Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease What Is Insulin Resistance Why Does It Matter Dr Rob Lustig
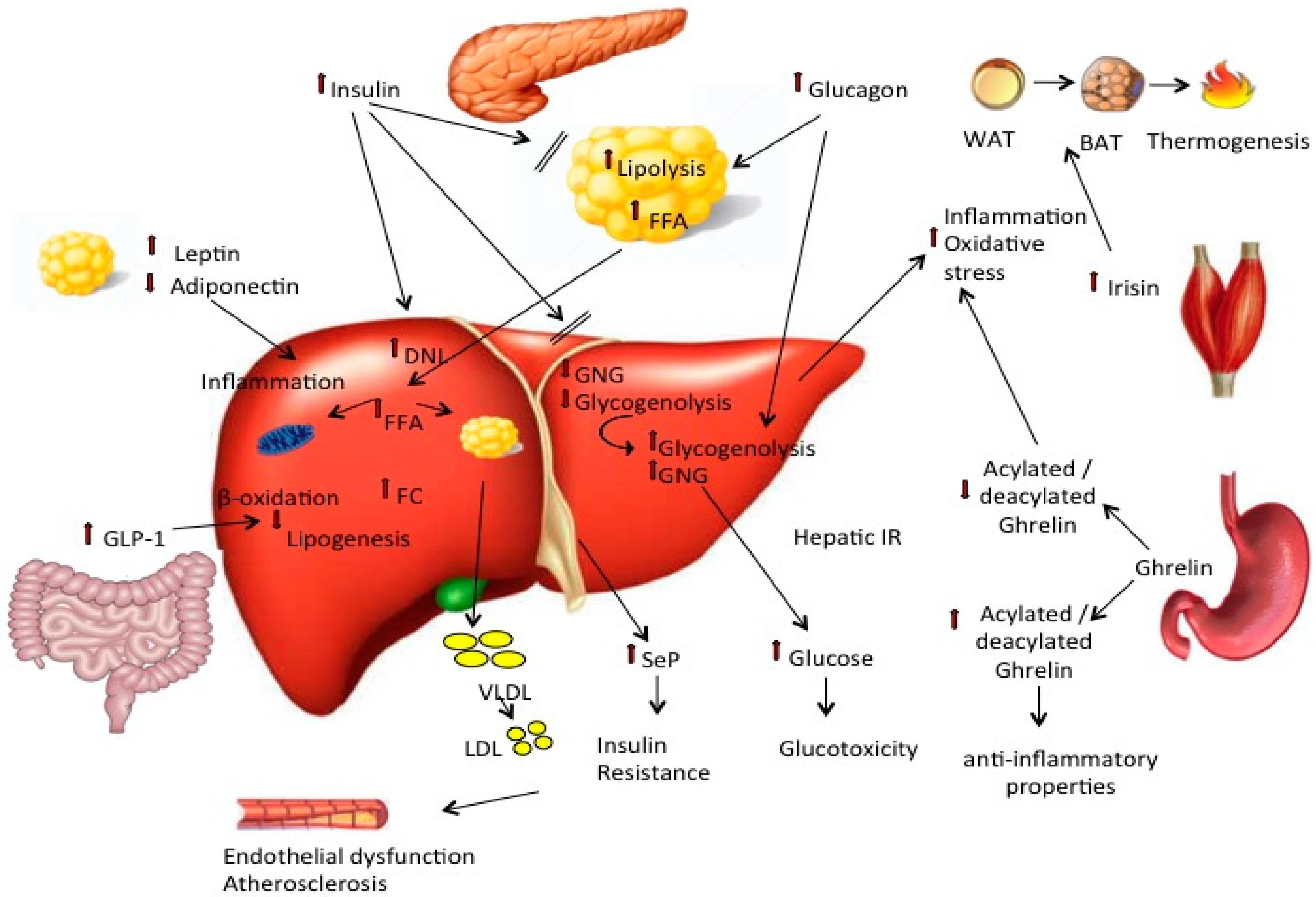
Ijms Free Full Text Pathophysiology Of Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) often coexist. obesity and metabolic syndrome are shared risk factors. insulin resistance may also promote storage of fat in your liver. Abstract. context: insulin resistance is an almost universal finding in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld). this review outlines the evidence linking insulin resistance and nafld, explores whether liver fat is a cause or consequence of insulin resistance, and reviews the current evidence for treatment of nafld.
