Muscles Of The Face And Their Functions
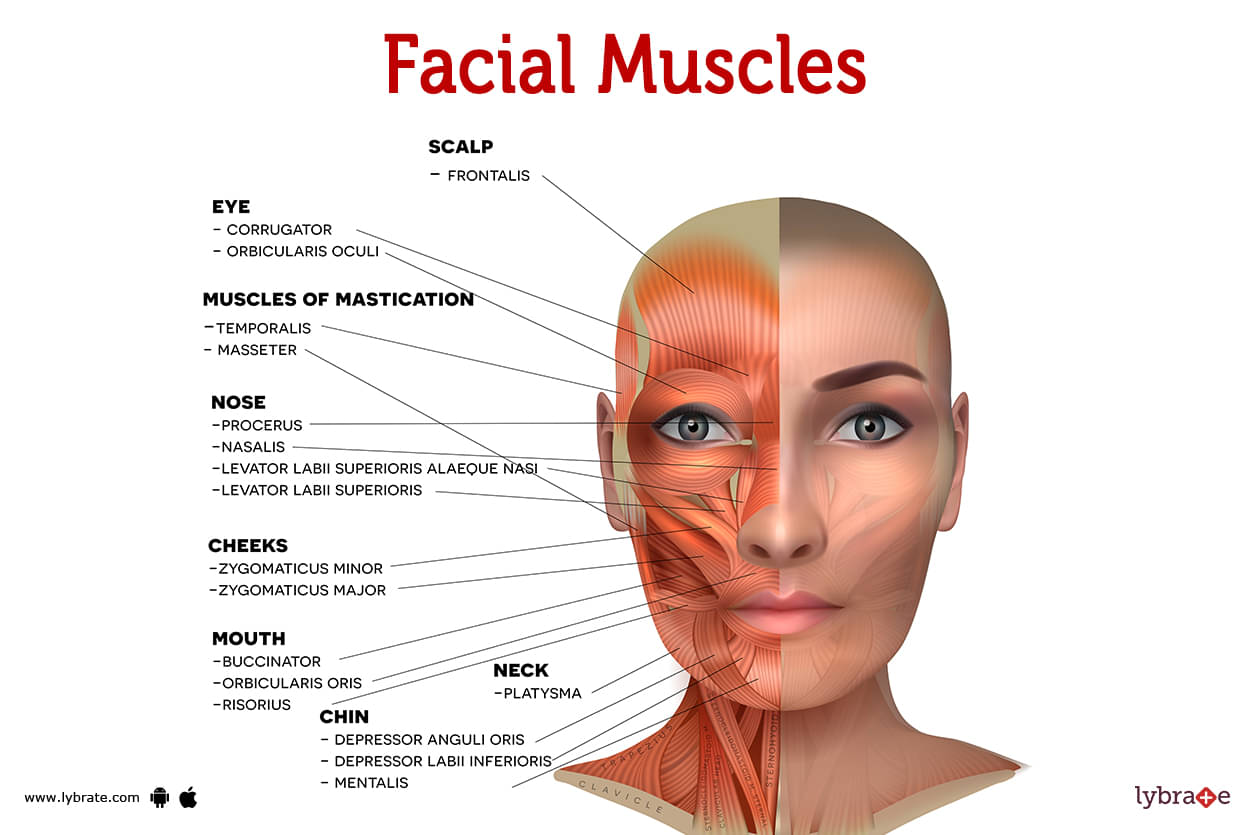
Facial Muscles Human Anatomy Image Functions Diseases And Treatments The facial muscles, also called craniofacial muscles, are a group of about 20 flat skeletal muscles lying underneath the skin of the face and scalp. most of them originate from the bones or fibrous structures of the skull and radiate to insert on the skin. contrary to the other skeletal muscles they are not surrounded by a fascia, with the. The facial muscles involved in chewing are: buccinator, a thin muscle in your cheek that holds each cheek toward your teeth. lateral pterygoid, a fan shaped muscle that helps your jaw open. masseter, a muscle that runs from each cheek to each side of your jaw and helps your jaw close. medial pterygoid, a thick muscle that helps your jaw close.
