Nucleotides Dna Rna Guanine Cytosine Adenine Thymine
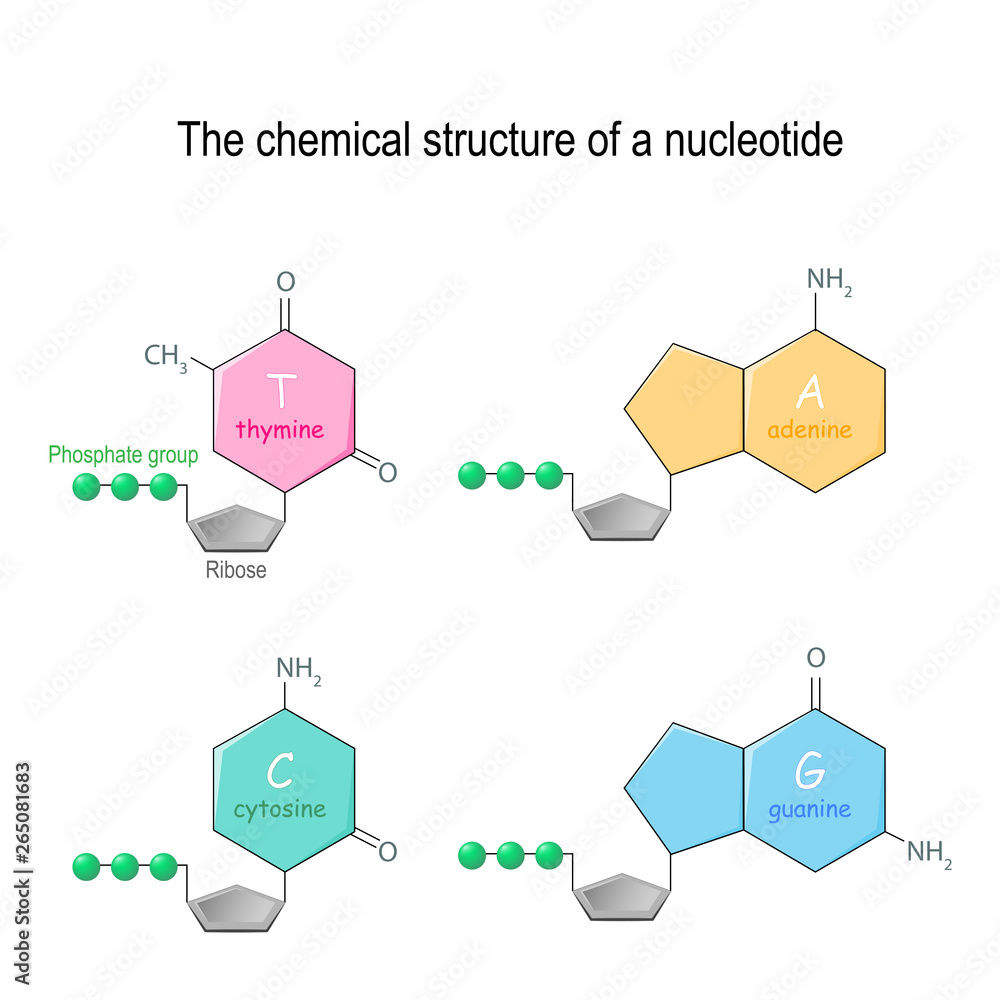
The Chemical Structure Of A Nucleotide Four Main Bases Found In Dna Five nucleobases— adenine (a), cytosine (c), guanine (g), thymine (t), and uracil (u)—are called primary or canonical. they function as the fundamental units of the genetic code, with the bases a, g, c, and t being found in dna while a, g, c, and u are found in rna. thymine and uracil are distinguished by merely the presence or absence of a. Figure 14.5.2.2 14.5.2. 2: the pyrimidine and purine nucleotides. apart from being the monomer units of dna and rna, the nucleotides and some of their derivatives have other functions as well. adenosine diphosphate (adp) and adenosine triphosphate (atp), shown in figure 14.5.2.3 14.5.2. 3, have a role in cell metabolism.

Nitrogenous Bases In Dna Nucleotides containing ribose are called ribonucleotides and are found in rna. both dna and rna contain nucleotides with adenine, guanine, and cytosine, but with very minor exceptions, rna contains uracil nucleotides, whereas dna contains thymine nucleotides. when a base is attached to a sugar, the product, a nucleoside, gains a new name. Nucleic acids, macromolecules made out of units called nucleotides, come in two naturally occurring varieties: deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ). dna is the genetic material found in living organisms, all the way from single celled bacteria to multicellular mammals like you and me. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base . there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five carbon sugar ( ribose or deoxyribose ), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. the four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in rna, uracil is used in place of thymine.
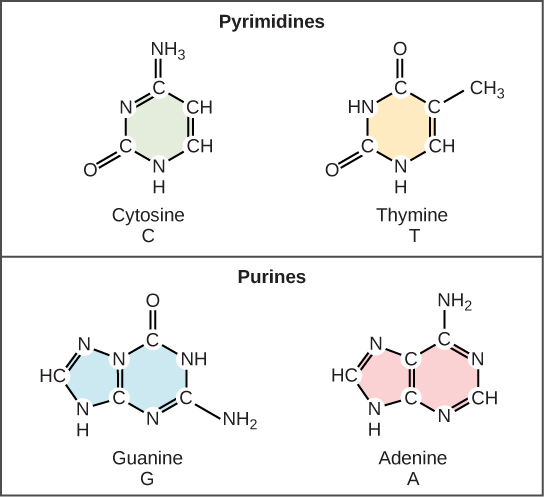
9 1 The Structure Of Dna вђ Concepts Of Biology вђ 1st Canadian Edition The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base . there are four types of nitrogenous bases in dna. adenine (a) and guanine (g) are double ringed purines, and cytosine (c) and thymine (t) are smaller, single ringed pyrimidines. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five carbon sugar ( ribose or deoxyribose ), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. the four nucleobases in dna are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in rna, uracil is used in place of thymine. Adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine are the four nucleotides found in dna. this image is linked to the following scitable pages: dna is a structure that encodes biological information. Rna nucleotides also contain one of four possible bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil (u) rather than thymine. adenine and guanine are classified as purines. the primary structure of a purine is two carbon nitrogen rings. cytosine, thymine, and uracil are classified as pyrimidines which have a single carbon nitrogen ring as their.

Comments are closed.