Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Lumbar Discectomy In Kenya

Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Lumbar Discectomy In Kenya First, ield is a complementary surgical technique to teld. the use of teld alone in situations such as highly migrated disc herniation or large disc herniation may put patients at risk of neural injury or incomplete surgery, 9,10 but these challenges can be addressed using ield. 5,11–13 second, advanced techniques, such as endoscopic. According to the approach, peld can be classified into percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd) and percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (peid). petd shows good results for nerve root decompression, with low complication rates in herniated lumbar disc removal [ 4 , 7 , 8 , 9 ].

Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy For Lumbar Disc Herniation Background: percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (peld) often refers to percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd) and percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (peid). as a minimally invasive spinal procedure, peld has gained increasing recognition for its small incision, quick recovery, short hospital stay, and. The interlaminar approach for lumbar discectomy has been done with the aid of microscope since 1970s ( 20 22) and microendoscopic system since late 1990s ( 23 25 ). spine surgeons have been familiar with this corridor by posterior approach to do lumbar spine surgeries. Compared with percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd), the wide interlaminar space between l5 and s1 makes it easy to enter the spinal canal, decompress the nerve root and remove the protruding disc. 16, 17 however, in peid, the operating procedure involves entry into the spinal canal and direct retraction of the nerve root. Objective although spinal endoscopic techniques have shown great advantages in the treatment of single segment lumbar disk herniation (ldh), the therapeutic advantages for double segment ldh are controversial. to compare the outcomes of percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (peid) versus conventional open lumbar discectomy (cold) for the treatment of l4 5 and l5 s1 double segmental.

Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy A Lateral Radioscopic Compared with percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd), the wide interlaminar space between l5 and s1 makes it easy to enter the spinal canal, decompress the nerve root and remove the protruding disc. 16, 17 however, in peid, the operating procedure involves entry into the spinal canal and direct retraction of the nerve root. Objective although spinal endoscopic techniques have shown great advantages in the treatment of single segment lumbar disk herniation (ldh), the therapeutic advantages for double segment ldh are controversial. to compare the outcomes of percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (peid) versus conventional open lumbar discectomy (cold) for the treatment of l4 5 and l5 s1 double segmental. Percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd) for l5–s1 disc herniation. a, place the needle into the disc to perform discography. b–e, when the dilator is blocked by the facet joint, use the trephine to enlarge the foramen. f–g, confirm the location of the working cannula with c arm fluoroscopy. h, disc pulposus. Results: peld is an effective and safe treatment for lumbar disc herniation, lumbar spinal stenosis, recurrent lumbar disc herniation, and other lumbar diseases. complications related to peld include dural tear, nerve root injury, recurrence, and so on. limitations:some results drawn in this review are based on retrospective study or small.

Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Lumbar Diskectomy Structural Percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd) for l5–s1 disc herniation. a, place the needle into the disc to perform discography. b–e, when the dilator is blocked by the facet joint, use the trephine to enlarge the foramen. f–g, confirm the location of the working cannula with c arm fluoroscopy. h, disc pulposus. Results: peld is an effective and safe treatment for lumbar disc herniation, lumbar spinal stenosis, recurrent lumbar disc herniation, and other lumbar diseases. complications related to peld include dural tear, nerve root injury, recurrence, and so on. limitations:some results drawn in this review are based on retrospective study or small.
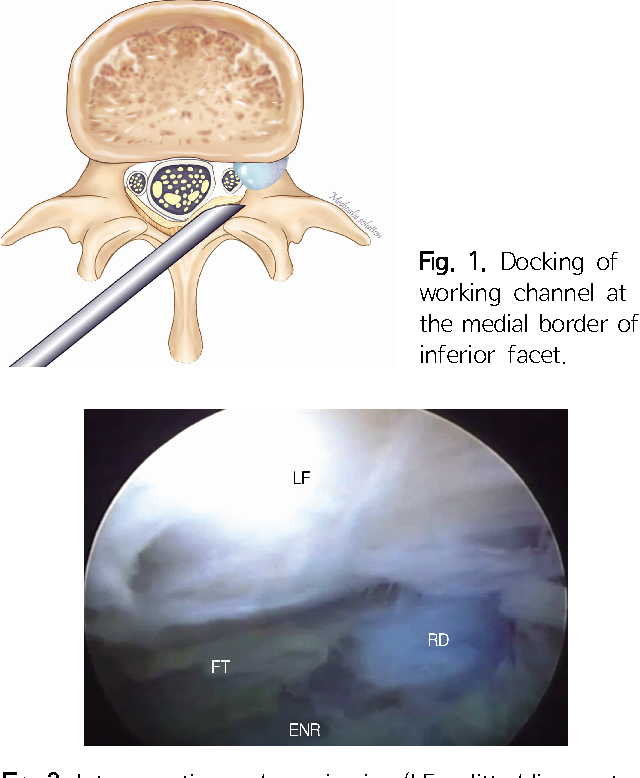
Figure 1 From Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy For L5 S1

Comments are closed.