Nutrients Free Full Text Benefits And Risks Of Moderate Alcohol
Nutrients Free Full Text Benefits And Risks Of Moderate Alcohol Alcohol has a hormetic physiological behavior that results in either increased or decreased cardiovascular risk depending on the amount consumed, drinking frequency, pattern of consumption, and the outcomes under study or even the type of alcoholic beverage consumed. however, the vast majority of studies elucidating the role of alcohol in cardiovascular and in the global burden of disease. Background: for the last 25 years, the debate on the benefit–risk balance of moderate alcohol consumption has been ongoing. this study explored the relationships between the pattern of alcohol consumption and subjective quality of life in healthy adults. material and methods: participants were 247 healthy adults aged 25–45 years, with a moderate alcohol consumption, classified in three.
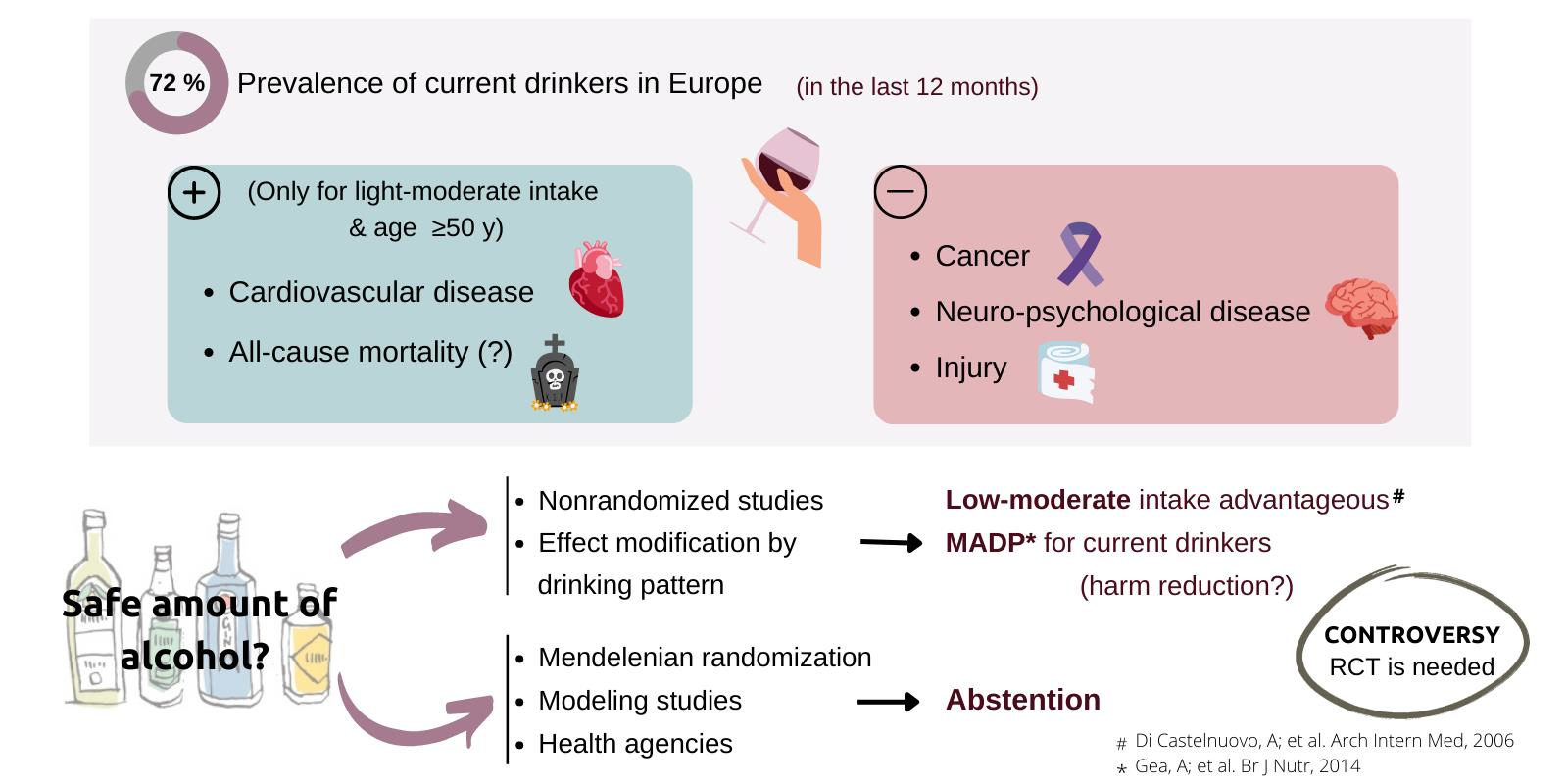
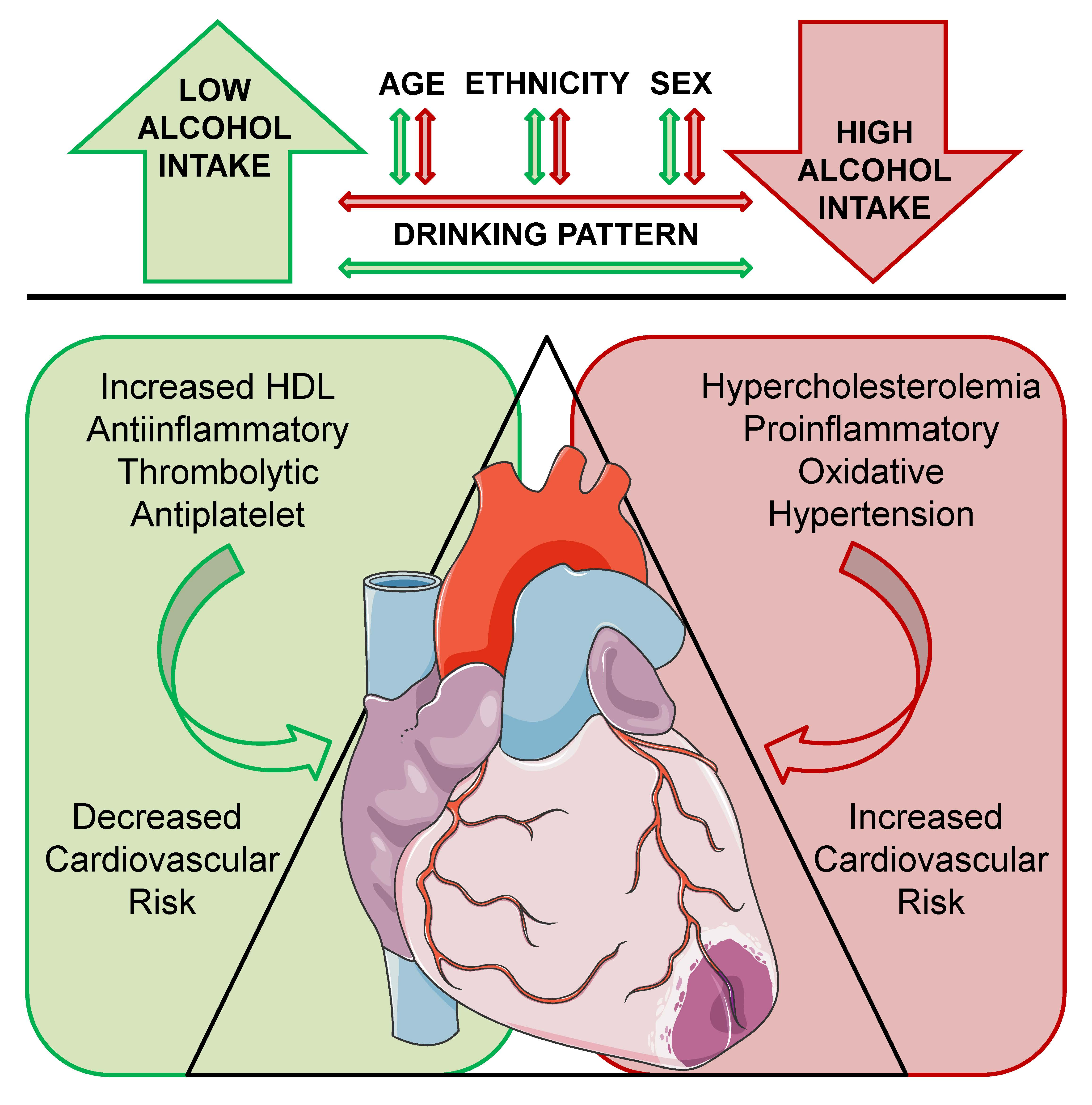
Nutrients Free Full Text Alcohol Drinking Pattern And Chronic Disease We examined whether the often reported protective association of alcohol with cardiovascular disease (cvd) risk could arise from confounding. our sample comprised 908 men (56–67 years), free of prevalent cvd. participants were categorized into 6 groups: never drinkers, former drinkers, and very light (1–4 drinks in past 14 days), light (5–14 drinks), moderate (15–28 drinks), and at. 1. introduction. cardiovascular disease (cvd) is the leading cause of mortality in europe (47% of total mortality) and one of the main causes of death worldwide (31% of all worldwide deaths) [. 1. Alcohol and weight gain. one serving of alcohol on average contains 100 150 calories, so even a moderate amount of 3 drinks a day can contribute 300 calories. mixed drinks that add juice, tonic, or syrups will further drive up calories, increasing the risk of weight gain over time. In contrast to excessive alcohol intake, moderate alcohol intake has been shown to provide health benefits. the data is most convincing for preventing heart disease in middle aged and older people. a review of twenty nine studies concluded that moderate alcohol intake reduces the risk of coronary heart disease by about 30 percent in comparison.

Comments are closed.