Offshore Wind Explained Intro
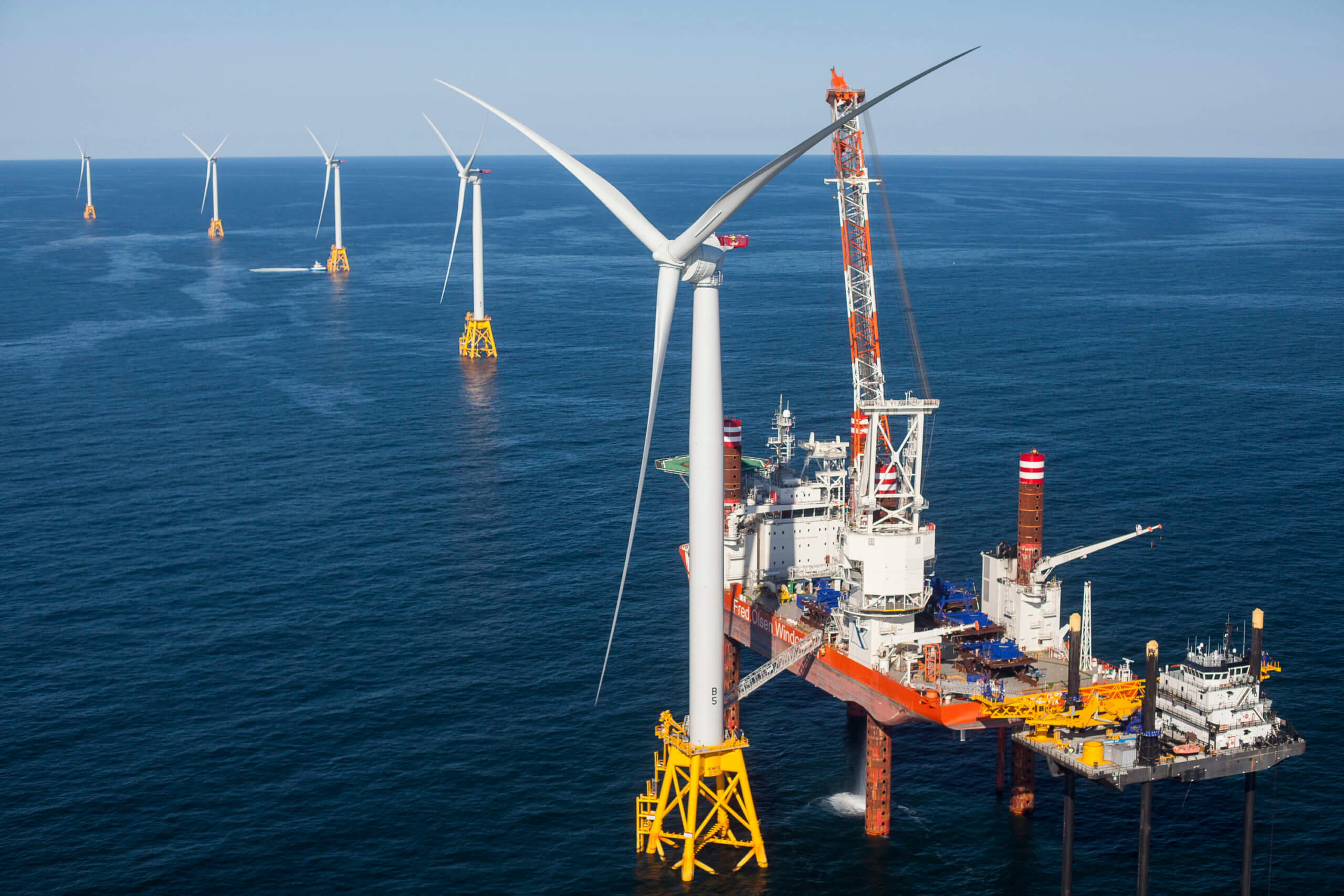

Emerging Offshore Wind Industry Provides Careers Of The Future Acp Offshore wind explained | a new video series by dnv digital solutions welcome to the offshore wind explained video series, brought to you by dnv digital solu. Offshore wind farms are hitting the headlines across the globe for their sheer scale and as countries increasingly turn to them to decrease their dependency on energy from russia as well as speed up their energy transition. global capacity of large scale wind farms is expected to increase 10 fold, from 34 gw in 2020 to 330 gw in 2030, and.

California Must Consider Economic Needs In Pursuit Of Offshore Wind What is offshore wind power? offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the energy taken from the force of the winds out at sea, transformed into electricity and supplied into the electricity network onshore. if you look out to the north sea from the uk’s east coast, you’ll see line upon line of these immense white wind turbines. Hornsea offshore wind farm. hornsea 2, located about 55 mi off the coast of yorkshire in the north sea, is the world’s largest operating offshore wind farm as of august, 2023. this powerful wind farm has 165 8 mw wind turbines—all together, that’s over 1,300 mw of renewable energy. fully operational as of august 31, 2022, hornsea 2 has. Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. there are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of capacity installed. [ 1] offshore wind farms are also less controversial [ 2] than those on land, as. 3. offshore wind is right on time: in many areas where offshore wind projects are planned, offshore wind speeds are highest during the afternoon and evening, when consumer demand is at its peak. most land based wind resources are stronger at night when electricity demands are lower. 2.

