Part 3 How To Feed Enteral Feeding For Preterm Infants Guidelines Sns

Part 3 How To Feed Enteral Feeding For Preterm Infants Guidelines Sns Orogastric vs. nasogastric feed? intermittent vs. continuous feeding , push vs. gravity for intermittent feeding, trophic feeding,. 2.1. enteral nutrient provision. early enteral feeding provides vital nutrients and promotes necessary growth in preterm infants. though priority may often be on adequacy of total energy and protein provision for these infants, adequate delivery of micronutrients (including 13 vitamins and multiple minerals) also remains essential to promote optimal physical growth and neurodevelopment [].
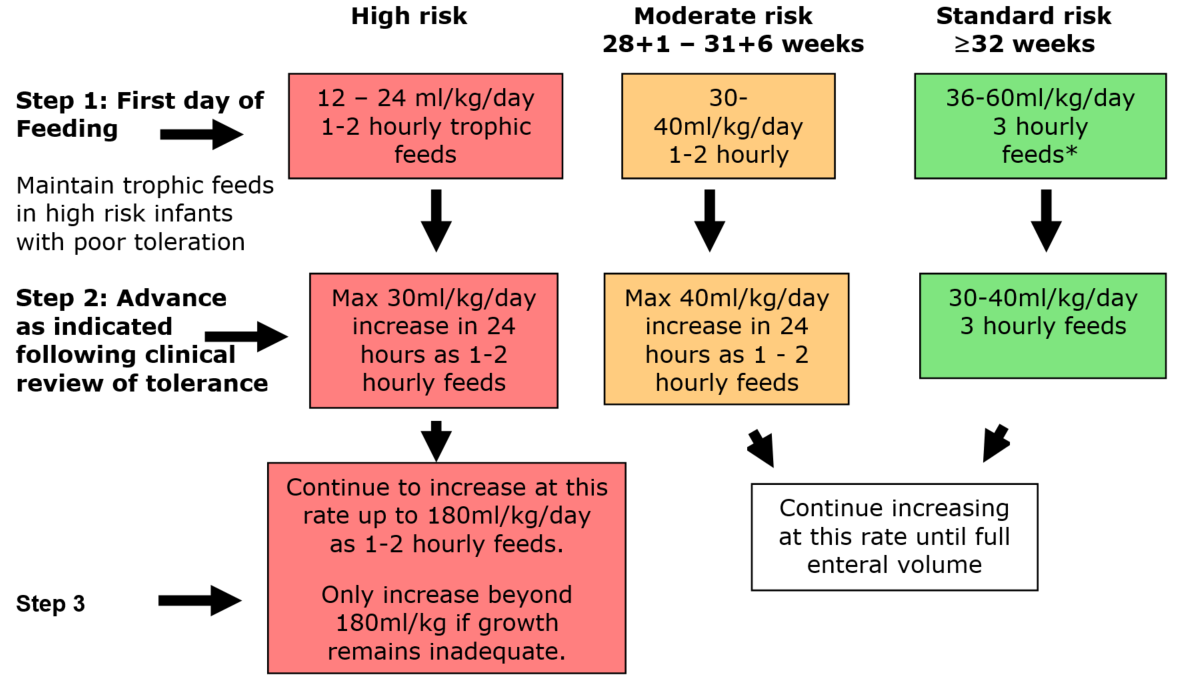
Enteral Feeding Of Preterm Infants Premature infants have greater nutritional needs in the neonatal period than at any other time of their lives. the nutrient needs are inherently high at this stage of development to match the high rates of nutrient deposition achieved by infants in utero [1]. in addition, they often have medical conditions that increase their metabolic energy. Although delayed breastfeeding initiation has been linked to increased risk of mortality and morbidity generally, the potential impact of delayed feeding for preterm infants is less clear. 3–5 three systematic literature reviews completed in the last 10 years report that early trophic feeding (also called minimal enteral nutrition) and nearly full volume feeding improves health outcomes in. Objectives. this guideline is applicable to all medical and nursing staff caring for preterm infants in neonatal units in the west of scotland. it aims to describe safe feeding practices for preterm infants, especially those at increased risk of feed intolerance and necrotising enterocolitis. it is not applicable to babies with congenital. Vlbw infants wherein the median time to reach 170ml kg day was 7 days after fast advancement of enteral feeding, with no increase in apneas, feed interruptions, and intolerance [13] frequency of feedings – in an rct of 92 neonates weighing <1750 g allocated to either three hourly or two hourly feeds, the incidence of feeding intolerance, apnea,.

Comments are closed.