Parts Of The Eukaryotic Cell Diagram Quizlet
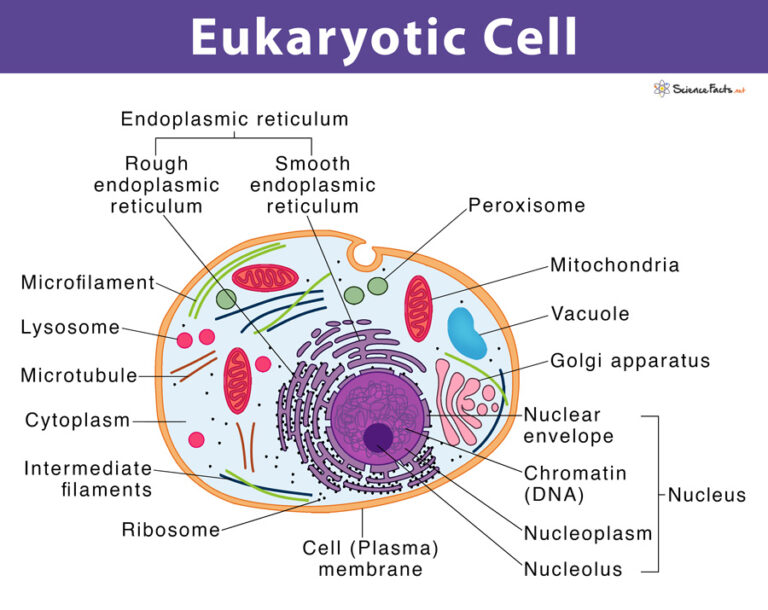
Eukaryotic Cell Definition Structure Examples Definition. a continuous membrane system formed by a series of flattened sacs that synthesizes, folds, modifies, and transports proteins. 1 more side. term. golgi complex. definition. gathers simple molecules and combines them to make molecules that are more complex. it then takes those big molecules, packages them in vesicles, and either. Organelles. cell parts that carry out specific activities of a cell. eukaryote eukaryotic. cells with membrane bound nucleus. nucleus. region of eukaryotic cells that controls activities of cells; contains chromosomes (dna) and nucleolus; filled with nucleoplasm. cytoskeleton. keeps cell from collapsing. plastids.
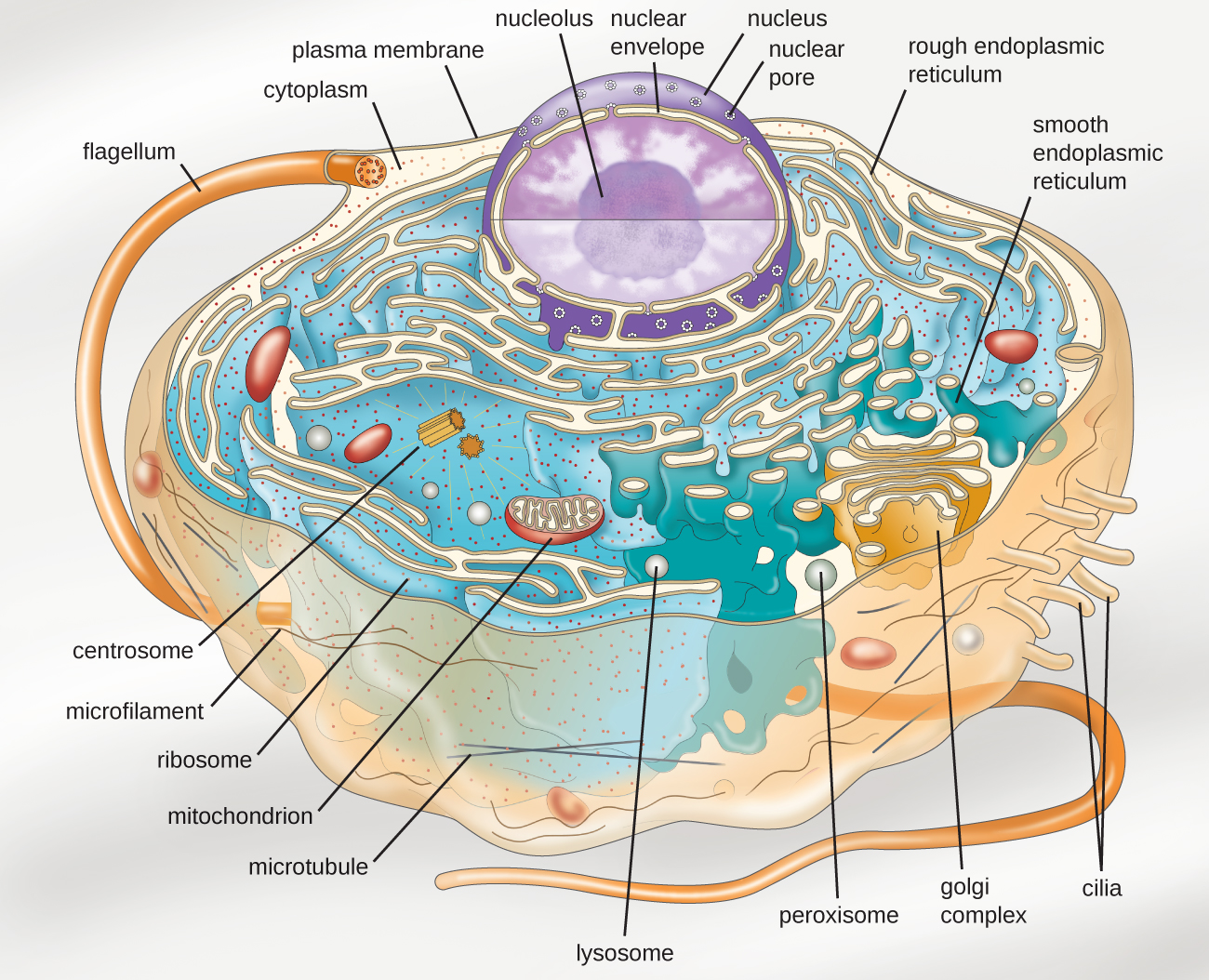
3 4 вђ Unique Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cells вђ Microbiology 201 Cells with a true nucleus. contains a cell wall, chloroplast and large vacuole. does not have a cell wall or chloroplast and a small vacuole. information center for the cell. contains dna. produces energy for the cell. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like eukaryotes, plant cell, animal cell and more. 2.3: eukaryotic cell: structure and function is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. by definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. in addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells …. The cell wall. in figure 3.7b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. fungal