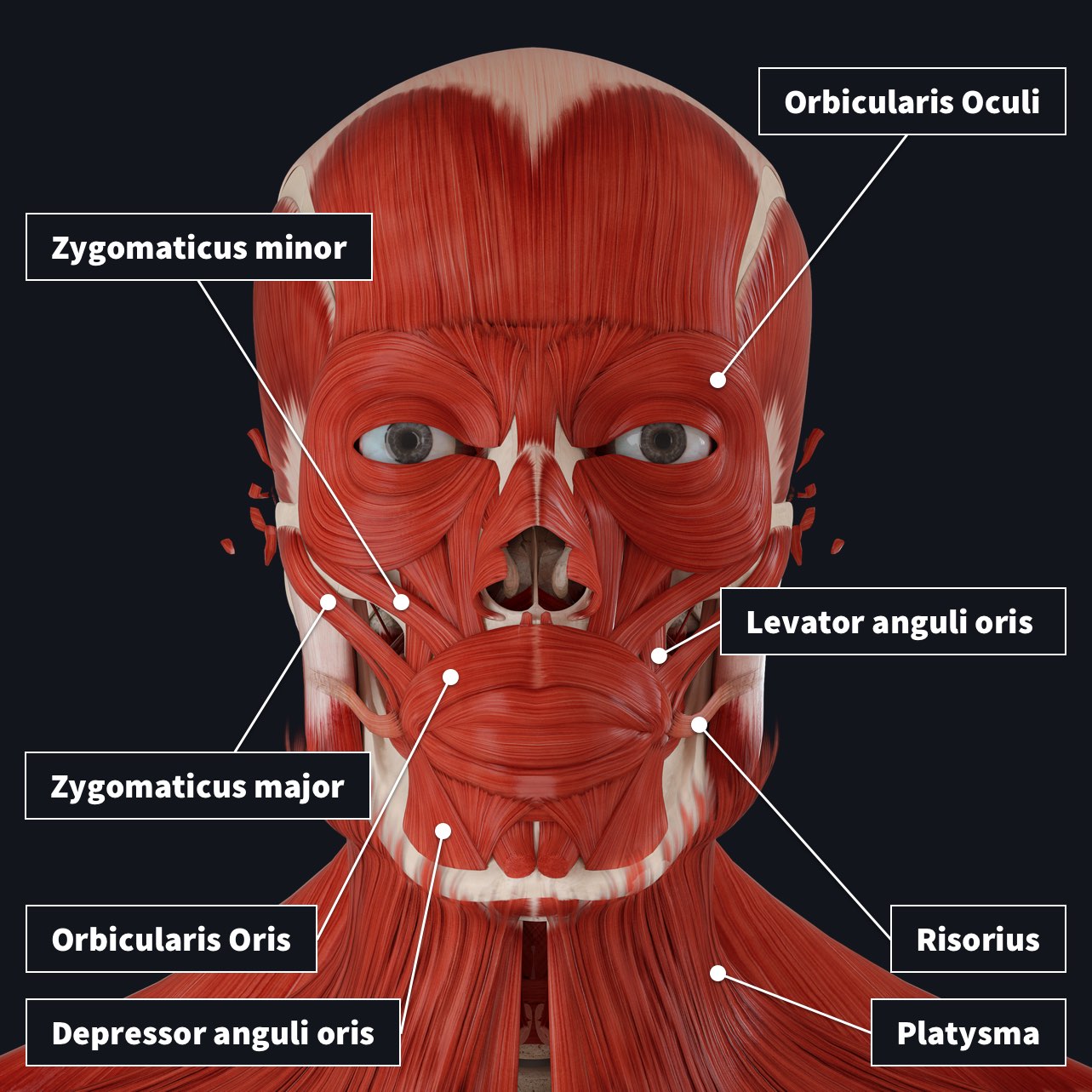
The Muscles Of Facial Expression Complete Anatomy The facial muscles are just under the skin (subcutaneous) muscles that control facial expression. they generally originate from the surface of the skull bone (rarely the fascia), and insert on the skin of the face. when they contract, the skin moves. these muscles also cause wrinkles at right angles to the muscles’ action line. Face muscle anatomy. found situated around openings like the mouth, eyes and nose or stretched across the skull and neck, the facial muscles are a group of around 20 skeletal muscles which lie underneath the facial skin. the majority originate from the skull or fibrous structures, and connect to the skin through an elastic tendon.

Comments are closed.