Neuron And Neurotransmitters Diagram
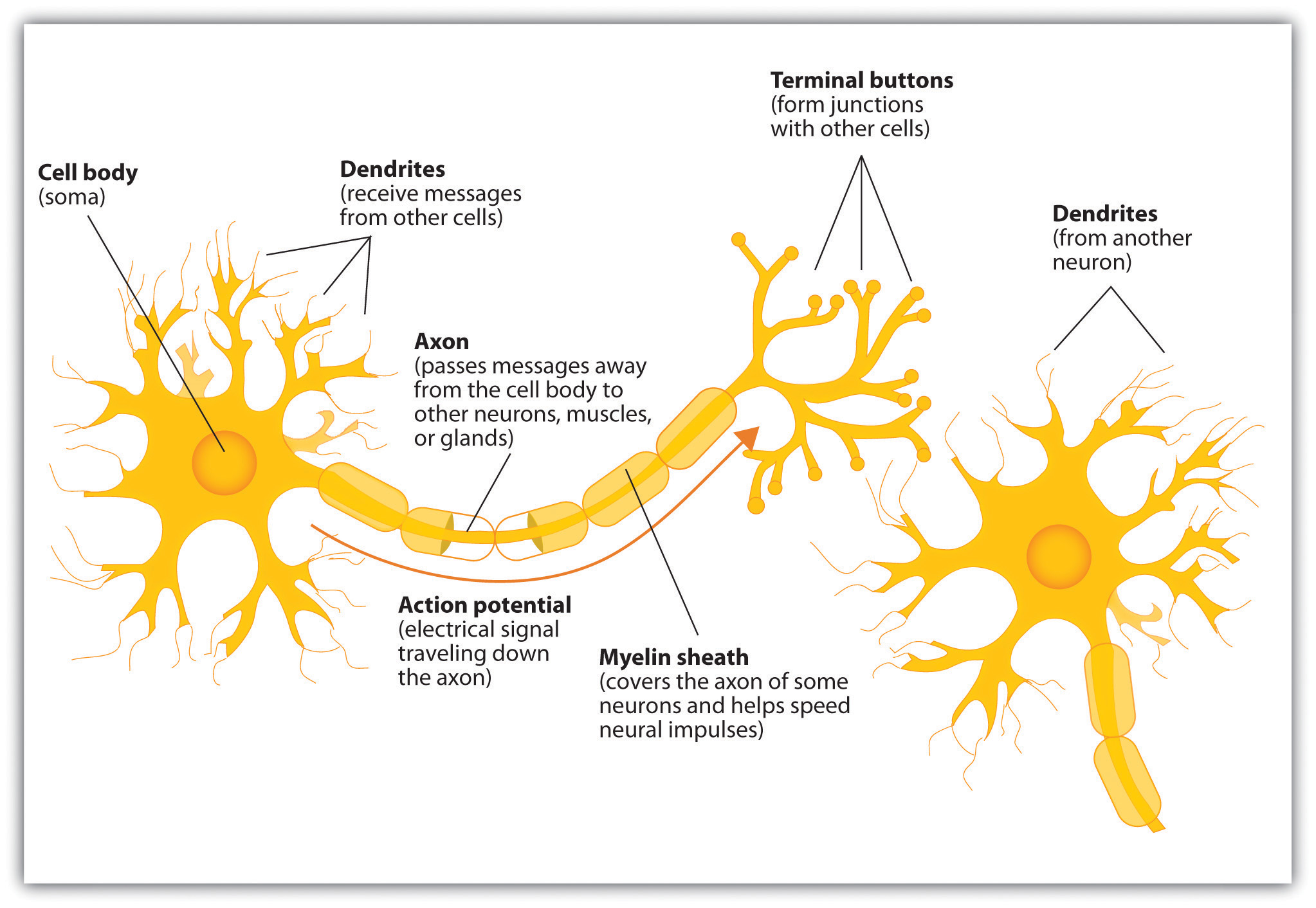
The Neuron Is The Building Block Of The Nervous System Ligand activated ion channels typically produce very quick physiological responses. current starts to flow (ions start to cross the membrane) within tens of microseconds of neurotransmitter binding, and the current stops as soon as the neurotransmitter is no longer bound to its receptors. The best known neurotransmitters responsible for such fast, but short lived excitatory action are acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine while gaba is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter. repeated synaptic activities can have long lasting effects on the receptor neuron, including structural changes such as the formation of new synapses, alterations in the dendritic tree, or growth of.
