Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Chart

Cpsc Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Table 2.4 subordinate groups. we will go through several examples for more details about the naming rules. 1. the parent structure is the 6 carbon carboxylic acid with a double bond, so the last name comes from “hexene”. to add the suffix, the last letter “e” will be dropped, so the parent name is “hexeneoicacid”. Iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry. in chemical nomenclature, the iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended [ 1][ 2] by the international union of pure and applied chemistry (iupac). it is published in the nomenclature of organic chemistry (informally called the blue book ).
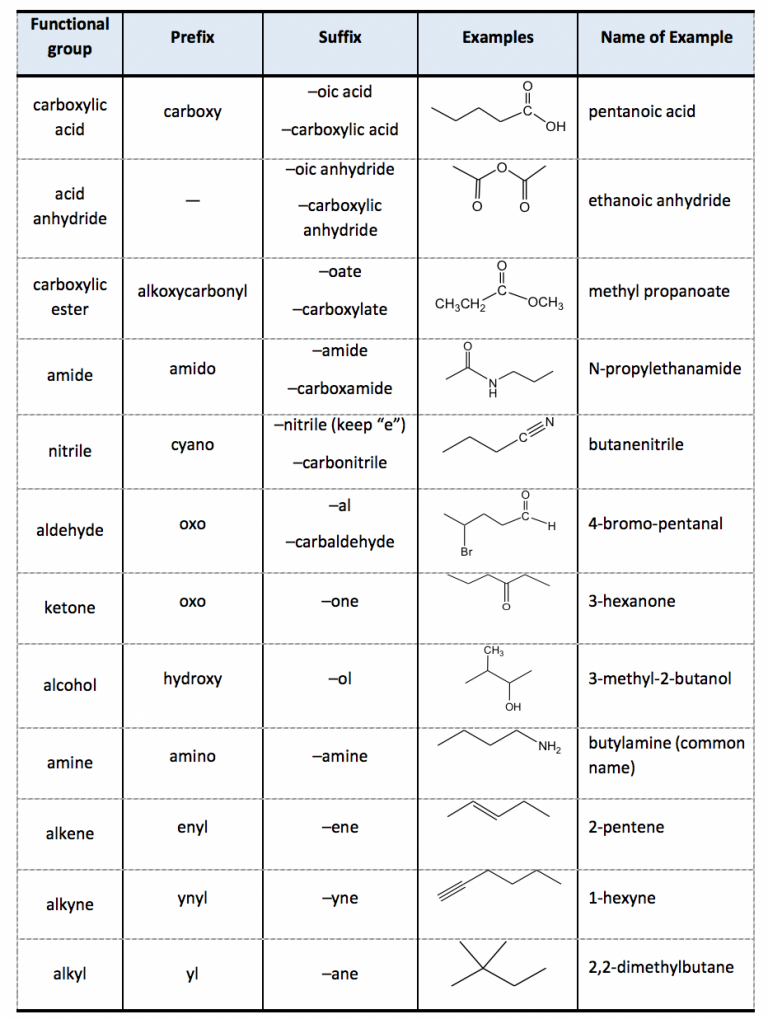
2 4 Iupac Naming Of Organic Compounds With Functional Groups вђ Organic Principles of chemical nomenclature.4 comprehensive detail can be found in nomenclature of organic chemistry, colloquially known as the blue book,5 and in the related publications for inorganic compounds (the red book),6 and polymers (the purple book).7 it should be noted that many compounds may have non systematic. The iupac system of nomenclature is a universally recognized method for naming organic chemical compounds. the goal of the system is to provide each organic compound with a unique and unambiguous name based on its chemical formula and structure. the name of any organic compound consists of three essential parts: the root word, prefix, and. For nomenclature purposes we consider all compounds containing carbon as the principal element to be organic compounds as qualified above (see p 10). oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen are the three elements usually associated with carbon to form the system of functional or characteristic groups. other elements, among them the halogens and sulfur. Compounds like methane, ch 4, and ethane, ch 3 ch 3, are members of a family of compounds called alkanes. if you remove a hydrogen atom from one of these you get an alkyl group. for example: a methyl group is ch 3. an ethyl group is ch 3 ch 2. these groups must, of course, always be attached to something else.

Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Organic Chemistry Teaching Chemistry For nomenclature purposes we consider all compounds containing carbon as the principal element to be organic compounds as qualified above (see p 10). oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen are the three elements usually associated with carbon to form the system of functional or characteristic groups. other elements, among them the halogens and sulfur. Compounds like methane, ch 4, and ethane, ch 3 ch 3, are members of a family of compounds called alkanes. if you remove a hydrogen atom from one of these you get an alkyl group. for example: a methyl group is ch 3. an ethyl group is ch 3 ch 2. these groups must, of course, always be attached to something else. Simply put, aliphatic compounds are compounds that do not incorporate any aromatic rings in their molecular structure. the following table lists the iupac names assigned to simple continuous chain alkanes from c 1 to c 10. a common "ane" suffix identifies these compounds as alkanes. longer chain alkanes are well known, and their names may be. For naming organic compounds some have had limit scope or become embedded in common us age and some have persisted over time the international union of pure and applied chemistry (i.u.p.a.c.) periodically reviews naming practice, attempting to standardise nomenclature. the following guidelines for organic nomenclature are based on the def.

Gcse Chemistry Chemistry Worksheets Organic Chemistry Counting Atoms Simply put, aliphatic compounds are compounds that do not incorporate any aromatic rings in their molecular structure. the following table lists the iupac names assigned to simple continuous chain alkanes from c 1 to c 10. a common "ane" suffix identifies these compounds as alkanes. longer chain alkanes are well known, and their names may be. For naming organic compounds some have had limit scope or become embedded in common us age and some have persisted over time the international union of pure and applied chemistry (i.u.p.a.c.) periodically reviews naming practice, attempting to standardise nomenclature. the following guidelines for organic nomenclature are based on the def.

Comments are closed.