Overview Metabolism
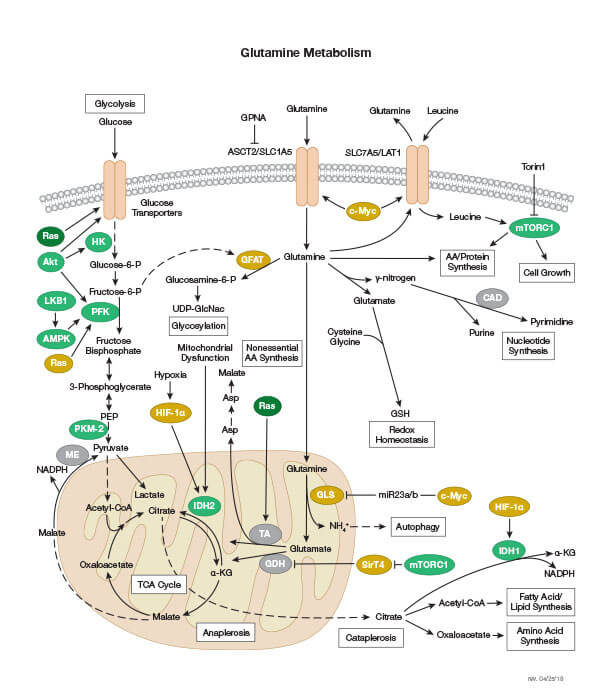
Metabolism Of Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids Nucleotides And Vitamins Metabolism. your metabolism constantly provides your body with energy for essential body functions like breathing and digestion. your body needs a minimum number of calories (the basal metabolic rate or bmr) to sustain these functions. factors like age, sex, muscle mass and physical activity affect metabolism or bmr. Overview of metabolism cells are constantly carrying out thousands of chemical reactions needed to keep the cell, and your body as a whole, alive and healthy. these chemical reactions are often linked together in chains, or pathways.

Pin On Nursing School Metabolism, the sum of chemical reactions that take place in living cells, providing energy for life processes and the synthesis of cellular material. living organisms are unique in that they extract energy from their environments via hundreds of coordinated, multistep, enzyme mediated reactions. Metabolism ( m ə ˈ t æ b ə l ɪ z ə m , from greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of life sustaining chemical reactions in organisms.the three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the. An overview of metabolic pathways catabolism. biological cells have a daunting task. they must carry out 1000s of different chemical reactions required to carry out cell function. these reactions can include opposing goals such as energy production and energy storage, macromolecule degradation and synthesis, and breakdown and synthesis of. Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body required to sustain life. these chemical processes involve energy and the breakdown and buildup of molecules and are regulated by hormones. your metabolism can be impacted by age, sex, diet, exercise, sleep, and injury or disease. while some lifestyle factors can affect your metabolism.
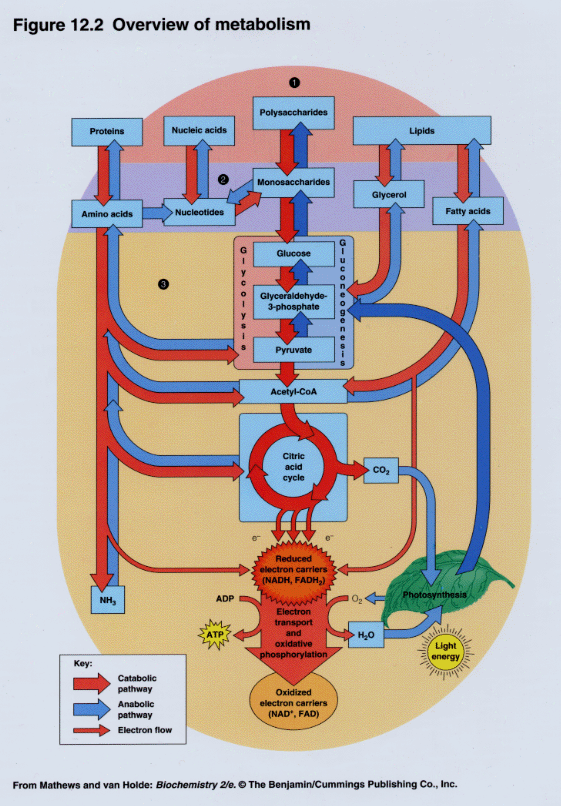
Overview Of Metabolism An overview of metabolic pathways catabolism. biological cells have a daunting task. they must carry out 1000s of different chemical reactions required to carry out cell function. these reactions can include opposing goals such as energy production and energy storage, macromolecule degradation and synthesis, and breakdown and synthesis of. Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in the body required to sustain life. these chemical processes involve energy and the breakdown and buildup of molecules and are regulated by hormones. your metabolism can be impacted by age, sex, diet, exercise, sleep, and injury or disease. while some lifestyle factors can affect your metabolism. What is the purpose of metabolism? learn about the two major divisions in metabolism: anabolism (building up) and catabolism (breaking down). by jasmine ran. Anabolism is the building of complex molecules from numerous simple ones. think of protein synthesis. catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into numerous simple ones. think the break down of glucose. this was such a good overview of metabolism. how is the digestion of food compared to metabolism.
