Myelinated Motor Neurons Function Location Types

Myelinated Motor Neurons Function Location Types Location of myelinated motor neurons. motor neurons are present in the cerebral cortex of the brain or brain stem, and spinal cord. the motor neurons of the cerebral cortex are involved in voluntary actions in the body. they have projections that can communicate with the effect organs to show a response due to a stimulus. This type of conduction has important consequences: increased conduction velocity; reduced metabolic cost of conduction as the amount of energy needed in myelinated fibers to conduct the impulse is less; the conduction velocity of an axon can be linked to the diameter. myelinated axons are quite large in diameter, ranging from 1 13 µm.

Myelinated Neuron Diagram Motor neurons integrate signals from the brain to the muscles, glands, and organs that intend to carry out the required motor function. motor neurons allow us to move, talk, eat, swallow, and breathe; therefore, without these cells, we would be unable to complete many basic life functions. there are two types of motor neurons: lower motor. While the term “motor neuron” evokes the idea that there is only one type of neuron that conducts movement, this is far from the truth. in fact, within the classification of a “motor neuron,” there lies both upper and lower motor neurons, which are entirely different in terms of their origins, synapse points, pathways, neurotransmitters, and lesion characteristics. Different types of neurons include sensory, motor, and interneurons, as well as structurally based neurons, which include unipolar, multipolar, bipolar, and pseudo unipolar neurons. these cells coordinate bodily functions and movement so quickly, we don't even notice it happening. 9 sources. by kevin james cyr. Myelinated axons are ensheathed along their entire length. the axon caliber (diameter) in mammalian pns ranges from 0.1 μm to 20 μm, with unmyelinated axons being less than 2 μm and myelinated.
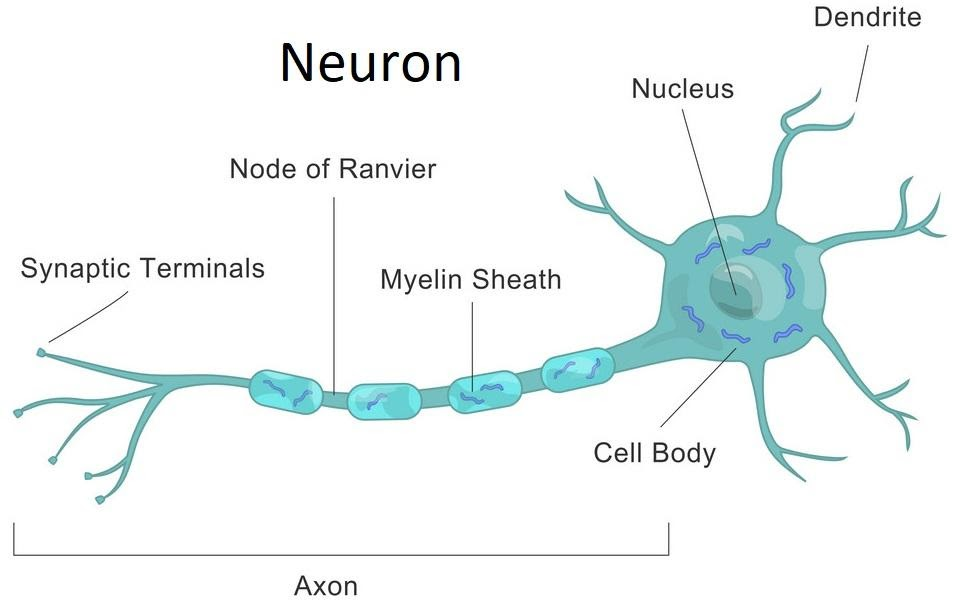
Draw A Labelled Diagram Of A Myelinated Neuron Different types of neurons include sensory, motor, and interneurons, as well as structurally based neurons, which include unipolar, multipolar, bipolar, and pseudo unipolar neurons. these cells coordinate bodily functions and movement so quickly, we don't even notice it happening. 9 sources. by kevin james cyr. Myelinated axons are ensheathed along their entire length. the axon caliber (diameter) in mammalian pns ranges from 0.1 μm to 20 μm, with unmyelinated axons being less than 2 μm and myelinated. Myelin is a fatty material that wraps around nerve cell projections. in this image, myelin can be seen on either end of the nerve fibers. the gaps in the middle of the fibers are called nodes, which help transmit electrical signals in neurons. desmazieres, et al. journal of neuroscience, 2014. in this illustration of a neuron, myelin is shown. Summary. myelin is a key evolutionary acquisition that underlay the development of the large, complex nervous systems of all hinged jaw vertebrates. by promoting rapid, efficient nerve conduction, myelination also made possible the development of the large body size of these vertebrates. in addition to increasing the speed of nerve conduction.

Motor Neuron Function Types And Structure Myelin is a fatty material that wraps around nerve cell projections. in this image, myelin can be seen on either end of the nerve fibers. the gaps in the middle of the fibers are called nodes, which help transmit electrical signals in neurons. desmazieres, et al. journal of neuroscience, 2014. in this illustration of a neuron, myelin is shown. Summary. myelin is a key evolutionary acquisition that underlay the development of the large, complex nervous systems of all hinged jaw vertebrates. by promoting rapid, efficient nerve conduction, myelination also made possible the development of the large body size of these vertebrates. in addition to increasing the speed of nerve conduction.

Comments are closed.