Parts Of A Neuron Labeled And Their Functions

Neuron Function And Its Important Types Simplestudy Net Although they have a characteristic elongated shape, they vary widely in size and properties based on their location and type of functions they perform. while they have the common features of a typical cell, they are structurally and functionally unique from other cells in many ways. all neurons have three main parts: 1) dendrites , 2) cell. As such, neurons typically consist of four main functional parts which include the: receptive part ( dendrites), which receive and conduct electrical signals toward the cell body. integrative part (usually equated with the cell body soma ), containing the nucleus and most of the cell's organelles, acting as the trophic center of the entire neuron.
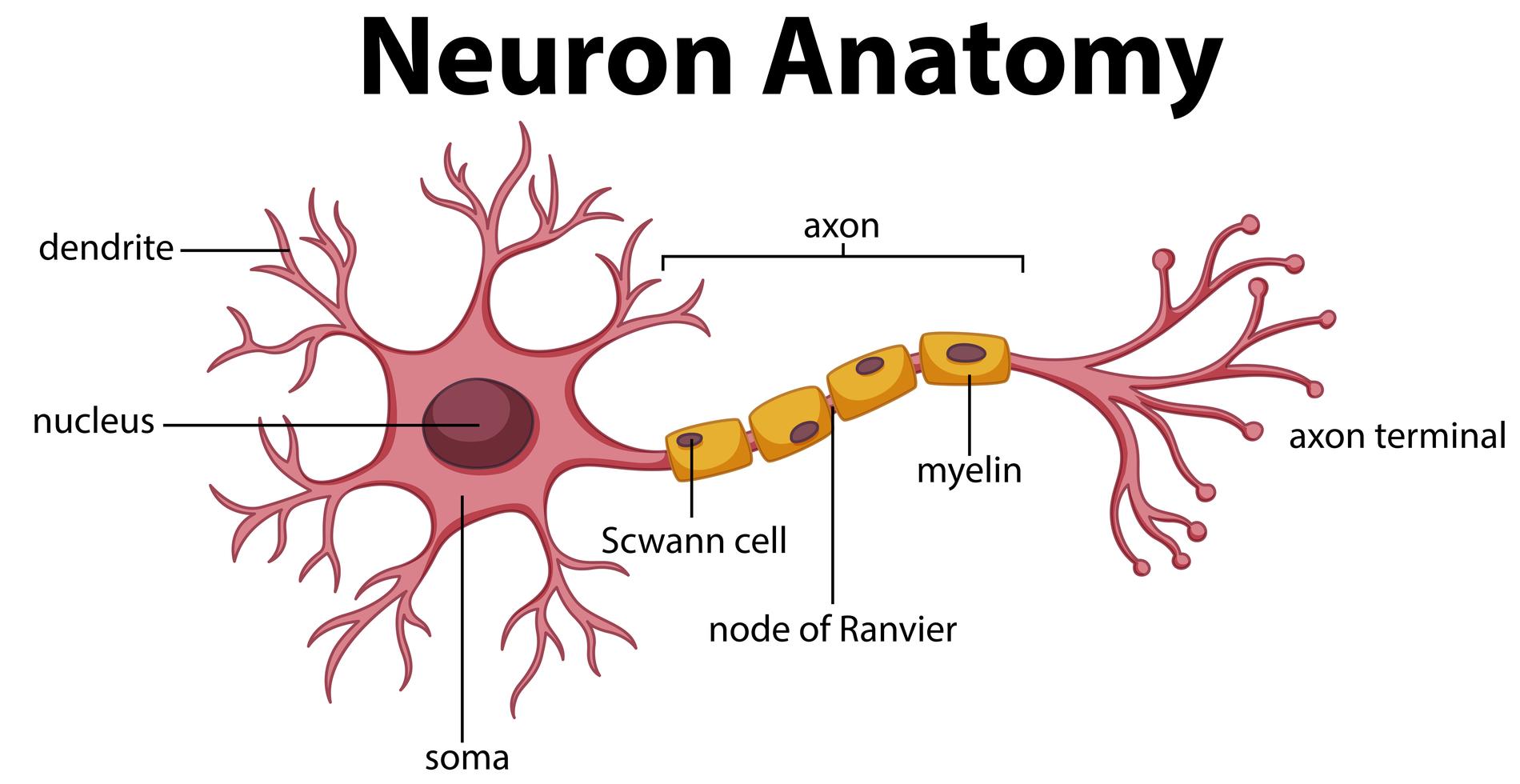
Diagram Of Neuron Anatomy 358962 Vector Art At Vecteezy A neuron is a nerve cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system. neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which sends signals). synaptic connections allow communication between neurons, facilitating the relay of information throughout the body. Like the heart, lungs, and stomach, the nervous system is made up of specialized cells. these include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ). neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which allow them to quickly transmit information over long distances. Parts of a neuron neurons vary in size, shape, and structure depending on their role and location. however, nearly all neurons have three essential parts: a cell body, an axon, and dendrites. There are three main categories of neurons: motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. each is responsible for a different aspect of perception and movement, as well as essential brain functions like learning and decision making. this article provides an overview of neurons, the types of neurons, their structure, and how they work.