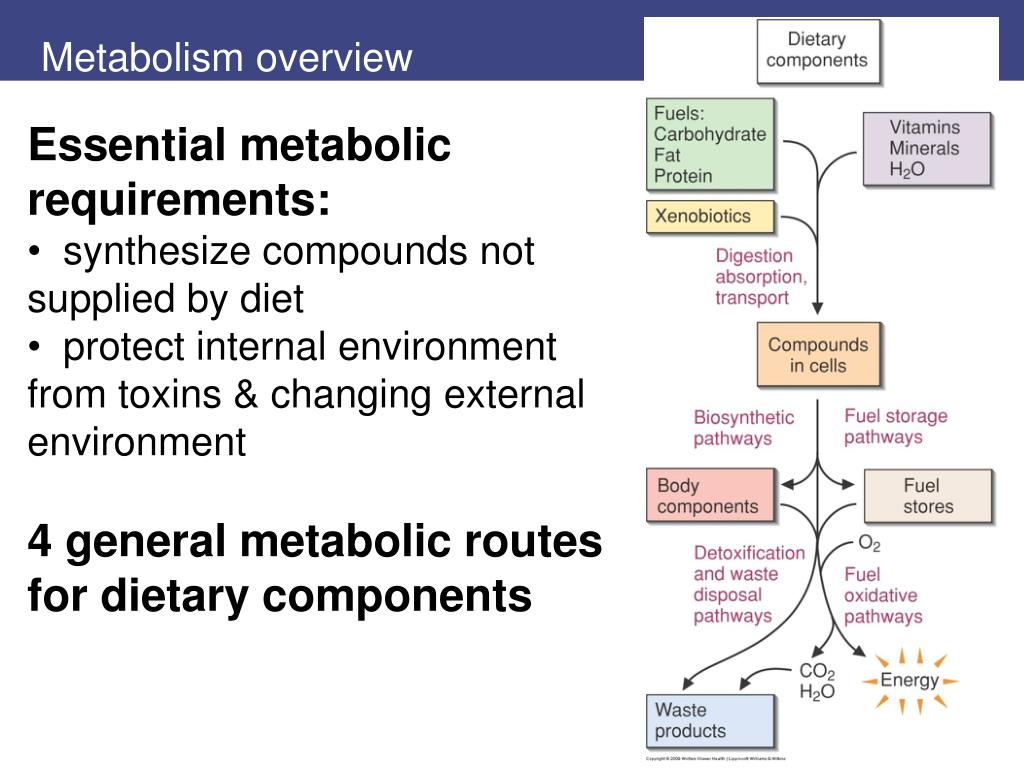
Ppt Section 1 Overview Metabolism Powerpoint Presentation Free What is the purpose of metabolism? learn about the two major divisions in metabolism: anabolism (building up) and catabolism (breaking down). by jasmine ran. Anabolism is the building of complex molecules from numerous simple ones. think of protein synthesis. catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into numerous simple ones. think the break down of glucose. this was such a good overview of metabolism. how is the digestion of food compared to metabolism.

Comments are closed.