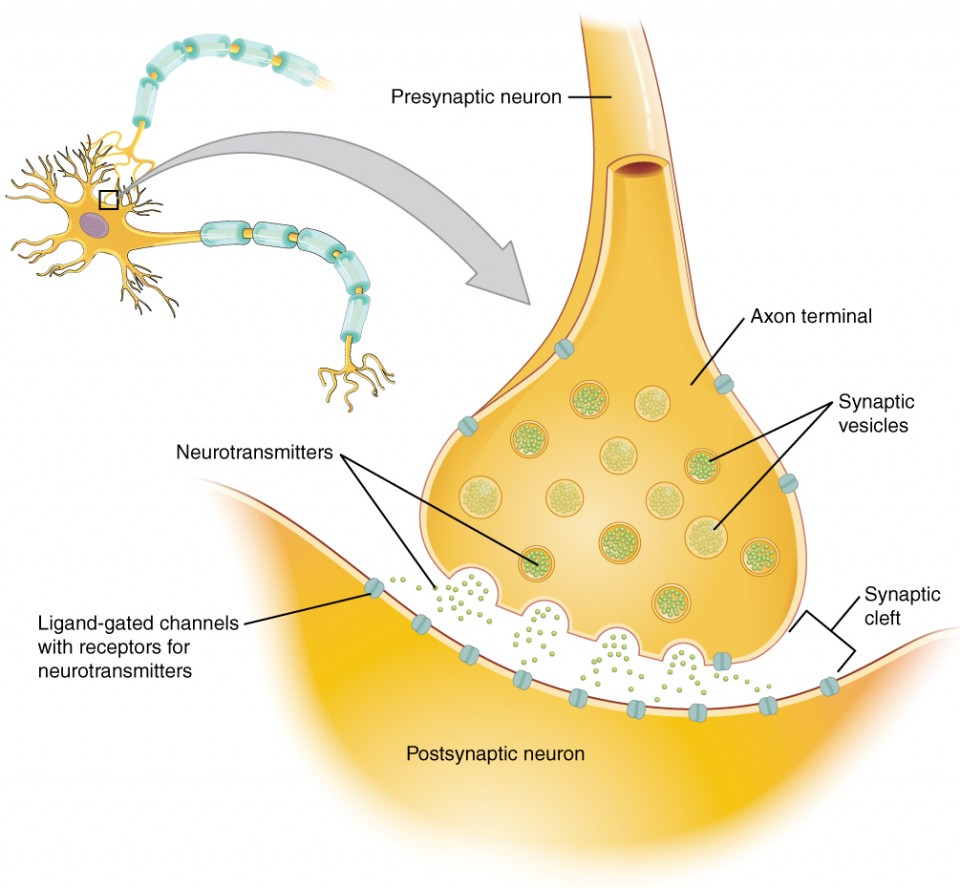
Communication Between Neurons Anatomy And Physiology I Like the heart, lungs, and stomach, the nervous system is made up of specialized cells. these include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ). neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which allow them to quickly transmit information over long distances. 1. excitatory neurotransmitters. these types have an excitatory stimulating effect on the neurons. if a neurotransmitter is excitatory, it will increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire action potential. examples of these types of neurotransmitters are epinephrine and norepinephrine. 2. A synapse is the site of communication between a neuron and another cell. there are two types of synapses: chemical synapses and electrical synapses. in a chemical synapse, a chemical signal— a neurotransmitter—is released from the neuron and it binds to a receptor on the other cell. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that your body can’t function without. their job is to carry chemical signals (“messages”) from one neuron (nerve cell) to the next target cell. the next target cell can be another nerve cell, a muscle cell or a gland. your body has a vast network of nerves (your nervous system) that send and.

Comments are closed.