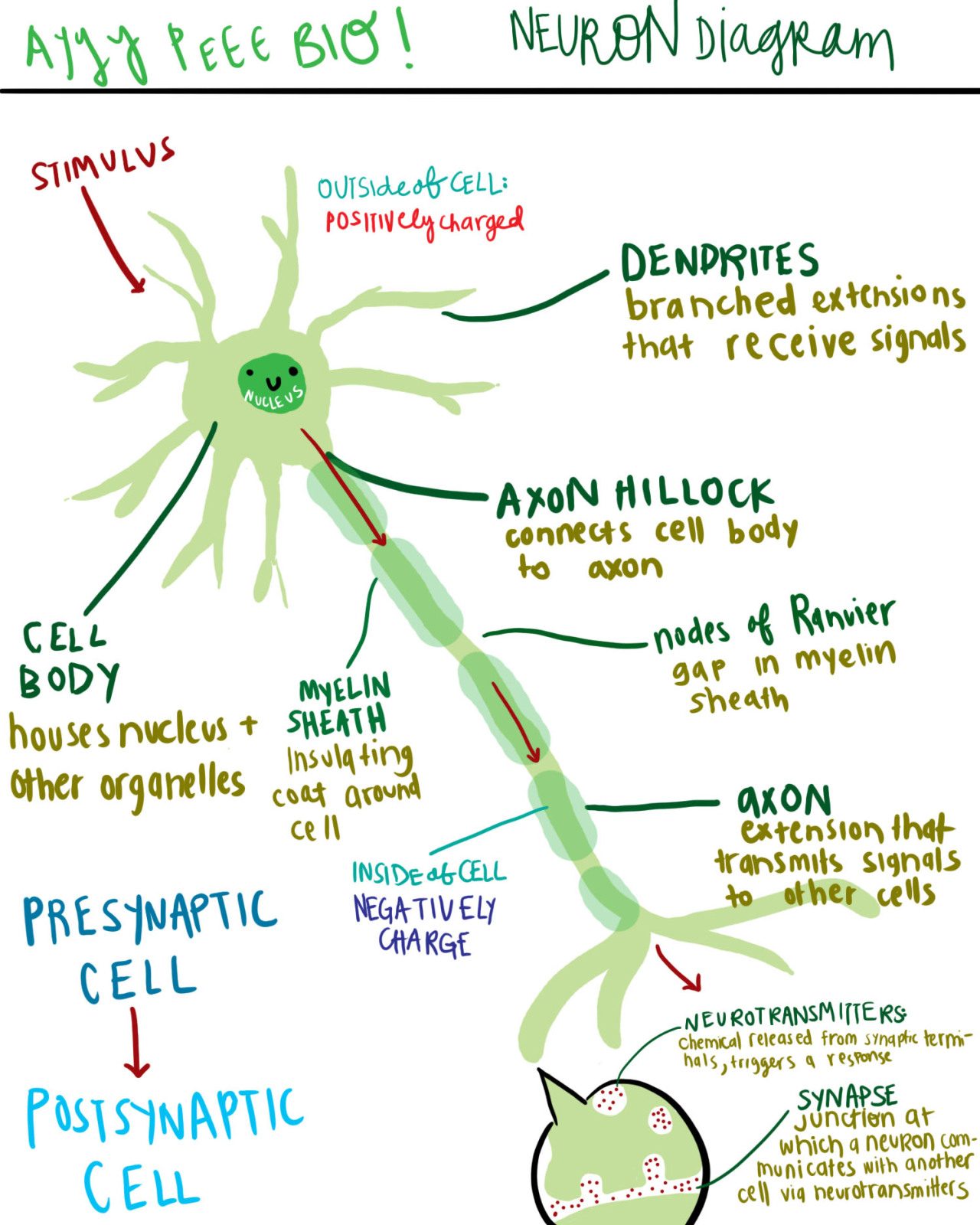
A Diagram Of A Neuron And Its Functions A Study In Chartreuse Parts of a neuron neurons vary in size, shape, and structure depending on their role and location. however, nearly all neurons have three essential parts: a cell body, an axon, and dendrites. There are three main categories of neurons: motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. each is responsible for a different aspect of perception and movement, as well as essential brain functions like learning and decision making. this article provides an overview of neurons, the types of neurons, their structure, and how they work. Neuron structure. figure \(\pageindex{2}\) shows the structure of a typical neuron. the main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. figure \(\pageindex{2}\): somatic motor neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of the bulbs, and other associated. Terminal buttons are found at the end of the axon, below the myelin