Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Tissue
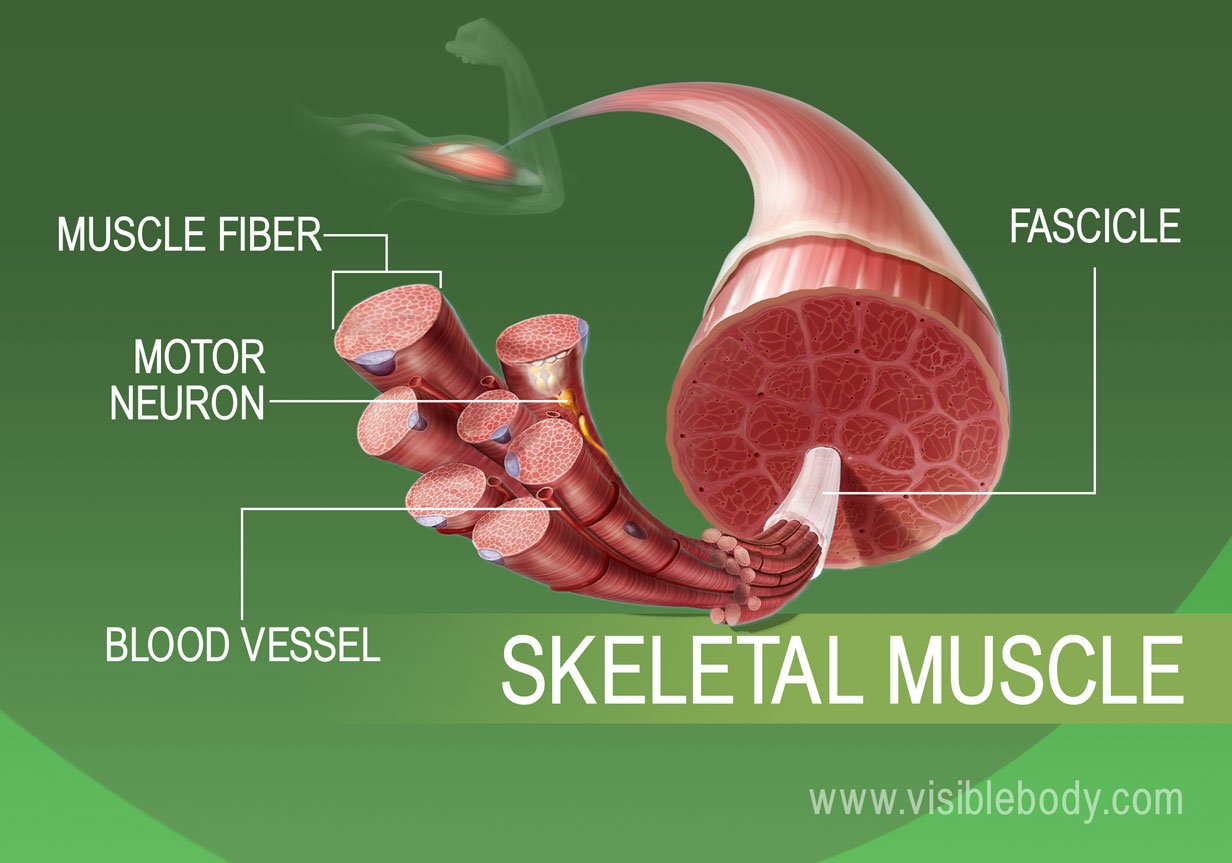
Muscle Tissue Types Learn Muscular Anatomy The skeletal muscles are a vital part of your musculoskeletal system. they serve a variety of functions, including: chewing and swallowing, which are the first parts of digestion. expanding and contracting your chest cavity so you can inhale and exhale at will. maintaining body posture. The musculoskeletal system (locomotor system) is a human body system that provides our body with movement, stability, shape, and support. it is subdivided into two broad systems: muscular system, which includes all types of muscles in the body. skeletal muscles, in particular, are the ones that act on the body joints to produce movements.
