Muscles Of The Thorax Origin Insertion Function
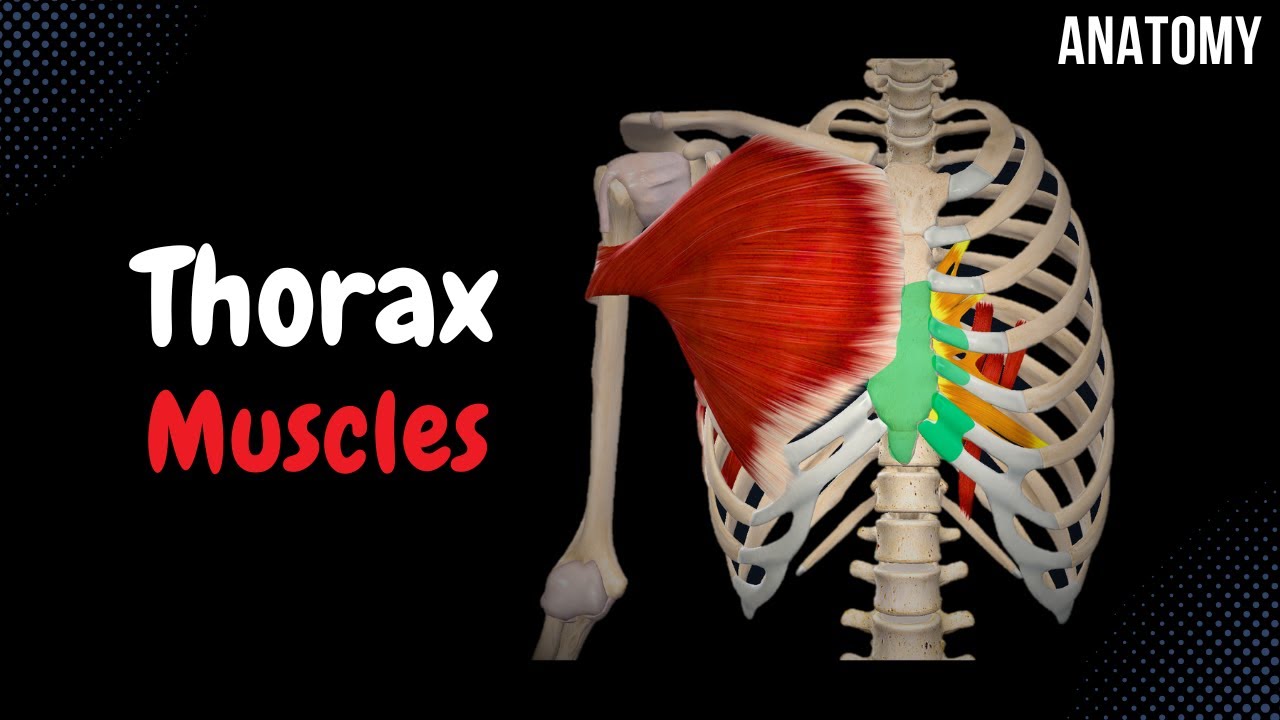
Muscles Of The Thorax Origin Insertion Function Youtube Content0:00 introduction0:10 division of the thoracic muscles1:05 subclavius muscle1:24 serratus anterior1:58 pectoralis minor2:23 pectoralis major2:56 subco. Drawing the lip downward. mandible bone. lower lip. epicranius. raising eyebrows, wrinkling forehead, pulling scalp posteriorly. frontal belly, occipital belly, temporal bone. skin of brow, epicranial aponeurosis. lateral pterygoid. protruding the mandible, opening the jaw, moving the mandible outward and right and left.
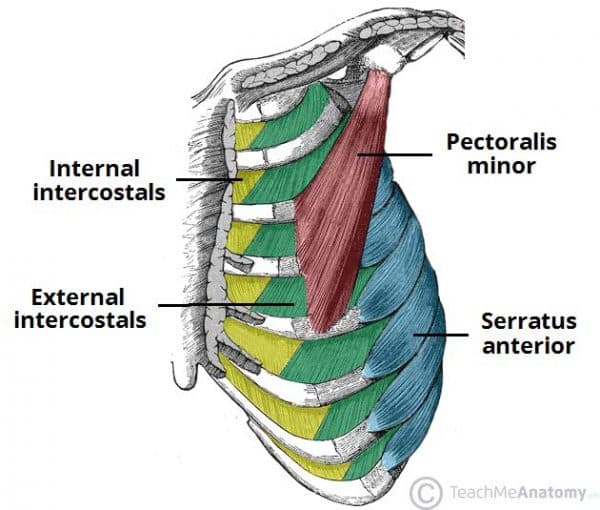
Thoracic Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy Subcostalis, transversus thoracis & innermost intercostal mm. make up the deepest intercostal muscle layer. transversus thoracis. posterior surface of the sternum. inner surfaces of costal cartilages 2 6. compresses the thorax for forced expiration. intercostal nerves 2 6. internal thoracic a. The thoracic wall is made up of five muscles: the external intercostal muscles, internal intercostal muscles, innermost intercostal muscles, subcostalis, and transversus thoracis. these muscles are primarily responsible for changing the volume of the thoracic cavity during respiration. other muscles that do not make up the thoracic wall, but attach to it include the pectoralis major and minor. Muscles of the thorax. the muscles of the thorax include both the diaphragm as well as the muscles of the thoracic cage. the diaphragm can be located below the lungs and consists of a sheet of skeletal muscle which displays a double domed structure. the diaphragm is important as it separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and. There are 11 pairs of external intercostal muscles. they run inferoanteriorly from the rib above to the rib below, and are continuous with the external oblique of the abdomen. attachments: originate at the lower border of the rib, inserting into the superior border of the rib below. actions: elevates the ribs, increasing the thoracic volume.

Axial Muscles Of The Abdominal Wall And Thorax Anatomy And Physiology I Muscles of the thorax. the muscles of the thorax include both the diaphragm as well as the muscles of the thoracic cage. the diaphragm can be located below the lungs and consists of a sheet of skeletal muscle which displays a double domed structure. the diaphragm is important as it separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and. There are 11 pairs of external intercostal muscles. they run inferoanteriorly from the rib above to the rib below, and are continuous with the external oblique of the abdomen. attachments: originate at the lower border of the rib, inserting into the superior border of the rib below. actions: elevates the ribs, increasing the thoracic volume. The pectoralis major has a broad origin, based on which it is divided into three parts: clavicular part, sternocostal part and abdominal part. all three parts converge laterally and insert onto the greater tubercle of humerus . the main function of this chest muscle as a whole is the adduction and internal rotation of the arm in the shoulder joint. The serratus anterior is a fan shaped muscle that originates on the superolateral surfaces of the first to eighth ribs or the first to ninth ribs at the lateral wall of the thorax and inserts along the superior angle, medial border, and inferior angle of the scapula. the main part of the serratus anterior lies deep to the scapula and the pectoral muscles and is easily palpated between the.

Thoracic Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy The pectoralis major has a broad origin, based on which it is divided into three parts: clavicular part, sternocostal part and abdominal part. all three parts converge laterally and insert onto the greater tubercle of humerus . the main function of this chest muscle as a whole is the adduction and internal rotation of the arm in the shoulder joint. The serratus anterior is a fan shaped muscle that originates on the superolateral surfaces of the first to eighth ribs or the first to ninth ribs at the lateral wall of the thorax and inserts along the superior angle, medial border, and inferior angle of the scapula. the main part of the serratus anterior lies deep to the scapula and the pectoral muscles and is easily palpated between the.

Thorax Region Of The Body Between The Neck

Comments are closed.