sheath, and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons. at the end of the terminal button is a gap known as a synapse. neurotransmitters carry signals across the synapse to other neurons. when an electrical signal reaches the terminal buttons, neurotransmitters.
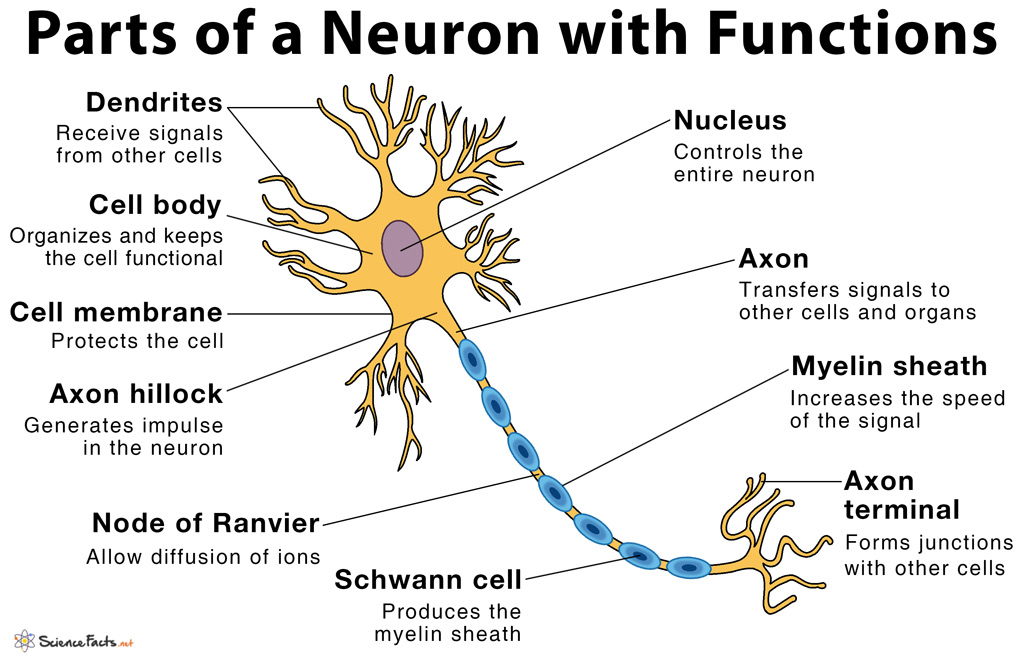
Parts Of A Neuron And Their Functions With Labelled Diagram Neuron structure. figure \(\pageindex{2}\) shows the structure of a typical neuron. the main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. figure \(\pageindex{2}\): somatic motor neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of the bulbs, and other associated. Terminal buttons are found at the end of the axon, below the myelin sheath, and are responsible for sending the signal on to other neurons. at the end of the terminal button is a gap known as a synapse. neurotransmitters carry signals across the synapse to other neurons. when an electrical signal reaches the terminal buttons, neurotransmitters.

Biology Entrance Exam

Comments are closed.