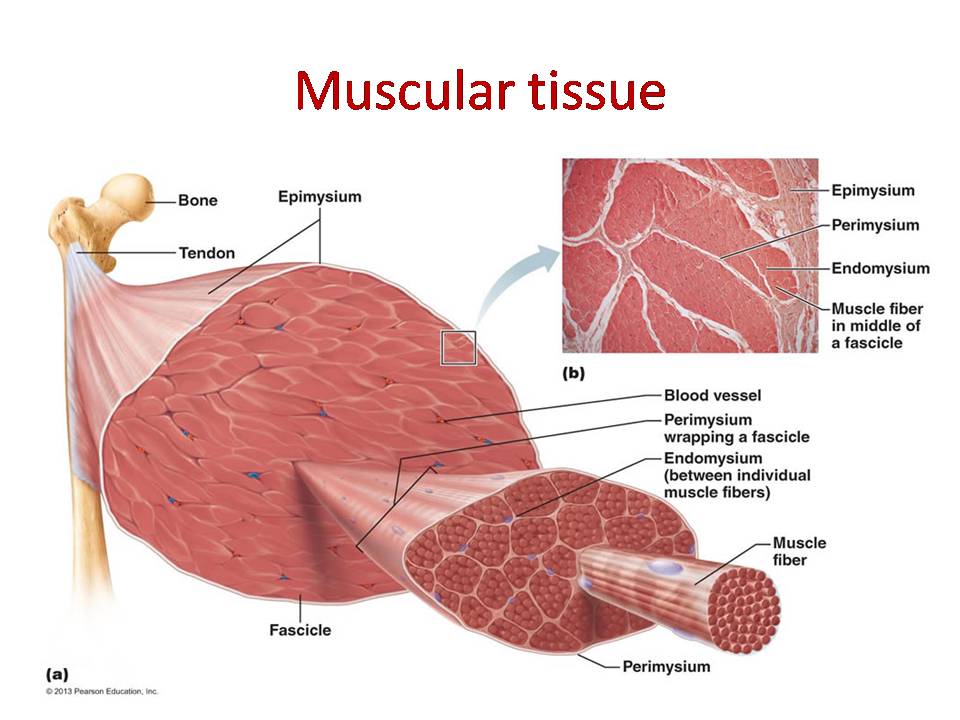
Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle Online Biology Notes Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles. blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. The muscular system is made up of muscle tissue and is responsible for functions such as maintenance of posture, locomotion and control of various circulatory systems. this includes the beating of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system. the muscular system is closely associated with the skeletal system in facilitating. Skeletal muscle tissue can be found across the animal kingdom, in most multi cellular forms of life. skeletal muscle structure. skeletal muscle is comprised of a series of muscle fibers made of muscle cells. these muscle cells are long and multinucleated. at the ends of each skeletal muscle a tendon connects the muscle to bone. Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external.
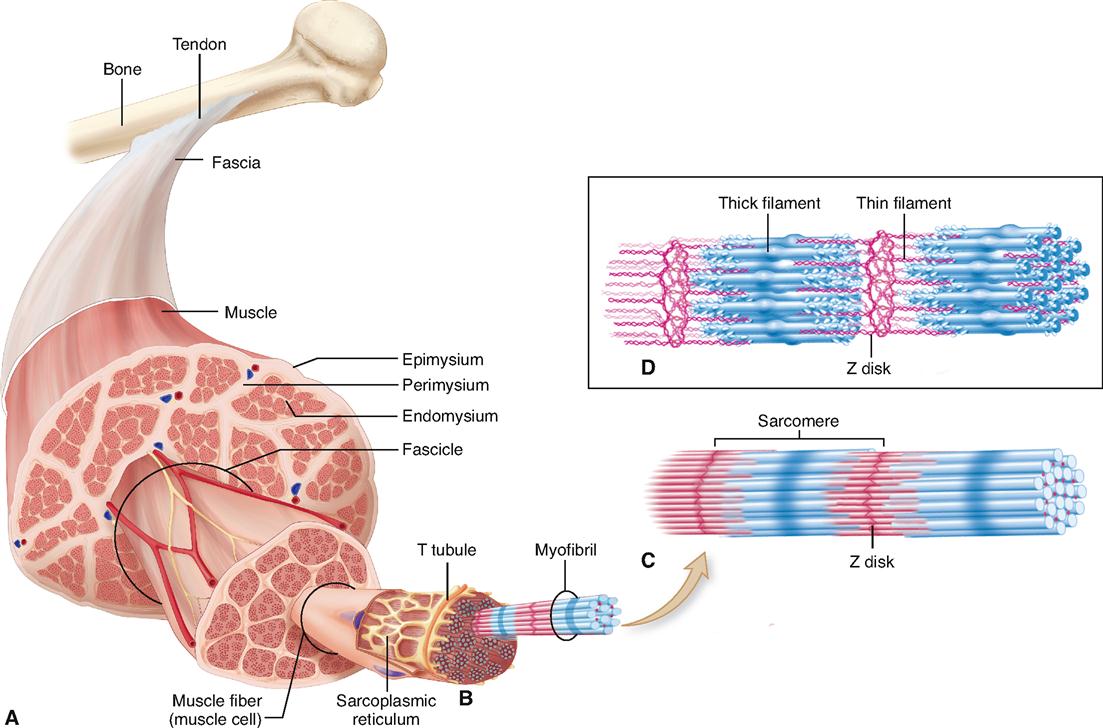
Physiology Of The Muscular System Basicmedical Key Skeletal muscle tissue can be found across the animal kingdom, in most multi cellular forms of life. skeletal muscle structure. skeletal muscle is comprised of a series of muscle fibers made of muscle cells. these muscle cells are long and multinucleated. at the ends of each skeletal muscle a tendon connects the muscle to bone. Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external. Figure 4.4.1 – muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle cells have prominent striation and nuclei on their periphery. (b) smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) cardiac muscle cells appear striated and have a single nucleus. from top, lm × 1600, lm × 1600, lm × 1600. Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the other being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. they are part of the voluntary muscular system [1] and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. [2][3] the skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of.

Comments are closed.