Newton S Laws Of Motion Experiment рџ рџ ґрџ ґ Shorts Scienc

Easy Inertia Experiment 5 simple and fun experiments for newton’s laws of motion experiment 1: balloon rocket. for this experiment, you will need a long piece of string, a drinking straw, a balloon, and some tape. cut a piece of string about 5 feet long and tie one end to a chair or doorknob. thread the straw onto the other end of the string and tape it in place. Newton's laws of motion.

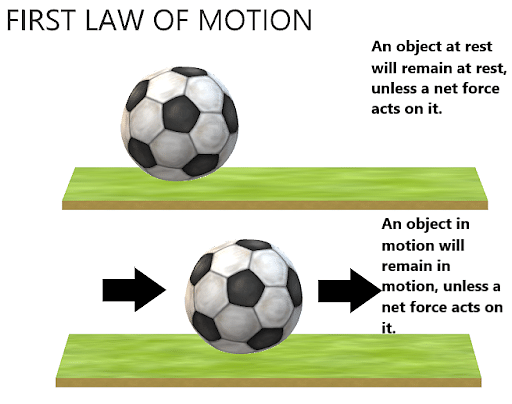
Newton S Laws Of Motion Newton’s first law activities 1. ball bounce experiment. one way to demonstrate newton’s first law is by observing a ball in motion. head to your garage and grab any type of ball you can find — a basketball, tennis ball, bouncy ball — the more varied the better. Newton’s three laws of motion were the first quantitative and predictive laws of mechanics. for over two hundred years, physicists were unable to produce any experiment that invalidated any one of these laws, and even today they function as close approximations for the vast majority of real world problems, which is why engineers still use them for calculations. Teach about newton's laws of motion. Newton's laws of motion | definition, examples, & history.
юааnewtonюабтащюааsюаб First Law юааof Motionюаб Definition Applications Teach about newton's laws of motion. Newton's laws of motion | definition, examples, & history. The rate of change of an object’s momentum equals the force acting upon it or the applied force equal’s an object’s mass times its acceleration. the two equations for newton’s second law are: f = m*a. f = Δp Δt. here, f is the applied force, m is mass, a is acceleration, p is momentum, and t is time. note that the second law tells us. The second law. newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. it states that when an external force acts on a body, it produces an acceleration (change in velocity) of the body in the direction of the force. this postulate is most commonly written as f = ma, where f (force.

Comments are closed.