The Eu Gives 290 Million Nok To Test Floating Offshore Wind In Rogaland Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. there are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of capacity installed. [ 1] offshore wind farms are also less controversial [ 2] than those on land, as. 3. offshore wind is right on time: in many areas where offshore wind projects are planned, offshore wind speeds are highest during the afternoon and evening, when consumer demand is at its peak. most land based wind resources are stronger at night when electricity demands are lower. 2. Sending the power ashore. each wind turbine sends its power through cables down the tower and under the seabed to an offshore substation. here the energy is stepped up to a higher voltage ready to send ashore via high voltage cables. higher voltage means less energy is lost in transmission. on land, another substation adjusts the voltage again. An onshore wind farm’s construction and operation creates significantly less emissions than other energy sources, while the sites they’re placed on can still be farmed. cost effective. it’s one of the least expensive forms of renewable energy (along with solar pv) and significantly less expensive than offshore wind power.

Sbm Offshore Enters Nova Scotia Floating Offshore Wind Partnership Sending the power ashore. each wind turbine sends its power through cables down the tower and under the seabed to an offshore substation. here the energy is stepped up to a higher voltage ready to send ashore via high voltage cables. higher voltage means less energy is lost in transmission. on land, another substation adjusts the voltage again. An onshore wind farm’s construction and operation creates significantly less emissions than other energy sources, while the sites they’re placed on can still be farmed. cost effective. it’s one of the least expensive forms of renewable energy (along with solar pv) and significantly less expensive than offshore wind power.
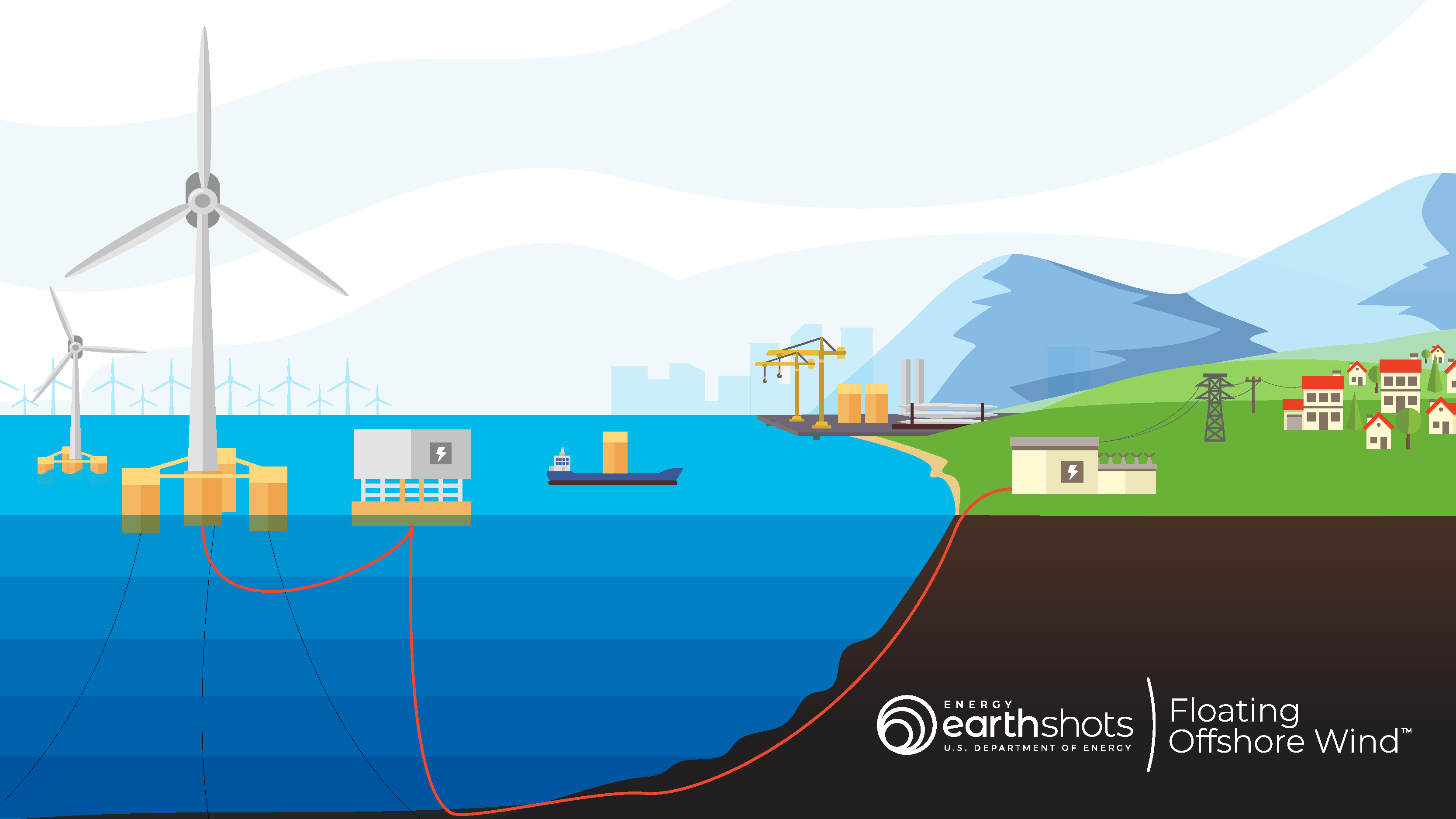
Floating Offshore Wind Shot Department Of Energy

Comments are closed.