Overview Of Metabolic Reactions Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Mcat Biochemistry Review Summary Gold Standard Mcat Prep Metabolic processes are constantly taking place in the body. metabolism is the sum of all of the chemical reactions that are involved in catabolism and anabolism. the reactions governing the breakdown of food to obtain energy are called catabolic reactions. conversely, anabolic reactions use the energy produced by catabolic reactions to. By the end of this section, you will be able to: metabolic processes are constantly taking place in the body. metabolism is the sum of all of the chemical reactions that are involved in catabolism and anabolism. the reactions governing the breakdown of food to obtain energy are called catabolic reactions.
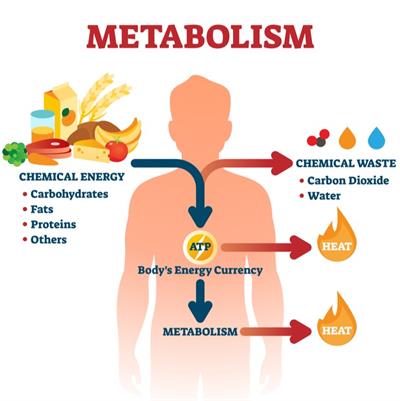
Metabolism Lesson Science Cbse Class 10 The chemical reactions underlying metabolism involve the transfer of electrons from one compound to another by processes catalyzed by enzymes. the electrons in these reactions commonly come from hydrogen atoms, which consist of an electron and a proton. Metabolic processes are constantly taking place in the body. metabolism is the sum of all of the chemical reactions that are involved in catabolism and anabolism. the reactions governing the breakdown of food to obtain energy are called catabolic reactions. conversely, anabolic reactions use the energy produced by catabolic reactions to. The libretexts libraries are powered by nice cxone expert and are supported by the department of education open textbook pilot project, the uc davis office of the provost, the uc davis library, the california state university affordable learning solutions program, and merlot. we also acknowledge previous national science foundation support. 24.1 overview of metabolic reactions . metabolism is the sum of all catabolic (break down) and anabolic (synthesis) reactions in the body. the metabolic rate measures the amount of energy used to maintain life. an organism must ingest a sufficient amount of food to maintain its metabolic rate if the organism is to stay alive for very long.

Přehled Metabolických Reakcí Anatomie A Fyziologie Ii Société The libretexts libraries are powered by nice cxone expert and are supported by the department of education open textbook pilot project, the uc davis office of the provost, the uc davis library, the california state university affordable learning solutions program, and merlot. we also acknowledge previous national science foundation support. 24.1 overview of metabolic reactions . metabolism is the sum of all catabolic (break down) and anabolic (synthesis) reactions in the body. the metabolic rate measures the amount of energy used to maintain life. an organism must ingest a sufficient amount of food to maintain its metabolic rate if the organism is to stay alive for very long. Human anatomy and physiology ii – theory (bio 1300) lecture notes. 100% (6) 4. the digestive system lab notes. 24. overview of metabolic reactions i. background. The rate of this reaction is controlled by negative feedback and the amount of atp available. if atp levels increase, the rate of this reaction decreases. if atp is in short supply, the rate increases. step 2. citrate loses one water molecule and gains another as citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate.

24 1 Overview Of Metabolic Reactions Anatomy And Physiology Openstax Human anatomy and physiology ii – theory (bio 1300) lecture notes. 100% (6) 4. the digestive system lab notes. 24. overview of metabolic reactions i. background. The rate of this reaction is controlled by negative feedback and the amount of atp available. if atp levels increase, the rate of this reaction decreases. if atp is in short supply, the rate increases. step 2. citrate loses one water molecule and gains another as citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate.
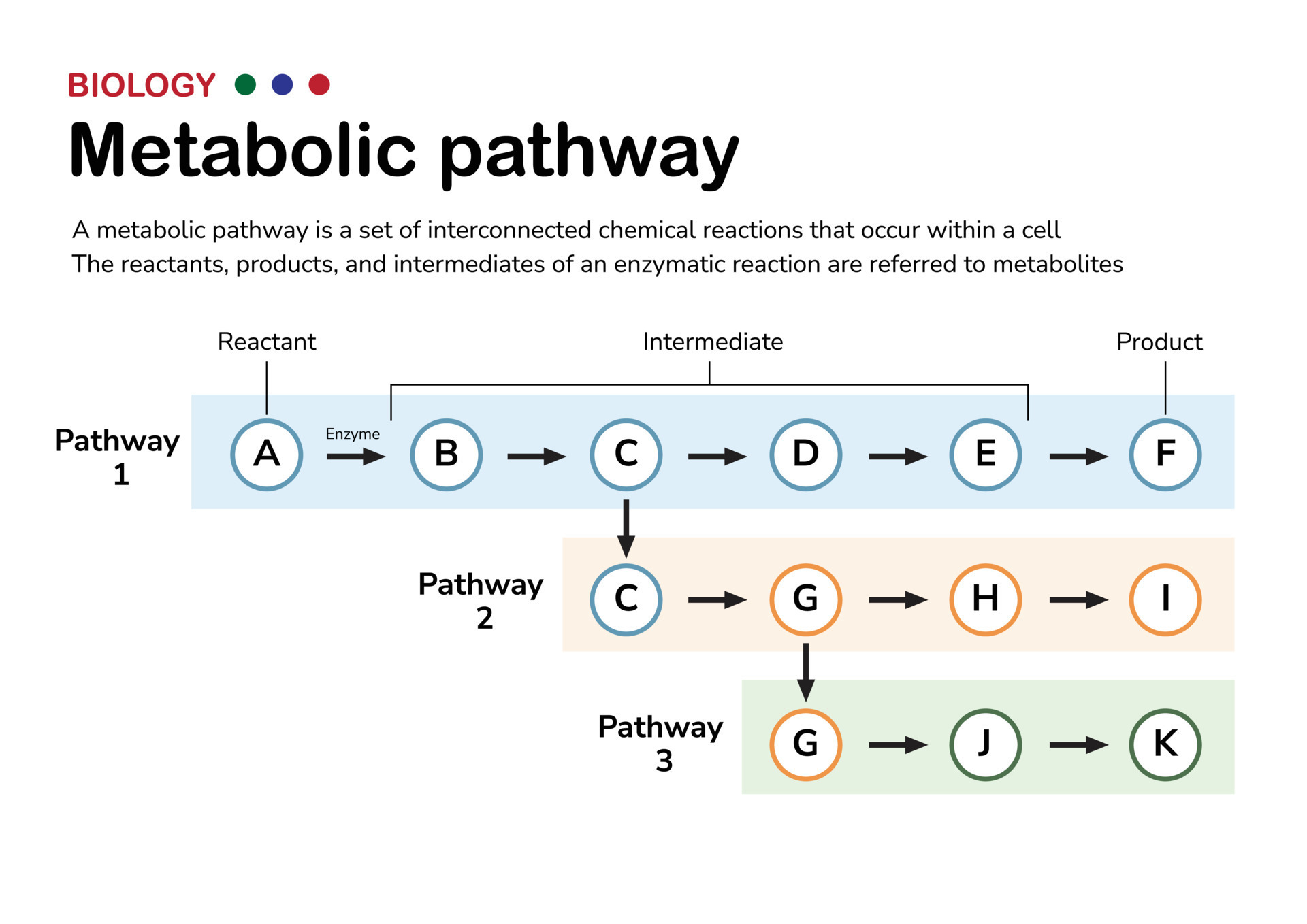
Scientific Diagram Illustrate The Explanation And Concept Of Metabolic

Comments are closed.