Normal Vital Signs You Need To Know In Nursing School Click Through To
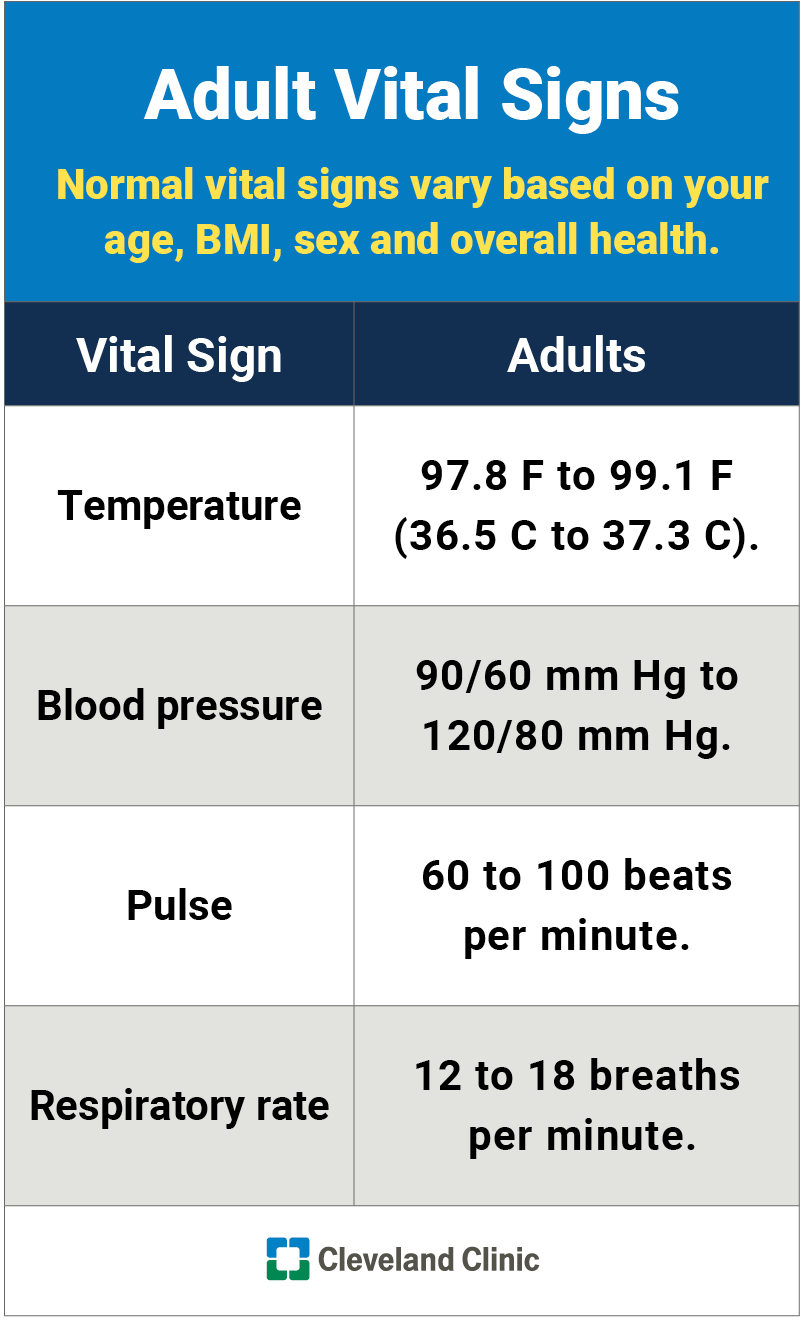
Vital Signs Vital signs are one of the most important tools to assess a patient’s baseline health and to detect changes in their condition. taking vital signs as well as correctly interpreting them and recognizing warning signs is a fundamental nursing skill. review the summary below and download the printable vital signs cheat sheet!. Journey.all my best, christin. cheat sheet is intended for educational purposes only. this is not medical advice and. 2. temperature (oral): 97.8°f 99°f. heart rate: 60 100 beats per minute. respiratory rate: 12 16 breaths per minute. blood pressure: less than 120mmhg systolic and less than 80mmhg diastolic. pulse oximetry: 95 100%.

Normal Vital Signs You Need To Know In Nursing School Click Through To The four main vital signs routinely monitored by medical professionals and health care providers include the following: body temperature. pulse rate. respiration rate (rate of breathing) blood pressure (blood pressure is not considered a vital sign, but is often measured along with the vital signs.) vital signs are useful in detecting or. Vital signs are typically obtained prior to performing a physical assessment. vital signs include temperature recorded in celsius or fahrenheit, pulse, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation using a pulse oximeter. see figure 1.8 [1] for an image of a nurse obtaining vital signs. obtaining vital signs may be delegated to. Note the rate, strength, and rhythm. grade the strength of the pulse with the following scale: 0: absent. 1 : weak. 2 : normal. 3 : bounding. count the heart rate (if regular) for 30 seconds and multiply by 2. if the heart rate is irregular count for 1 full minute. Normal vital signs: newborn. blood pressure (bp) 60 40 – 80 50 mmhg. respirations. 30 – 60 minute (diaphragmatic abdomen moves is normal) pulse. 120 – 140 beats minute (increases with crying) temperature. 97.8 – 99.1 degrees fahrenheit average 98.6 degrees fahrenheit.

Chapter 1 Nursing Assistant Chapter 1 Nursing Assistant In Long Term Note the rate, strength, and rhythm. grade the strength of the pulse with the following scale: 0: absent. 1 : weak. 2 : normal. 3 : bounding. count the heart rate (if regular) for 30 seconds and multiply by 2. if the heart rate is irregular count for 1 full minute. Normal vital signs: newborn. blood pressure (bp) 60 40 – 80 50 mmhg. respirations. 30 – 60 minute (diaphragmatic abdomen moves is normal) pulse. 120 – 140 beats minute (increases with crying) temperature. 97.8 – 99.1 degrees fahrenheit average 98.6 degrees fahrenheit. Measuring vital signs is a crucial component in taking care of a client’s health. vital signs help assess the general physical health of a person, provide clues to possible diseases, and help monitor the progress of the client’s health status. as a nurse, you will measure and interpret vital signs. figure 1: commonly measured vital signs. Vital signs are typically obtained prior to performing a physical assessment. vital signs include temperature recorded in celsius or fahrenheit, pulse, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation using a pulse oximeter. see figure 1.3.1 1.3. 1 [1] for an image of a nurse obtaining vital signs.

Comments are closed.