Parts Of The Human Body Human Body Science Human Body O

Parts Of The Human Body Human Body Organs Human Body Sc It consists of the heart, blood, blood vessels, arteries and veins. according to the cleveland clinic, the adult human body's network of blood vessels is more than 60,000 miles (around 100,000. The human body is the physical substance of the human organism. characteristic of the vertebrate form, the human body has an internal skeleton with a backbone, and, as with the mammalian form, it has hair and mammary glands. learn more about the composition, form, and physical adaptations of the human body.

Science 3вє Primaria Pedro I Body Parts And Body Organs The human body is the entire structure of a human being. it is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organs and then organ systems. the external human body consists of a head, hair, neck, torso (which includes the thorax and abdomen ), genitals, arms, hands, legs, and feet. Anatomy systems. skeletal system the skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body. muscular system the muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. cardiovascular system the cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and the approximately 5 liters of blood that the blood vessels transport. Explore the human body's anatomy and learn about the roles of its various systems with national geographic's "human body 101" video on . The body has levels of organization that build on each other. cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, and organs make up organ systems. the function of an organ system depends on the integrated activity of its organs. for instance, digestive system organs cooperate to process food. the survival of the organism depends on the integrated.

Human Body Fun Science Facts For Kids About The Human Bodyeasy Explore the human body's anatomy and learn about the roles of its various systems with national geographic's "human body 101" video on . The body has levels of organization that build on each other. cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, and organs make up organ systems. the function of an organ system depends on the integrated activity of its organs. for instance, digestive system organs cooperate to process food. the survival of the organism depends on the integrated. A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions in the body. musculoskeletal system. mechanical support, posture and locomotion. cardiovascular system. transportation of oxygen, nutrients and hormones throughout the body and elimination of cellular metabolic waste. respiratory system. The human body has many different parts. the science that studies the structures and arrangement of those parts is called anatomy, while the study of how they function is called physiology. to understand how the human body works, let’s start at a microscopic level and look at cells. cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of the.
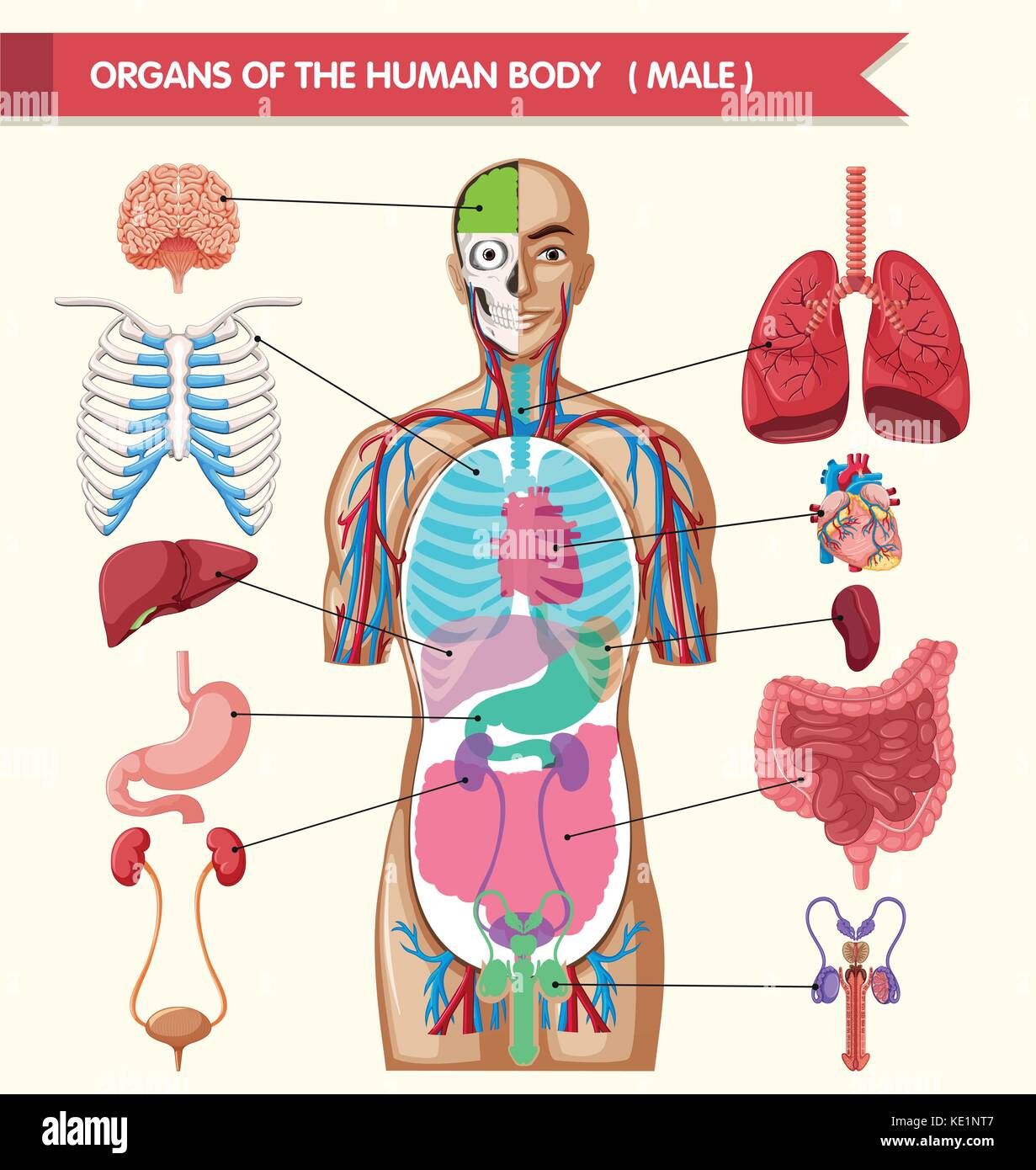
Chart Showing Organs Of Human Body Illustration Stock Vector Image A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions in the body. musculoskeletal system. mechanical support, posture and locomotion. cardiovascular system. transportation of oxygen, nutrients and hormones throughout the body and elimination of cellular metabolic waste. respiratory system. The human body has many different parts. the science that studies the structures and arrangement of those parts is called anatomy, while the study of how they function is called physiology. to understand how the human body works, let’s start at a microscopic level and look at cells. cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of the.

Comments are closed.