Parasitology Ii Module 3 Introduction To Protozoa Gi Protozoa

Parasitology Ii Module 3 Introduction To Protozoa Gi Protozoa Pyriform to elliptical measure 10 18 x 5 10 um, and are bilaterally symmetrical. organism is dorsoventrally flattened and has a bilobed disk at the ventral surface. What modes of transmission are used among protozoa? 1. encystation (i.e., ingestion of cysts via contaminated food or water) and excystation (i.e., occurs w in new host) 2. intermediate host and vectors (i.e., biological or mechanical) t f: protozoa can either be intracellular or extracellular. true.

Introduction To Protozoa Pptx Parasitology Medical Protozoology C U Learn protozoa parasitology introduction with free interactive flashcards. choose from 500 different sets of protozoa parasitology introduction flashcards on quizlet. Gi infections: protozoa. a 26 year old woman presents to the emergency room for large amounts of watery, nonbloody diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and lots of flatulence. she was trying to hydrate with water and sports drinks; however, she started feeling lightheaded and was brought to the hospital for treatment. Introduction to parasitology medical microbiology. 1.34: protozoan parasites.
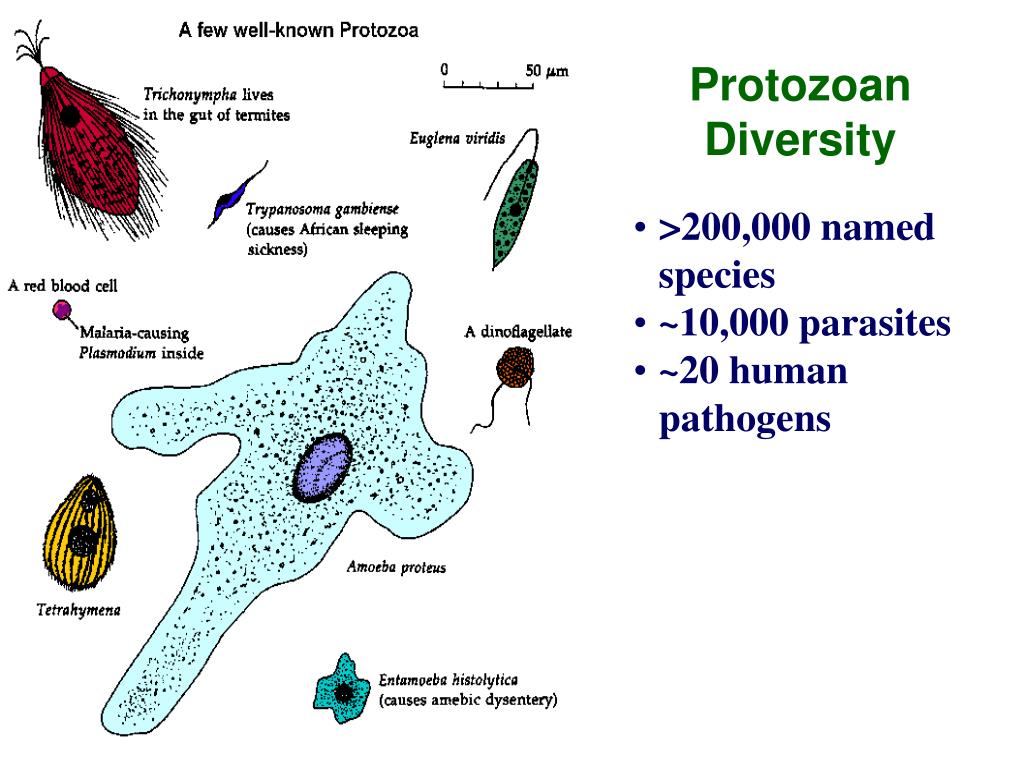
Classification Of Protozoa Introduction to parasitology medical microbiology. 1.34: protozoan parasites. Parasitic protozoans are protists—i.e., unicellular eukaryotes. besides, they share the common features of being heterotrophic, motile in at least one of their stages, and dependent on a host for survival. protists are a highly diverse evolutionary unrelated grouping that is at present taxonomically divided into at least five supergroups or. Introduction; 24.1 anatomy and normal microbiota of the digestive system; 24.2 microbial diseases of the mouth and oral cavity; 24.3 bacterial infections of the gastrointestinal tract; 24.4 viral infections of the gastrointestinal tract; 24.5 protozoan infections of the gastrointestinal tract; 24.6 helminthic infections of the gastrointestinal.

Comments are closed.