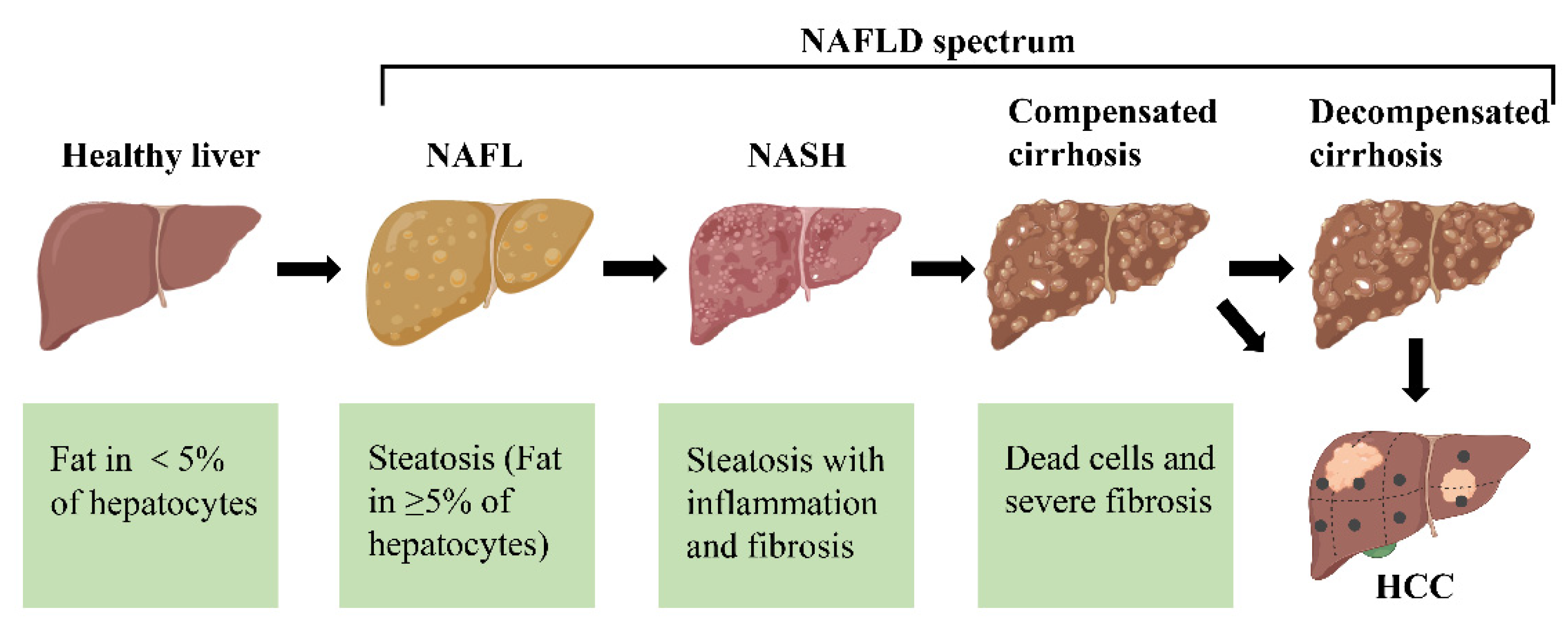
Ijms Free Full Text Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Nafld 1. introduction. nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nafld) is a major form of chronic liver disease that affects both adults and children worldwide [].it is one of the clinical consequences of obesity and can progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (nash), which is pathologically characterized by the presence of steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis in the liver parenchyma, which ultimately. 18:00 — there are three types of insulin resistance. dr. rob lustig explains the three types of insulin resistance he sees: when too much energy is forced into subcutaneous fat cells, when stress elevates cortisol, and when non alcoholic fatty liver disease occurs. the following is an the explanation of the latter. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, often called nafld, is a liver problem that affects people who drink little to no alcohol. in nafld, too much fat builds up in the liver. it is seen most often in people who are overweight or obese. nafld is becoming more common, especially in middle eastern and western nations as the number of people with. By recruiting immune cells to adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle, chemokines lead to acute inflammation and the development of insulin resistance, as well as fatty liver disease [48,49,50]. mcp 1, also known as ccl2, is up regulated in obese adipose tissue, secondary to macrophage infiltration [51,52]. by binding to the ccr2 receptor.

Comments are closed.