Not The An Murders Event Probability Nope

Ppt Basic Terms Of Probability Powerpoint Presentation Id 401623 Solution. there are 13 cards that are clubs, 12 face cards (j, q, k in each suit) and 3 face cards that are clubs. p(club or face card) = p(club) p(face card) − p(club and face card) = 13 52 12 52 − 3 52 = 22 52 = 11 26 ≈ 0.423. the probability that the card is a club or a face card is approximately 0.423 or 42.3%. Is nope's gordy attack based on a true story?.
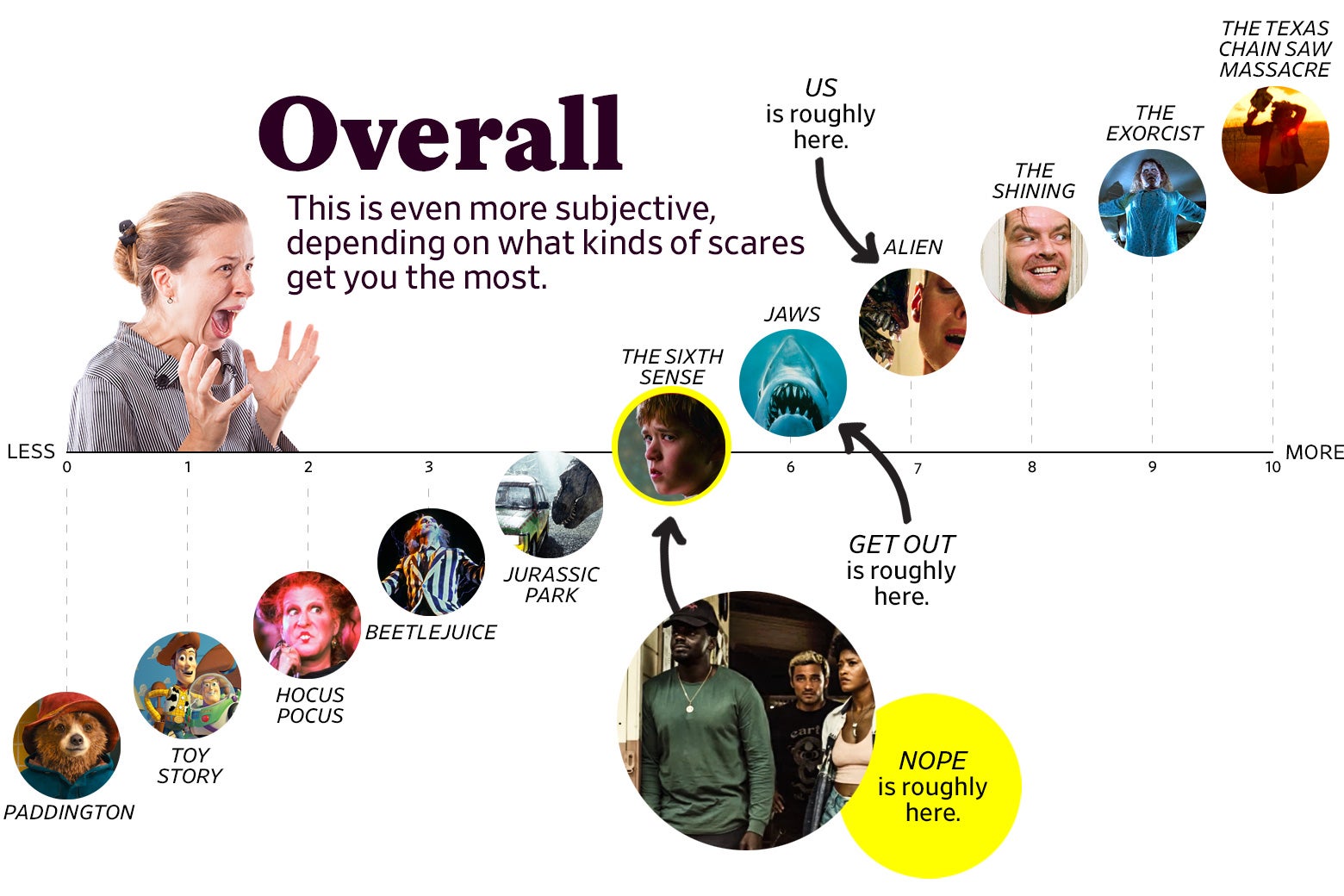
юааnopeюаб Movie How Scary Is Jordan Peeleтащs Latest Scarier Than Us And Get In contrast, my statistical analysis is a simple formula used to calculate the probability of an outcome of repetitive events each having a binomial probability. to do this, all you need to know is the probability of a single event (e.g. 1 2 for a coin toss), how many events there will be, and what the desired outcome will be. How do i solve this and is there a formula? according to a survey, 63 % of murders committed last year were cleared by arrest or exceptional means. fifty murders committed last year are randomly selected, and the number cleared by arrest or exceptional means is recorded. (a) find the probability that exactly 38 of the murders were cleared. The poisson distribution of the number of murders in a period of time is essentially a consequence of the probability model in which the events occur randomly in time. thus if we have 5 events in the month the probability that they all occur in the second period is $(3 4)^5$. Assuming the number of homicides is a poisson distributed random variable (often not too unreasonable for low counts over long time periods) the probability is 5.7%. small, but not totally improbable. to calculate this probability it is just 1 minus the cumulative distribution function for a poisson distribution with the given mean.

I M Totally Not A Murderer Nope Roblox Survive The Night Youtube The poisson distribution of the number of murders in a period of time is essentially a consequence of the probability model in which the events occur randomly in time. thus if we have 5 events in the month the probability that they all occur in the second period is $(3 4)^5$. Assuming the number of homicides is a poisson distributed random variable (often not too unreasonable for low counts over long time periods) the probability is 5.7%. small, but not totally improbable. to calculate this probability it is just 1 minus the cumulative distribution function for a poisson distribution with the given mean. The event "not e" is called the complement of e. in an experiment, an event must occur or its complement must occur (if not "heads" then "tails"; if not "hearts" then "spades", "diamonds" and "clubs"). the sum of the probability that an event will occur and the probability that it will not occur is 1. that is, therefore, the probability that an. Example 8.2.5. if a card is drawn from a deck, use the addition rule to find the probability of obtaining an ace or a heart. solution. let a be the event that the card is an ace, and h the event that it is a heart. since there are four aces, and thirteen hearts in the deck, p (a) = 4 52 and p (h) = 13 52.

Calculating Probability Of An Event Not Happening Youtube The event "not e" is called the complement of e. in an experiment, an event must occur or its complement must occur (if not "heads" then "tails"; if not "hearts" then "spades", "diamonds" and "clubs"). the sum of the probability that an event will occur and the probability that it will not occur is 1. that is, therefore, the probability that an. Example 8.2.5. if a card is drawn from a deck, use the addition rule to find the probability of obtaining an ace or a heart. solution. let a be the event that the card is an ace, and h the event that it is a heart. since there are four aces, and thirteen hearts in the deck, p (a) = 4 52 and p (h) = 13 52.

Comments are closed.