and protist cells also have cell walls. Eukaryote specific organelles. organelle. function. nucleus. stores genetic information; controls all cell activities. endoplasmic reticulum (er) network of tubes and membranes that carry material through the cell and play a role in protein modification and lipid synthesis; has two parts: rough er (contains ribosomes) and smooth er (does not.
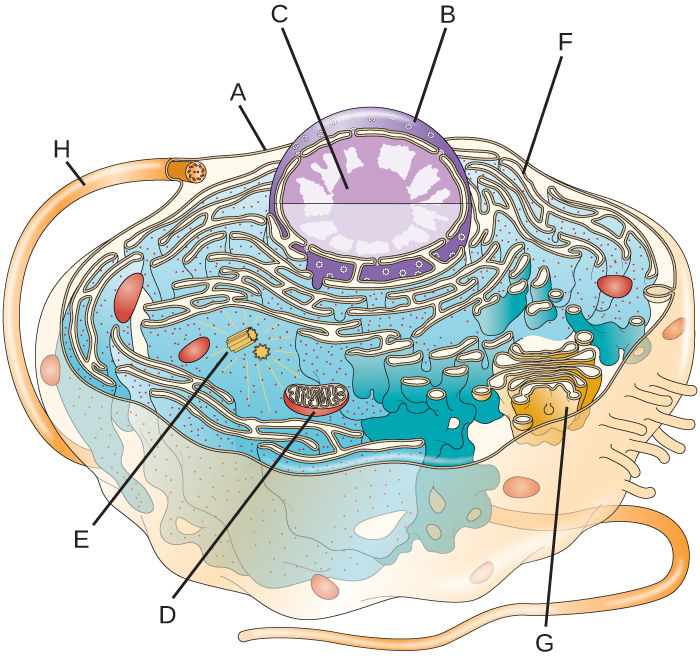
Solved Label The Following Parts Of This Eukaryotic Cell Chegg The cell wall. in figure 3.7b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. fungal and protist cells also have cell walls. Eukaryote specific organelles. organelle. function. nucleus. stores genetic information; controls all cell activities. endoplasmic reticulum (er) network of tubes and membranes that carry material through the cell and play a role in protein modification and lipid synthesis; has two parts: rough er (contains ribosomes) and smooth er (does not. 8 years ago. the endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of a cell. but then whenever we draw a diagram of a typical plant or animal cell, we never extend it to the plasma membrane we always leave it somewhere in the cytoplasm. Key points: all cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. the cell membrane surrounds a cell’s cytoplasm, which is a jelly like substance containing the cell’s parts. cells contain parts called organelles. each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.

Comments are closed.