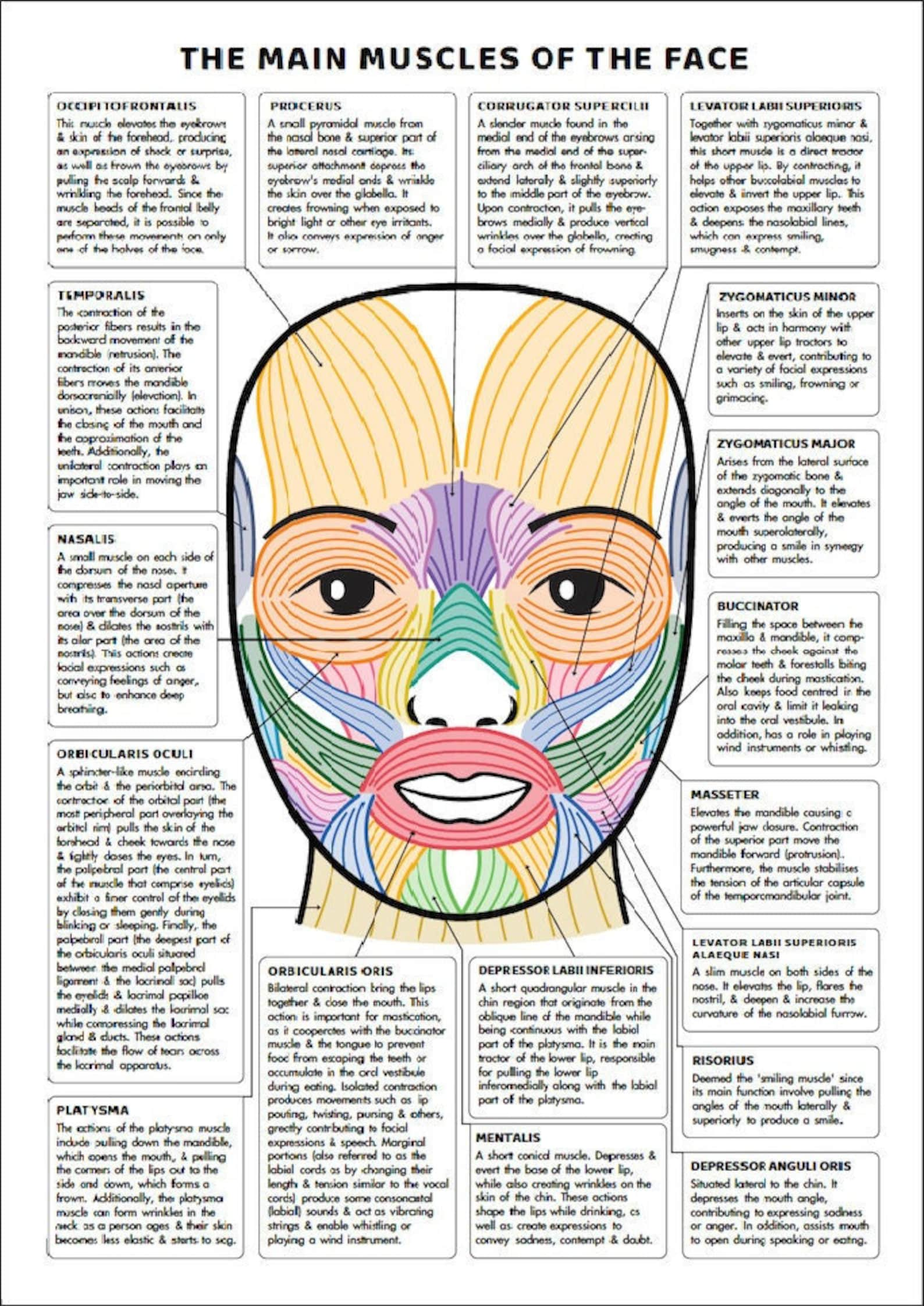
Facial Muscles And Their Functions Guide Printable Instant Etsy Uk The facial muscles are also known as the muscles of the facial expression or the mimetic muscles. these muscles are a group of approximately 20 superficial skeletal muscles of the face and scalp divided into five different groups according to their location and function. The muscles of facial expression. the muscles of facial expression are located within the subcutaneous tissue of the face. they originate from bone or fascia and insert onto the skin. as they contract, the muscles pull on the skin to exert their effects. these muscles all develop from the second pharyngeal arch. The facial muscles (also called the muscles of facial expression) are situated within the subcutaneous tissue of the face. they are responsible for the movements of skin folds, providing different facial expressions. the facial muscles originate from the bones of the facial skeleton (viscerocranium) and insert into the skin. The human face possesses around 30 muscles on each side, depending on how they are counted. the facial muscles are striated muscles that link the facial skin to the skull bone to perform important daily life functions, such as mastication and emotion expression. the facial muscles produce various movements but are often categorized into facial expression (mimetic) and mastication muscles. the.
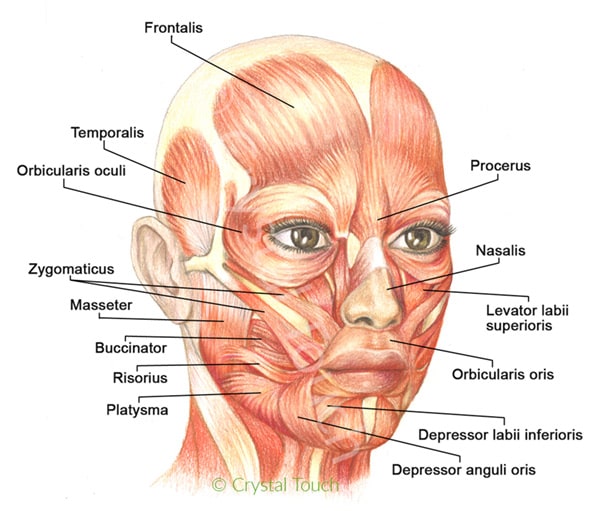
Our Facial Muscles And Their Functions вђў Crystal Touch Bell S Palsy Clinic The facial muscles (also called the muscles of facial expression) are situated within the subcutaneous tissue of the face. they are responsible for the movements of skin folds, providing different facial expressions. the facial muscles originate from the bones of the facial skeleton (viscerocranium) and insert into the skin. The human face possesses around 30 muscles on each side, depending on how they are counted. the facial muscles are striated muscles that link the facial skin to the skull bone to perform important daily life functions, such as mastication and emotion expression. the facial muscles produce various movements but are often categorized into facial expression (mimetic) and mastication muscles. the. The facial muscles are just under the skin (subcutaneous) muscles that control facial expression. they generally originate from the surface of the skull bone (rarely the fascia), and insert on the skin of the face. when they contract, the skin moves. these muscles also cause wrinkles at right angles to the muscles’ action line. Practice test. to begin, spend a few minutes analysing the face muscles diagram above in which all the face muscles are clearly labeled. once you think you’ve got a solid idea of the location of each muscle (top tip: try to associate the location with the function to aid your memory!), you can try labelling the muscles yourself using our.

Comments are closed.