Organic Chemistry Reactions Summary

Organic Reactions Summary Sheet 6.1: kinds of organic reactions. addition reactions increase the number of sigma bonds in a molecule. elimination reactions reduce the number of sigma bonds in a molecule. substitution reactions incorporate replacement of an atom or group with another. rearrangement reactions cause a molecule to be converted to a constitutional isomer without. Figure 27.1.3 27.1. 3: elimination reactions.these are the reverse of addiion reactions. this reaction results in the forming of a new c c double bond (π bond) and breaking two single bonds to carbon (in these cases, one of them is h and the other is a halide such as cl or br). we are also forming a new bond between h and the o.

Solution Organic Chemistry Reaction Summary Sheet Studypool This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into common reactions taught in the first semester of a typical college course of organic. The organic chemistry reaction and mechanism guide will help you understand more than 185 of the most common reactions encountered in undergraduate organic chemistry. the guide covers all the necessary reactions from the beginning of org 1 (structure and bonding) to the end of org 2 (amino acids) and everything in between (stereochemistry. 6.1 kinds of organic reactions; 6.2 how organic reactions occur: mechanisms; 6.3 polar reactions; 6.4 an example of a polar reaction: addition of hbr to ethylene; 6.5 using curved arrows in polar reaction mechanisms; 6.6 radical reactions; 6.7 describing a reaction: equilibria, rates, and energy changes; 6.8 describing a reaction: bond. Handout: organic chemistry reactions reactions organized by compound families alkanes 1. combustion 2. halogenation alkenes and alkynes 1. additions: hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, hydration 2. polymerization aromatic compounds substitutions: nitration, halogenation, sulfonation alcohols 1. elimination: dehydration 2.
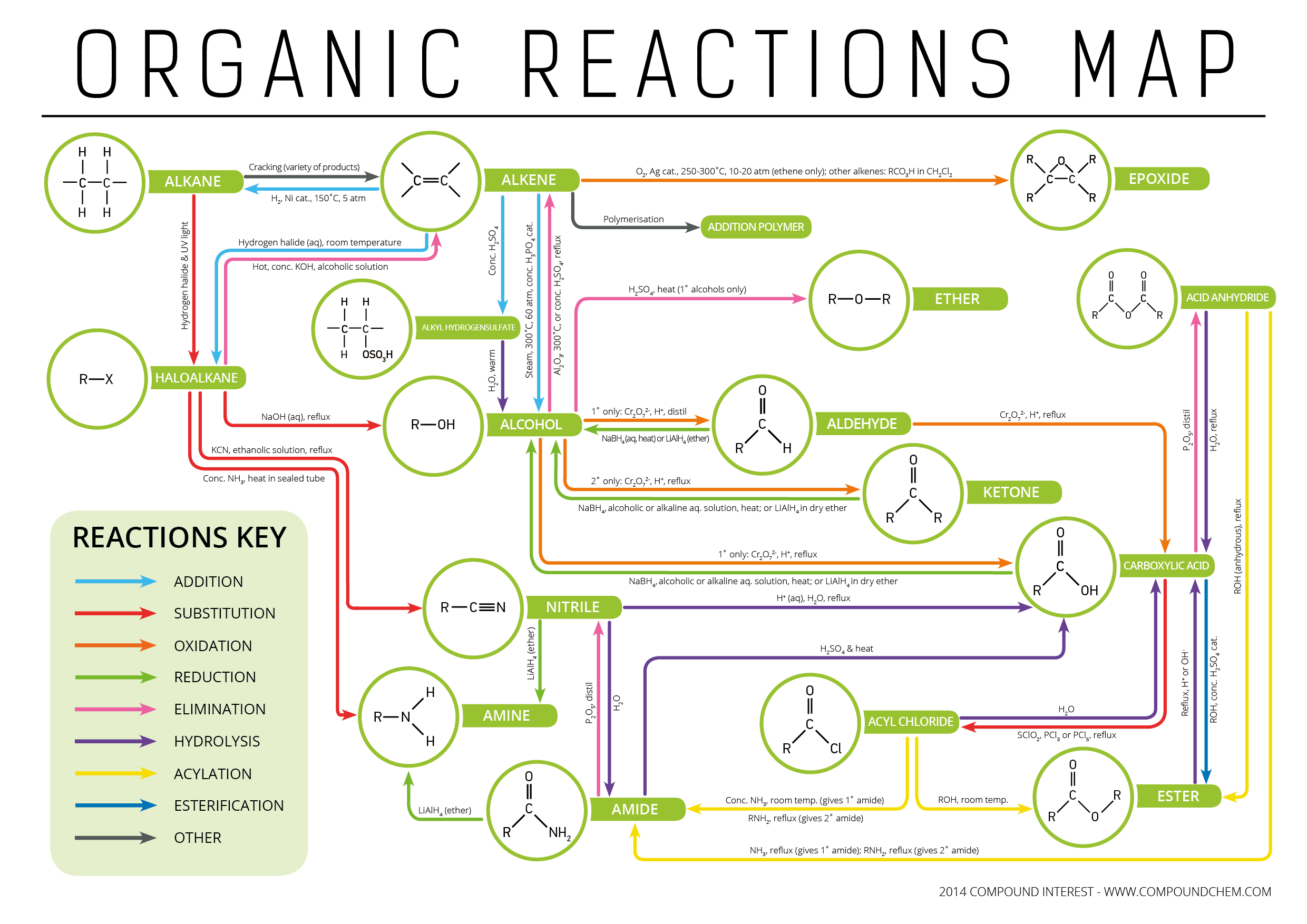
Types Of Organic Reactions Functional Groups Interconversion 6.1 kinds of organic reactions; 6.2 how organic reactions occur: mechanisms; 6.3 polar reactions; 6.4 an example of a polar reaction: addition of hbr to ethylene; 6.5 using curved arrows in polar reaction mechanisms; 6.6 radical reactions; 6.7 describing a reaction: equilibria, rates, and energy changes; 6.8 describing a reaction: bond. Handout: organic chemistry reactions reactions organized by compound families alkanes 1. combustion 2. halogenation alkenes and alkynes 1. additions: hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, hydration 2. polymerization aromatic compounds substitutions: nitration, halogenation, sulfonation alcohols 1. elimination: dehydration 2. Summary of reactions alkenes and alkynes electrophilic addition alcohols – acid base, elimination, oxidation amines – acid base, substitution alkyl halides – nucleophilic substitution and elimination a b a b a b 2 ab ab oh oh [o] oh oo ab h2 pd c cl2, br2 hcl, hbr, hi h2o h (dil h2so4) alkenes only = h = hot, conc. h2so4 [o. Organic chemistry has a strong tradition of naming a specific reaction to its inventor or inventors and a long list of so called named reactions exists, conservatively estimated at 1000. a very old named reaction is the claisen rearrangement (1912) and a recent named reaction is the bingel reaction (1993).

Organic Chemistry Summary Of Reactions Learning Made Simple Summary of reactions alkenes and alkynes electrophilic addition alcohols – acid base, elimination, oxidation amines – acid base, substitution alkyl halides – nucleophilic substitution and elimination a b a b a b 2 ab ab oh oh [o] oh oo ab h2 pd c cl2, br2 hcl, hbr, hi h2o h (dil h2so4) alkenes only = h = hot, conc. h2so4 [o. Organic chemistry has a strong tradition of naming a specific reaction to its inventor or inventors and a long list of so called named reactions exists, conservatively estimated at 1000. a very old named reaction is the claisen rearrangement (1912) and a recent named reaction is the bingel reaction (1993).

Comments are closed.